Decay – Revision Pack (B4)
... isotope of oxygen (O18). This formed part of a water molecule. The experiment showed that the light energy is used to split up the water, rather than the carbon dioxide. The oxygen gas made was O18 while the oxygen present in glucose was normal oxygen (O16). An isotope is a different form of a certa ...
... isotope of oxygen (O18). This formed part of a water molecule. The experiment showed that the light energy is used to split up the water, rather than the carbon dioxide. The oxygen gas made was O18 while the oxygen present in glucose was normal oxygen (O16). An isotope is a different form of a certa ...
Lysosomes in iron metabolism, ageing and apoptosis
... the old opinion, and thus demonstrate the truth of Billings’ (1818–1885) statement: ‘‘The trouble with people is not that they don’t know, but that they know so much that ain’t so’’ (Billings 1874). The finding that the membranes of rat liver lysosomes contain a 37-fold higher specific content of a- ...
... the old opinion, and thus demonstrate the truth of Billings’ (1818–1885) statement: ‘‘The trouble with people is not that they don’t know, but that they know so much that ain’t so’’ (Billings 1874). The finding that the membranes of rat liver lysosomes contain a 37-fold higher specific content of a- ...
Neurotoxin-induced degeneration of dopamine neurons
... hermaphrodite without any apparent expression in other cell types (Fig 1 a and d; see Movie 1, which is available as supporting information on the PNAS web site, www.pnas.org). Labeled cells match the position of cells visualized with tyrosine hydroxylase (cat-2) GFP reporter construct (EM641, gift ...
... hermaphrodite without any apparent expression in other cell types (Fig 1 a and d; see Movie 1, which is available as supporting information on the PNAS web site, www.pnas.org). Labeled cells match the position of cells visualized with tyrosine hydroxylase (cat-2) GFP reporter construct (EM641, gift ...
Chapter 6
... weight loss. Theoretically, BAT volume and activity can be increased in several ways. Generally, a distinction is made between methods that activate already present brown fat cells, and methods that stimulate the recruitment of new brown fat. Activation of existing brown adipose tissue BAT is strong ...
... weight loss. Theoretically, BAT volume and activity can be increased in several ways. Generally, a distinction is made between methods that activate already present brown fat cells, and methods that stimulate the recruitment of new brown fat. Activation of existing brown adipose tissue BAT is strong ...
Influence of genotype and nutrition on survival and metabolism of starving yeast.
... substantial differences: When deprived of leucine or uracil, viability declined exponentially with a half-life of <2 days, whereas when the same strains were deprived of phosphate or sulfate, the half-life was ⬇10 days. The survival rates of nongrowing auxotrophs deprived of uracil or leucine depend ...
... substantial differences: When deprived of leucine or uracil, viability declined exponentially with a half-life of <2 days, whereas when the same strains were deprived of phosphate or sulfate, the half-life was ⬇10 days. The survival rates of nongrowing auxotrophs deprived of uracil or leucine depend ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... this are some of this classification; some are comma shaped; some of this bacteria are neither round, nor rod, it is a oval shaped bacteria; and, based on this, we can categorize the entire bacterial world into different segments. Now, if it is a spherical shaped bacteria, we call it as coccus, and ...
... this are some of this classification; some are comma shaped; some of this bacteria are neither round, nor rod, it is a oval shaped bacteria; and, based on this, we can categorize the entire bacterial world into different segments. Now, if it is a spherical shaped bacteria, we call it as coccus, and ...
Place cell references - The University of Texas at Dallas
... function consisting of two normal functions by means of the EM algorithm. The results show that the two components hypothesis is well applicable in each data set. The C1 at DG is advanced to CA1 in phase by 0.2 theta cycle (as shown in the figure), which strongly suggests that C1 is generated at an ...
... function consisting of two normal functions by means of the EM algorithm. The results show that the two components hypothesis is well applicable in each data set. The C1 at DG is advanced to CA1 in phase by 0.2 theta cycle (as shown in the figure), which strongly suggests that C1 is generated at an ...
Metabolism of lipids digestion, absorption, resynthesis in
... •Triacylglycerols (TGs) and glycogen two major forms of stored energy TGs which are more efficient energy stores because: (1) They are stored in an anhydrous form (2) Their fatty acids are more reduced than monosaccharides. ...
... •Triacylglycerols (TGs) and glycogen two major forms of stored energy TGs which are more efficient energy stores because: (1) They are stored in an anhydrous form (2) Their fatty acids are more reduced than monosaccharides. ...
Original Article Prediction of non-small cell lung cancer metastasis
... involved in the process of metastasis. Target of tumor metastasis is the current research focus. With the deepening of research in microRNA (miRNA), it is indicated that post-transcriptional regulation is widely present in organisms. miRNAs are single-strand small-molecule RNAs with 21-24 nucleotide ...
... involved in the process of metastasis. Target of tumor metastasis is the current research focus. With the deepening of research in microRNA (miRNA), it is indicated that post-transcriptional regulation is widely present in organisms. miRNAs are single-strand small-molecule RNAs with 21-24 nucleotide ...
Super-resolution microscopy of mitochondria
... located in the innermost mitochondrial compartment, the aqueous matrix [55,56]. The nucleoids are distributed throughout the mitochondrial network. In humans, the mtDNA encodes 13 proteins, which are essential for the function of OXPHOS. An important and still not conclusively answered question is w ...
... located in the innermost mitochondrial compartment, the aqueous matrix [55,56]. The nucleoids are distributed throughout the mitochondrial network. In humans, the mtDNA encodes 13 proteins, which are essential for the function of OXPHOS. An important and still not conclusively answered question is w ...
Plant synapses: actin-based domains for cell-to
... the concept of the ‘plant synapse’ should prove to be beneficial for the progress of contemporary plant cell biology, which currently lacks any satisfactory explanations for phenomena such as gravisensing and polar transport of auxin (Figure 1c–e). The polar transport of auxin not only mechanistical ...
... the concept of the ‘plant synapse’ should prove to be beneficial for the progress of contemporary plant cell biology, which currently lacks any satisfactory explanations for phenomena such as gravisensing and polar transport of auxin (Figure 1c–e). The polar transport of auxin not only mechanistical ...
Modernizing the nonhomologous end-joining repertoire: alternative
... exonucleolytic resection, which generates long single-stranded tails, the critical intermediates for initiating homologous pairing (129). ...
... exonucleolytic resection, which generates long single-stranded tails, the critical intermediates for initiating homologous pairing (129). ...
Transduction Cascade In Myeloid Cells: A Novel Cytokine Signal
... We have recently shown that IL-3R occupancy activates a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C, and the sustained diacylglycerol accumulation subsequently activates protein kinase C (PKC). In human IL-3-dependent myeloid cells (TF-1), the novel PKC⑀ isoform regulates bcl-2 expression and cell ...
... We have recently shown that IL-3R occupancy activates a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C, and the sustained diacylglycerol accumulation subsequently activates protein kinase C (PKC). In human IL-3-dependent myeloid cells (TF-1), the novel PKC⑀ isoform regulates bcl-2 expression and cell ...
Examiners` Report - Edexcel
... There were many candidates who guessed the answer to this by trying to work out what ‘polygenic’ could mean. Many lost marks by referring to the phenotype generally, rather than a specific characteristic or trait. There were also answers referring to alleles instead of genes – in this instance, we a ...
... There were many candidates who guessed the answer to this by trying to work out what ‘polygenic’ could mean. Many lost marks by referring to the phenotype generally, rather than a specific characteristic or trait. There were also answers referring to alleles instead of genes – in this instance, we a ...
the cell cycle in action - Oxford Academic
... to acquire the specific cell fate to form new tissues and organs (Brukhin, and Morozova, 2011). The cell cycle is a critical ...
... to acquire the specific cell fate to form new tissues and organs (Brukhin, and Morozova, 2011). The cell cycle is a critical ...
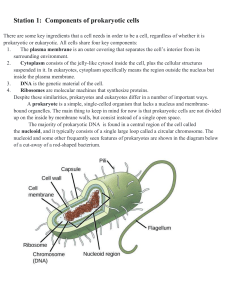
Station 1: Components of prokaryotic cells
... Bacteria exist as a single cell and there are thousands of species. The diet of bacteria is generally determined by their metabolic category. The process of bacteria breaking down food to get energy is called respiration. Phototrophic bacteria get their energy directly from the sun. Some bacteria fe ...
... Bacteria exist as a single cell and there are thousands of species. The diet of bacteria is generally determined by their metabolic category. The process of bacteria breaking down food to get energy is called respiration. Phototrophic bacteria get their energy directly from the sun. Some bacteria fe ...
Mechanism of Phage-induced Lysis in Pneumococci
... Fig. 1 . Phage-induced lysis of autolysin-defective and wild-type cultures as a function of the m.0.i. Both the mutant (curve B, x and D, A)and the wild-type (curve E, 0) cultures were grown in C Y medium. Cells were infected at the time indicated by the arrow, at the m.0.i. values indicated by the ...
... Fig. 1 . Phage-induced lysis of autolysin-defective and wild-type cultures as a function of the m.0.i. Both the mutant (curve B, x and D, A)and the wild-type (curve E, 0) cultures were grown in C Y medium. Cells were infected at the time indicated by the arrow, at the m.0.i. values indicated by the ...
1 Sister chromatids are often incompletely cohesed
... During preliminary investigations we occasionally found three or four instead of one or two FISH signals for chromosome-specific ~100 kb segments in 4C nuclei of A. thaliana indicating that not only homologues but also sister chromatids may occupy separate positions within a nucleus. Therefore, we b ...
... During preliminary investigations we occasionally found three or four instead of one or two FISH signals for chromosome-specific ~100 kb segments in 4C nuclei of A. thaliana indicating that not only homologues but also sister chromatids may occupy separate positions within a nucleus. Therefore, we b ...
Medicinal Chemistry of Antifungal Agents
... Fungal infections fall into two distinct categories: ...
... Fungal infections fall into two distinct categories: ...
5. Parvoviral Host Range and Cell Entry Mechanisms.
... Mature virions of most species in this genus contain a single 5-kb DNA strand that is negative sense with respect to transcription, while one virus, LuIII, packages approximately equimolar positive- and negative-sense strands. This remarkable variability illuminates the whole process of strand selec ...
... Mature virions of most species in this genus contain a single 5-kb DNA strand that is negative sense with respect to transcription, while one virus, LuIII, packages approximately equimolar positive- and negative-sense strands. This remarkable variability illuminates the whole process of strand selec ...