Grade 8 Science Cells and Systems
... unicellular, multicellular, specialized cells and tissues, organs, systems, arteries, veins, capillaries, terms related to cell structure, heart structure, components of blood, and primary and secondary defense systems ...
... unicellular, multicellular, specialized cells and tissues, organs, systems, arteries, veins, capillaries, terms related to cell structure, heart structure, components of blood, and primary and secondary defense systems ...
Cell organelles
... Labels them, which allows Them to go to their correct Destination. Modified protein transported in vesicles ...
... Labels them, which allows Them to go to their correct Destination. Modified protein transported in vesicles ...
Lesson 1
... Virchow revealed all cells come from existing cells. The modern tenets of the Cell Theory 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is the structural and functional unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (Spontaneous Generation does not o ...
... Virchow revealed all cells come from existing cells. The modern tenets of the Cell Theory 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is the structural and functional unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (Spontaneous Generation does not o ...
Cell Structure & Function
... Life is Cellular SPI.1.1 Identify the cellular organelles associated with major cell processes. SPI.1.2 Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
... Life is Cellular SPI.1.1 Identify the cellular organelles associated with major cell processes. SPI.1.2 Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
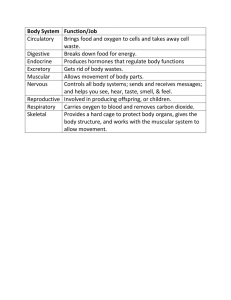
BODY SYSTEMS
... haploid sperm (male) results in diploid zygote. The zygote continues to develop with specific tissue differentiation until the fetus is full term and ready to be born. ...
... haploid sperm (male) results in diploid zygote. The zygote continues to develop with specific tissue differentiation until the fetus is full term and ready to be born. ...
Body Organization
... • Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. • The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. • Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. ...
... • Different body tissues and organs are made up of different kinds of cells. • The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. • Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multi-cellular organisms. ...
II. The Cell - Quakertown Community School District
... All organisms are made of cells, the organism’s basic unit of structure and function. ...
... All organisms are made of cells, the organism’s basic unit of structure and function. ...
Fly Cells Divide by the Clock
... Clock Gates the Intestinal Stem Cell Regenerative State] The researchers say the circadian clock might inform healing in us too, since it's such an ancient trait. If so, they say doctors might want to time surgeries or chemotherapy for when the body is primed to heal, helping patients clock a faster ...
... Clock Gates the Intestinal Stem Cell Regenerative State] The researchers say the circadian clock might inform healing in us too, since it's such an ancient trait. If so, they say doctors might want to time surgeries or chemotherapy for when the body is primed to heal, helping patients clock a faster ...
Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment
... 47.Gametes unite to form a _______________. ...
... 47.Gametes unite to form a _______________. ...
Name__________________________ Date_______________
... b. In what organelle is this process taking place? c. In addition to the gas, what other compound is being made? d. What does the sun provide? 2. In the scenarios below, ONLY THE WATER can move through the membrane. What will happen to the level of the water? Draw an AFTER picture. ...
... b. In what organelle is this process taking place? c. In addition to the gas, what other compound is being made? d. What does the sun provide? 2. In the scenarios below, ONLY THE WATER can move through the membrane. What will happen to the level of the water? Draw an AFTER picture. ...
file
... Homeostasis refers to.. A – an organism’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions B – an organism’s ability to compete for living space C- an organism’s ability to dissolve chemicals D – an organism’s ability to obtain energy ...
... Homeostasis refers to.. A – an organism’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions B – an organism’s ability to compete for living space C- an organism’s ability to dissolve chemicals D – an organism’s ability to obtain energy ...
Print Preview - C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\e3temp_5676\.aptcache
... The cell cycle is regulated by both external and internal factors. External factors come from outside the cell. These include cell–cell contact, which prevents further growth of normal cells, and chemical signals called growth factors. Growth factors stimulate cells to divide. Most cells respond to ...
... The cell cycle is regulated by both external and internal factors. External factors come from outside the cell. These include cell–cell contact, which prevents further growth of normal cells, and chemical signals called growth factors. Growth factors stimulate cells to divide. Most cells respond to ...
Reinforcement 5.3
... The cell cycle is regulated by both external and internal factors. External factors come from outside the cell. These include cell–cell contact, which prevents further growth of normal cells, and chemical signals called growth factors. Growth factors stimulate cells to divide. Most cells respond to ...
... The cell cycle is regulated by both external and internal factors. External factors come from outside the cell. These include cell–cell contact, which prevents further growth of normal cells, and chemical signals called growth factors. Growth factors stimulate cells to divide. Most cells respond to ...
cell
... A) Cells are the basic units of life. Every cell has got a cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm. ...
... A) Cells are the basic units of life. Every cell has got a cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm. ...
The Membrane: Achieving Balance
... A solution is a mixture in which one or more substances (Solutes) are dissolved in another substance (Solvent) The concentration of a solute is important to organisms. Organisms cannot live unless the concentration of dissolved substances stays within a narrow range. ...
... A solution is a mixture in which one or more substances (Solutes) are dissolved in another substance (Solvent) The concentration of a solute is important to organisms. Organisms cannot live unless the concentration of dissolved substances stays within a narrow range. ...
Bacteria and Viruses Study Guide (Test on 1.27.11)
... 10. Why are viruses like parasites? a. They destroy the cells they enter. c. They use energy to develop. b. They multiply. d. They make their own food. 11. Which phrase describes the size of virus particles? a. smaller than cells c. the same size as cells b. slightly larger than cells d. much larger ...
... 10. Why are viruses like parasites? a. They destroy the cells they enter. c. They use energy to develop. b. They multiply. d. They make their own food. 11. Which phrase describes the size of virus particles? a. smaller than cells c. the same size as cells b. slightly larger than cells d. much larger ...
BIO Cell Color Key
... You need to COLOR and LABEL the organelles (parts) of EACH cell. Attach the diagrams in your notebook, each on their own page. You will be writing notes beside the diagrams so put the picture in the middle so you have room to write. These should take up THREE separate pages. Use the internet OR the ...
... You need to COLOR and LABEL the organelles (parts) of EACH cell. Attach the diagrams in your notebook, each on their own page. You will be writing notes beside the diagrams so put the picture in the middle so you have room to write. These should take up THREE separate pages. Use the internet OR the ...
The Cell in its Environment
... •Cell membrane is found around the outside of an animal cell and it is the second layer of a plant cell •The job of a cell membrane is to let “things” in and out of the cell ...
... •Cell membrane is found around the outside of an animal cell and it is the second layer of a plant cell •The job of a cell membrane is to let “things” in and out of the cell ...
Chapter 6
... • Continuous with the rough ER • Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus • Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes ...
... • Continuous with the rough ER • Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus • Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes ...
Module A-1 (Principles of Biology)
... (A) cellular reactions that release energy (B) photosynthetic reactions that store energy (C) muscle reactions that use energy A) A and B, only C) A and C, only ...
... (A) cellular reactions that release energy (B) photosynthetic reactions that store energy (C) muscle reactions that use energy A) A and B, only C) A and C, only ...