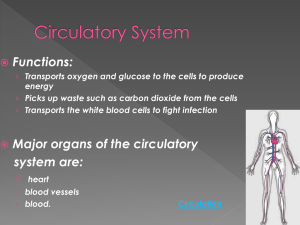
Plant Systems - My Teacher Pages
... • Plants may be grouped into Vascular or non-vascular • Plants are made up of plant cells. Plant cells have: - a strong cell wall, -large water vacuoles, and -several chloroplast for photosynthesis used in energy & food production. ...
... • Plants may be grouped into Vascular or non-vascular • Plants are made up of plant cells. Plant cells have: - a strong cell wall, -large water vacuoles, and -several chloroplast for photosynthesis used in energy & food production. ...
CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOSKELETON NUCLEUS
... • Inside cell wall (for plants) • Outermost layer (for animals) • Two layer phospholipid • Phospho (end that contains phosphorous) hydrophilic: water –loving • Lipid hydrophobic: water fearing • Selectively permeable: • Controls what goes in and out of the cell ...
... • Inside cell wall (for plants) • Outermost layer (for animals) • Two layer phospholipid • Phospho (end that contains phosphorous) hydrophilic: water –loving • Lipid hydrophobic: water fearing • Selectively permeable: • Controls what goes in and out of the cell ...
answers - Biology Resources
... cell wall are not living materials. 4 High temperature kills most living materials (by denaturing their proteins, e.g. enzymes and structures in the cell membrane). 5 It seems likely that a living process in the cytoplasm controls the diffusion of the pigment. Diffusion of pigment is prevented when ...
... cell wall are not living materials. 4 High temperature kills most living materials (by denaturing their proteins, e.g. enzymes and structures in the cell membrane). 5 It seems likely that a living process in the cytoplasm controls the diffusion of the pigment. Diffusion of pigment is prevented when ...
The Cell The Discovery of the Cell The Discovery of
... • The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. • Cell typing is categorized by their nucleus: – Eukaryotes (Greek for “true nucleus/center”) – Prokaryotes (Greek for “before nucleus/center”) ...
... • The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. • Cell typing is categorized by their nucleus: – Eukaryotes (Greek for “true nucleus/center”) – Prokaryotes (Greek for “before nucleus/center”) ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... • Muscle tissue is made up of elongated cells called muscle fibres. ...
... • Muscle tissue is made up of elongated cells called muscle fibres. ...
Chapter 9
... Maybe you noticed already but the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite of each other They are closely connected in a cycle ...
... Maybe you noticed already but the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite of each other They are closely connected in a cycle ...
Solar Energy - Photovoltaics
... • To do this, contacts must be placed across the entire surface of a PV cell. • This is normally done with a gird of metal strips or fingers. Since this grid will absorb light, the design must balance shading and electrical losses. ...
... • To do this, contacts must be placed across the entire surface of a PV cell. • This is normally done with a gird of metal strips or fingers. Since this grid will absorb light, the design must balance shading and electrical losses. ...
Cell Transport
... mixed with distilled water, the blood cells burst. • Living plant tissues that had lost water become firm when supplied with water. ...
... mixed with distilled water, the blood cells burst. • Living plant tissues that had lost water become firm when supplied with water. ...
Proteins
... different monomers in order to make the polymers it requires! The food we eat must be broken down so that it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to ...
... different monomers in order to make the polymers it requires! The food we eat must be broken down so that it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to ...
Cells Information Gap Activity
... vacuoles. They are not normally visible under light microscopes. The ________________________________________ is the “control room” of the cell. It contains ____________, which is like a _________________________________________________________ that tells the cell how to develop and ________________ ...
... vacuoles. They are not normally visible under light microscopes. The ________________________________________ is the “control room” of the cell. It contains ____________, which is like a _________________________________________________________ that tells the cell how to develop and ________________ ...
Cell Observation Lab Activity
... Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what enter/exits a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell is the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the control cent ...
... Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what enter/exits a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell is the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the control cent ...
Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
... The WNYSTEM Stem Cell Center invites you to the 4th Annual WNYSTEM Stem Cell Symposium: ...
... The WNYSTEM Stem Cell Center invites you to the 4th Annual WNYSTEM Stem Cell Symposium: ...
Name
... 14. Isotonic means _____________________________ Hypertonic means ___________________________ Hypotonic means ____________________________ 15. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water (the water would be considered hypotonic), water will move ___________ of the cell. If that happens, ...
... 14. Isotonic means _____________________________ Hypertonic means ___________________________ Hypotonic means ____________________________ 15. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water (the water would be considered hypotonic), water will move ___________ of the cell. If that happens, ...
Cells need to produce new cells in order to
... carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water to make glucose and oxygen is called a. Osmosis b. Photosynthesis c. Cellular respiration ...
... carbon dioxide, sunlight, and water to make glucose and oxygen is called a. Osmosis b. Photosynthesis c. Cellular respiration ...
Cells
... separate the outside of a cell from the inside; it controls what enters and leaves the cell, and much of the activity within the cell. Most of the cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer. Amphipathic molecule – phosphate heads on the outside and inside, and fatty acid tails in the middle. ...
... separate the outside of a cell from the inside; it controls what enters and leaves the cell, and much of the activity within the cell. Most of the cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer. Amphipathic molecule – phosphate heads on the outside and inside, and fatty acid tails in the middle. ...
Human Body Quiz 1 - Effingham County Schools
... Diagram Matching. Some of the letters will not be used. ...
... Diagram Matching. Some of the letters will not be used. ...
Parts of Plant and Animal Cells By
... • Bacteria which have flagella are either rod or spiral-shaped l and are known as bacilli. Which is found in the eukaryotic cells. ...
... • Bacteria which have flagella are either rod or spiral-shaped l and are known as bacilli. Which is found in the eukaryotic cells. ...
MICROTUBULES Tracks guide motor proteins to destination
... Also found in Prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists Composition varies with species/cell type Basic design: Microfibrils of polysaccharide cellulose embedded in matrix of other polysaccharides (like steel reinforced concrete) ...
... Also found in Prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists Composition varies with species/cell type Basic design: Microfibrils of polysaccharide cellulose embedded in matrix of other polysaccharides (like steel reinforced concrete) ...
Cells and Their Environment
... • Process by which molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Concentration gradient: a difference in the concentration of a substance • Examples: – Oxygen diffusing into cells – Beaker of water with food coloring – Smell of perfume in a room ***Molecules a ...
... • Process by which molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • Concentration gradient: a difference in the concentration of a substance • Examples: – Oxygen diffusing into cells – Beaker of water with food coloring – Smell of perfume in a room ***Molecules a ...
Organelles - Granbury ISD
... Cell wall • The Cell wall is the outer layer of the plant cell • It is located outside the cell membrane. It provides the cell with structural support and ...
... Cell wall • The Cell wall is the outer layer of the plant cell • It is located outside the cell membrane. It provides the cell with structural support and ...
partone7th - PAMS-Doyle
... Living organisms require food, water, shelter, energy, and space to survive ...
... Living organisms require food, water, shelter, energy, and space to survive ...