Document
... Mitochondria -Contain enzymes for transferring the energy in macromolecules into ATP using oxygen surrounded by 2 membranes -smooth outer membrane -folded inner membrane with layers called cristae -matrix is within the inner membrane -intermembrane space is located between the two membranes ...
... Mitochondria -Contain enzymes for transferring the energy in macromolecules into ATP using oxygen surrounded by 2 membranes -smooth outer membrane -folded inner membrane with layers called cristae -matrix is within the inner membrane -intermembrane space is located between the two membranes ...
CD1
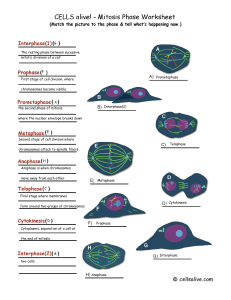
... cell has created two IDENTICAL nuclei so that it can reproduce into two IDENTICAL cells with all the correct information (DNA) that they need for functioning independently. They are related to one another because cell division cannot happen properly and successfully without mitosis – mitosis is a pa ...
... cell has created two IDENTICAL nuclei so that it can reproduce into two IDENTICAL cells with all the correct information (DNA) that they need for functioning independently. They are related to one another because cell division cannot happen properly and successfully without mitosis – mitosis is a pa ...
Pre-Lesson 10: Bacterial Diseases I
... protection from _______________________ by macrophages and other leukocytes, growth with in ___________ including macrophages, resistance to __________, Mycolic acid allows the cell to retain water and survive for months, ________________ to detergents, many antibiotics, and other water based or wat ...
... protection from _______________________ by macrophages and other leukocytes, growth with in ___________ including macrophages, resistance to __________, Mycolic acid allows the cell to retain water and survive for months, ________________ to detergents, many antibiotics, and other water based or wat ...
Cells - Latona
... a. Stores water. b. Very large Animals: a. Stores carbs., lipids, & proteins b. Small ...
... a. Stores water. b. Very large Animals: a. Stores carbs., lipids, & proteins b. Small ...
Organ Systems Reading
... similar function. Just as muscle cells work together, bone cells and many other cells do as well. A group of similar cells that work together is known as a tissue. Cells are grouped together to carry out specific functions. A group of cells that work together form a tissue. Your body has four main t ...
... similar function. Just as muscle cells work together, bone cells and many other cells do as well. A group of similar cells that work together is known as a tissue. Cells are grouped together to carry out specific functions. A group of cells that work together form a tissue. Your body has four main t ...
Cells Gizmo
... 2. What THREE structures are present in a plant cell, but not in an animal cell? ...
... 2. What THREE structures are present in a plant cell, but not in an animal cell? ...
Modern biology is guided by the cell theory, the view that ______.
... ________ are so different that each is assigned to a separate domain. ...
... ________ are so different that each is assigned to a separate domain. ...
Cell Model lesson
... 1. Students will draw a design of animal and plant Compare and contrast animal cells. and plant cells. What are the 2. Students will create models of plant and animal functions for the parts of the cells. Students will use various household items cell? to use as cell structures. Students will justif ...
... 1. Students will draw a design of animal and plant Compare and contrast animal cells. and plant cells. What are the 2. Students will create models of plant and animal functions for the parts of the cells. Students will use various household items cell? to use as cell structures. Students will justif ...
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells Prokaryotes
... • organized nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a "brain" for the cell. They have a discreet area where they keep their DNA. It is also said that they have a "true nucleus.“ • Complex internal structure: Eukaryotic cells usually have organelles. They might have mitochondria, maybe a ...
... • organized nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a "brain" for the cell. They have a discreet area where they keep their DNA. It is also said that they have a "true nucleus.“ • Complex internal structure: Eukaryotic cells usually have organelles. They might have mitochondria, maybe a ...
1. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in size and complexity
... a double layer of phospholipids with other lipids and diverse proteins. • Each type of membrane has a unique combination of lipids and proteins for its specific functions. • For example, those in the membranes of mitochondria function in cellular respiration. ...
... a double layer of phospholipids with other lipids and diverse proteins. • Each type of membrane has a unique combination of lipids and proteins for its specific functions. • For example, those in the membranes of mitochondria function in cellular respiration. ...
REVIEW FOR TEST 2: Cytology
... endergonic, catalyst, reduced and oxidized, coupled reactions 2. If metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions, what are catabolism and anabolism? 3. Distinguish between the two forms of energy: a. kinetic b. potential ...
... endergonic, catalyst, reduced and oxidized, coupled reactions 2. If metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions, what are catabolism and anabolism? 3. Distinguish between the two forms of energy: a. kinetic b. potential ...
CELLS The cell is the basic unit of life. All living organisms are
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All living organisms are composed of cells and their products. Under a microscope, the human body is seen to be composed of many different cells; muscle cells, brain cells, liver cells - all of which are quite dissimilar. Yet the differences, while important, shou ...
... The cell is the basic unit of life. All living organisms are composed of cells and their products. Under a microscope, the human body is seen to be composed of many different cells; muscle cells, brain cells, liver cells - all of which are quite dissimilar. Yet the differences, while important, shou ...
Artificial insemination
... anonymous sperm donor can be used. • Eugenics means the application of reproductive medicine not to help people have children and not to avoid different diseases but only to produce desirable or preferable types of humans. ...
... anonymous sperm donor can be used. • Eugenics means the application of reproductive medicine not to help people have children and not to avoid different diseases but only to produce desirable or preferable types of humans. ...
The Living Cell
... The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
... The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells • The cell is the fundamental unit of life • All cells arise from previous cells ...
7 Grade Science Sample Assessment Items S7L2d,e.
... that is most similar to which human body system? A. nervous* B. muscular C. respiratory D. circulatory ...
... that is most similar to which human body system? A. nervous* B. muscular C. respiratory D. circulatory ...
Cells Pretest - Warren County Schools
... 2. In the above figure, the structure labeled A is the a. Cell membrane b. Golgi Body c. Cytoplasm d. Nuclear Membrane 3. In the above figure, the structure labeled B is the a. Cell membrane b. Golgi Body c. Cytoplasm d. Nuclear Membrane 4. In the above figure, the structure labeled C is the a. Cell ...
... 2. In the above figure, the structure labeled A is the a. Cell membrane b. Golgi Body c. Cytoplasm d. Nuclear Membrane 3. In the above figure, the structure labeled B is the a. Cell membrane b. Golgi Body c. Cytoplasm d. Nuclear Membrane 4. In the above figure, the structure labeled C is the a. Cell ...
Biology End-of-Course Test Study Guide
... Enzymes (lock and key, characteristics, factors that effect enzyme function, etc.) Cellular Organelles structure and function (nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts and ribosomes) Microscope technique (total magnification) Cellular organization (cellstissuesorga ...
... Enzymes (lock and key, characteristics, factors that effect enzyme function, etc.) Cellular Organelles structure and function (nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts and ribosomes) Microscope technique (total magnification) Cellular organization (cellstissuesorga ...
Plant and Animal Cell Parts
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
Cell Unit Notes
... 4. Most cells contain hereditary information and can be passed on from cell to cell during reproduction Ex. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical structure and activities ...
... 4. Most cells contain hereditary information and can be passed on from cell to cell during reproduction Ex. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical structure and activities ...
From cell to an organism
... • Nerve cells, also called __________, are found in your brain. • Nerve cells transmit information from the ________ to other parts of the body, and back to the brain, through __________ and ___________ signals. • Some neurons have very long fibres extending from the cell, called ________, which ...
... • Nerve cells, also called __________, are found in your brain. • Nerve cells transmit information from the ________ to other parts of the body, and back to the brain, through __________ and ___________ signals. • Some neurons have very long fibres extending from the cell, called ________, which ...