Review: theory vs law the atomic theory contributions of early scientists
... Neutron Heavy (similar to nucleus protons) Oct 711:36 AM ...
... Neutron Heavy (similar to nucleus protons) Oct 711:36 AM ...
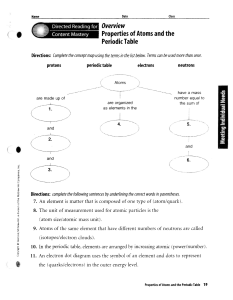
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once, protons ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once, protons ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. ...
... All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. ...
isotopes and atomic mass
... 1. Which of the data in the table must be measured and which must be calculated? 2. In all except step 11, the “Total” is calculated by adding the numbers across each row. Step 11 is an exception because it does not take into account the fact that there are different numbers of each isotope. Rather ...
... 1. Which of the data in the table must be measured and which must be calculated? 2. In all except step 11, the “Total” is calculated by adding the numbers across each row. Step 11 is an exception because it does not take into account the fact that there are different numbers of each isotope. Rather ...
Chap 03A-Atoms and Elements.pptx
... Ø explains the difference between an element and a compound. Ø explains two scientific laws, and Ø predicts a new scientific law. ...
... Ø explains the difference between an element and a compound. Ø explains two scientific laws, and Ø predicts a new scientific law. ...
1 - Bal Bharati Public School
... Q.22. The atom of an element 'A' has three electrons in the outermost shell. It loses one of hese to the atom of another element 'B'. What will be the nature and value of charge on the ion which results from 'A' ? Q.23.The atomic numbers of atoms of two elements are 18 and 20 respectively and their ...
... Q.22. The atom of an element 'A' has three electrons in the outermost shell. It loses one of hese to the atom of another element 'B'. What will be the nature and value of charge on the ion which results from 'A' ? Q.23.The atomic numbers of atoms of two elements are 18 and 20 respectively and their ...
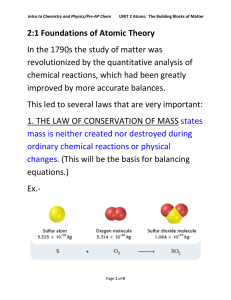
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... neutron are approximately the same size and are 2000 times larger than an electron. If a large football stadium were an atom, this would make the nucleus (including the protons and neutrons) about the size of a marble. The electrons would be similar to dust particles floating about the stadium. This ...
... neutron are approximately the same size and are 2000 times larger than an electron. If a large football stadium were an atom, this would make the nucleus (including the protons and neutrons) about the size of a marble. The electrons would be similar to dust particles floating about the stadium. This ...
Bean Bag Lab
... Introduction: John Dalton’s atomic theory that stated all atoms of the same element are identical and equal in mass was simple yet revolutionary. Unfortunately, it was not quite right. More research started to show that atoms of the same element could have different masses. These atoms were call iso ...
... Introduction: John Dalton’s atomic theory that stated all atoms of the same element are identical and equal in mass was simple yet revolutionary. Unfortunately, it was not quite right. More research started to show that atoms of the same element could have different masses. These atoms were call iso ...
Document
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
LAB ACTIVITY CALCULATING ATOMIC MASS
... believed to be element 114. The researchers have proposed that the element be named vabeachium (va-beach-e-m), after the city in which it was discovered. The proposed element symbol is Vb. Samples are currently being distributed to all of the local high schools. Each school is to isolate the individ ...
... believed to be element 114. The researchers have proposed that the element be named vabeachium (va-beach-e-m), after the city in which it was discovered. The proposed element symbol is Vb. Samples are currently being distributed to all of the local high schools. Each school is to isolate the individ ...
Distinguishing Among Atoms
... number of an atom of any element, you can determine the atom’s composition. ...
... number of an atom of any element, you can determine the atom’s composition. ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
September 20th, 2012
... Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. a) write the complete chemical symbol (subscript and superscript) of each. b) how many neutrons are in an atom of ...
... Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. a) write the complete chemical symbol (subscript and superscript) of each. b) how many neutrons are in an atom of ...
PS-CC-2test - Edquest Science
... B. iron and copper C. aluminum and carbon D. lead and zinc 13. The periodic table is organized by the patterns of the properties of the elements. The rows in the periodic table vary with the amount of elements they contain. These rows are called … A. groups B. families C. periods D. metals ...
... B. iron and copper C. aluminum and carbon D. lead and zinc 13. The periodic table is organized by the patterns of the properties of the elements. The rows in the periodic table vary with the amount of elements they contain. These rows are called … A. groups B. families C. periods D. metals ...
Basic Atomic Structure and Isotope Symbols
... Atomic Number - is the number of protons in the atom. If the atom is neutral the atomic number is also the number of electrons in the atom. Mass Number - is the number of protons + neutrons in the atom. Both of these numbers will be parts of the Isotope Symbol. Both of these numbers are found by cou ...
... Atomic Number - is the number of protons in the atom. If the atom is neutral the atomic number is also the number of electrons in the atom. Mass Number - is the number of protons + neutrons in the atom. Both of these numbers will be parts of the Isotope Symbol. Both of these numbers are found by cou ...
Name Period _____ Chemistry Review
... 7. Located on the left side of the periodic table. 8. Located on the far right of the periodic table. 9. Conduct electricity and are ductile. 10. Most of the elements on the periodic table are ________. 11. Are used as semiconductors of electricity. 12. Used to form alloys 13. This group includes th ...
... 7. Located on the left side of the periodic table. 8. Located on the far right of the periodic table. 9. Conduct electricity and are ductile. 10. Most of the elements on the periodic table are ________. 11. Are used as semiconductors of electricity. 12. Used to form alloys 13. This group includes th ...
Elements Elements (cont.) Elements (cont.)
... • Atoms are indivisible by chemical processes. – All atoms present at beginning are present at the end. – Atoms are not created or destroyed, just rearranged in chemical reactions reactions. – Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. ...
... • Atoms are indivisible by chemical processes. – All atoms present at beginning are present at the end. – Atoms are not created or destroyed, just rearranged in chemical reactions reactions. – Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... 1. Atoms are tiny, invisible particles. ...
... 1. Atoms are tiny, invisible particles. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... 1. Atoms are tiny, invisible particles. ...
... 1. Atoms are tiny, invisible particles. ...
Science notes on Atoms, Periodic table
... 1st discovered & named by Democritus, who believed it was a small indivisible particle of matter. Aristotle believed that it was infinitely divisible (you could keep on cutting it forever). He also believed that everything was composed of 5 elements: water, earth, fire, air & aether John Dalton then ...
... 1st discovered & named by Democritus, who believed it was a small indivisible particle of matter. Aristotle believed that it was infinitely divisible (you could keep on cutting it forever). He also believed that everything was composed of 5 elements: water, earth, fire, air & aether John Dalton then ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.