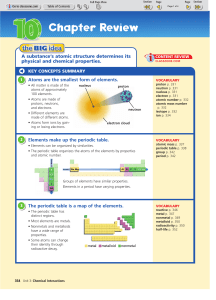
Dalton`s Atomic Theory
... • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the _______________ of that element. • The ___________ is a very small region located at the center of an atom. • The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a ___________ and usually one or more neutral part ...
... • An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the _______________ of that element. • The ___________ is a very small region located at the center of an atom. • The nucleus is made up of at least one positively charged particle called a ___________ and usually one or more neutral part ...
Elements, Isotopes, and Ions
... – Is the total mass of a certain ISOTOPE of an element. 1. How to calculate mass #: # of protons + # of neutrons = mass # 2. How to calculate # of neutrons from mass #: (Mass #) ...
... – Is the total mass of a certain ISOTOPE of an element. 1. How to calculate mass #: # of protons + # of neutrons = mass # 2. How to calculate # of neutrons from mass #: (Mass #) ...
Chapter Review - BAschools.org
... the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
... the world differed because each was made of atoms of different sizes and shapes. How does the modern view of atoms differ from this ancient view? How is it similar? ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Section 5.1
... – Explain how the atomic number identifies an element. – Use the atomic number and mass number of an element to find the numbers of protons, electrons, and neutrons. – Explain how isotopes differ, and why the atomic masses of elements are not whole numbers. – Calculate the average atomic mass of an ...
... – Explain how the atomic number identifies an element. – Use the atomic number and mass number of an element to find the numbers of protons, electrons, and neutrons. – Explain how isotopes differ, and why the atomic masses of elements are not whole numbers. – Calculate the average atomic mass of an ...
Chapter 10 Test A
... c. there are no elements associated with these light sources. d. all elements have the same spectral pattern. ____ 18. Heisenburg’s uncertainty principle tells us that: a. the act of observing in the quantum world changes the very system you are trying to measure. b. we are always uncertain about th ...
... c. there are no elements associated with these light sources. d. all elements have the same spectral pattern. ____ 18. Heisenburg’s uncertainty principle tells us that: a. the act of observing in the quantum world changes the very system you are trying to measure. b. we are always uncertain about th ...
atomic numbers
... than the proton 3. Found moving around the nucleus at near the speed of light. - sometimes called _______________________ or charge cloud electron cloud ______________________ 4. The Quantum Mechanical Model - currently accepted model of the atom (Chapter 11) - for now we will use the Bohr model, ri ...
... than the proton 3. Found moving around the nucleus at near the speed of light. - sometimes called _______________________ or charge cloud electron cloud ______________________ 4. The Quantum Mechanical Model - currently accepted model of the atom (Chapter 11) - for now we will use the Bohr model, ri ...
chapter-7-explore-page-248-protons-neutrons
... Becquerel and the Curies discovered that the radiation released by the uranium was made of energy and particles. This radiation came from the nuclei of the uranium atoms. When this happens, the number of protons in one atom of uranium changes. When uranium releases radiation, it changes to a diffe ...
... Becquerel and the Curies discovered that the radiation released by the uranium was made of energy and particles. This radiation came from the nuclei of the uranium atoms. When this happens, the number of protons in one atom of uranium changes. When uranium releases radiation, it changes to a diffe ...
atomic number - Net Start Class
... Synopsis of Structure • The atom is the smallest part of an element that retains its properties. • It is made of mostly empty space,with the majority of the mass concentrated in the middle (the nucleus). • The nucleus contains the positively charged protons and the chargeless neutrons. • The electr ...
... Synopsis of Structure • The atom is the smallest part of an element that retains its properties. • It is made of mostly empty space,with the majority of the mass concentrated in the middle (the nucleus). • The nucleus contains the positively charged protons and the chargeless neutrons. • The electr ...
8th-interlude-for-atoms - Epiphany Catholic School
... 1. A has 24 protons & 25 neutrons. B has 24 protons & 26 neutrons. Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...
... 1. A has 24 protons & 25 neutrons. B has 24 protons & 26 neutrons. Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...
05: Atoms and Molecules
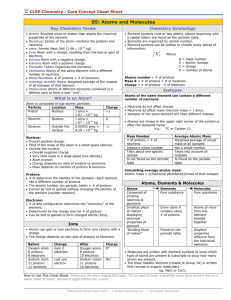
... number of neutrons. • Neutrons do not affect charge. • Neutrons do affect mass (neutron mass = 1 amu). • Isotopes of the same element will have different masses. • Masses are shown in the upper right corner of the symbol or after the elements name: e.g.: 13C or Carbon-13 Mass Number # of protons + # ...
... number of neutrons. • Neutrons do not affect charge. • Neutrons do affect mass (neutron mass = 1 amu). • Isotopes of the same element will have different masses. • Masses are shown in the upper right corner of the symbol or after the elements name: e.g.: 13C or Carbon-13 Mass Number # of protons + # ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
... • Compounds are pure substances that are composed of two or more atoms that are chemically combined • Compounds can only be changed into simpler substances called elements by chemical changes ...
Elements, Ions and Isotopes
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
History of the Atom
... We identify isotopes by their mass number. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons it ...
... We identify isotopes by their mass number. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons it ...
Reading Comprehension - Easy Peasy All-in
... The list of elements is arranged on a scientific chart. The chart is called the periodic table. Each element is grouped with other similar elements. Elements can be metals, nonmetals, or semimetals. Semimetals have some of the characteristics of metals, and some of the characteristics of nonmetals. M ...
... The list of elements is arranged on a scientific chart. The chart is called the periodic table. Each element is grouped with other similar elements. Elements can be metals, nonmetals, or semimetals. Semimetals have some of the characteristics of metals, and some of the characteristics of nonmetals. M ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
... The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different. What makes atoms of different elements different? The fundamental characteristic that all atoms of the same element share is the number of protons . All atoms of hydrogen have on ...
Chapter 18: Atoms and Elements
... Calculate the numbers of protons and neutrons in each stable isotope of an element. ...
... Calculate the numbers of protons and neutrons in each stable isotope of an element. ...
Dmitri Mendeleev
... Every element wants to be like the noble gases wants 0 or 8 valence electrons valence e- (outer electron shell used for bonding) ...
... Every element wants to be like the noble gases wants 0 or 8 valence electrons valence e- (outer electron shell used for bonding) ...
Average Atomic Mass 1213
... carbon--12/carbon carbon 12/carbon--14 or they man--made like can be man Einsteinium--252/Einsteinium Einsteinium 252/Einsteinium-251 Isotopes can be stable or unstable. Unstable isotopes will decay and are radioactive. ...
... carbon--12/carbon carbon 12/carbon--14 or they man--made like can be man Einsteinium--252/Einsteinium Einsteinium 252/Einsteinium-251 Isotopes can be stable or unstable. Unstable isotopes will decay and are radioactive. ...
Test Review Answers File
... 19. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15 and a mass number of 31. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does a neutral atom of phosphorus contain? a. Protons = 15 b. Neutrons = 16 c. Electrons = 15 20. Which part of the atom was discovered as a result of the Gold Foil experiment? ...
... 19. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15 and a mass number of 31. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does a neutral atom of phosphorus contain? a. Protons = 15 b. Neutrons = 16 c. Electrons = 15 20. Which part of the atom was discovered as a result of the Gold Foil experiment? ...
Study Guide 1-3
... isotopic notation given a drawing of an atom or isotopic notation. You must also be able to determine number of protons, neutrons, and electrons present. A) ...
... isotopic notation given a drawing of an atom or isotopic notation. You must also be able to determine number of protons, neutrons, and electrons present. A) ...
Exam #2 Review
... Neutrons - Chadwick 7. What did Rutherford discover from his Gold Foil Experiment? Atoms are mostly empty space and contain a dense, positive nucleus Basic Atomic Structure 8. List the three subatomic particles and their charge. ...
... Neutrons - Chadwick 7. What did Rutherford discover from his Gold Foil Experiment? Atoms are mostly empty space and contain a dense, positive nucleus Basic Atomic Structure 8. List the three subatomic particles and their charge. ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.