Atomic Structure Subatomic Particles Atoms are made up of even
... Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Because isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. To distinguish between isotopes of the same element, we write an isotope s ...
... Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Because isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. To distinguish between isotopes of the same element, we write an isotope s ...
Isotopes Article
... We all know what an atom is by now and we are aware that all matter is made up of them. Atoms themselves are made up of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of those has different charges. The protons (positive) and neutrons (no charge) are found in the densest area of t ...
... We all know what an atom is by now and we are aware that all matter is made up of them. Atoms themselves are made up of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of those has different charges. The protons (positive) and neutrons (no charge) are found in the densest area of t ...
Average Atomic Mass
... 62. Calculate the molar mass of magnesium phosphate. 63. How many moles are in 7.23 grams of strontium oxide? 64. How many moles are in 3.02 x 1023 atoms of zinc? 65. How many grams are in 7.2 x 1046 molecules of copper (II) sulfate? 66. How many grams are in 1.00 moles of sodium oxalate? 67. How ma ...
... 62. Calculate the molar mass of magnesium phosphate. 63. How many moles are in 7.23 grams of strontium oxide? 64. How many moles are in 3.02 x 1023 atoms of zinc? 65. How many grams are in 7.2 x 1046 molecules of copper (II) sulfate? 66. How many grams are in 1.00 moles of sodium oxalate? 67. How ma ...
atomic number
... • When a neutral atom gains one or more electrons, it now has more electrons than protons and has a negative charge. • An atom with a negative charge is called a negative ion or anion. ...
... • When a neutral atom gains one or more electrons, it now has more electrons than protons and has a negative charge. • An atom with a negative charge is called a negative ion or anion. ...
Introduction to atoms
... 4. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one element combine in small, whole number ratios. 5. A given compound always has the same relative number and kind of atoms. ...
... 4. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one element combine in small, whole number ratios. 5. A given compound always has the same relative number and kind of atoms. ...
Physical Science Chapter 3 Test
... their properties will emerge in a regular pattern. 12. Because atoms of elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of ____________________, they have similar properties. 13. Some elements are highly ____________________ because their outermost energy levels are only partia ...
... their properties will emerge in a regular pattern. 12. Because atoms of elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of ____________________, they have similar properties. 13. Some elements are highly ____________________ because their outermost energy levels are only partia ...
Unit 2 Test Review - Liberty High School
... 5. If sodium melts at 97.72° C and boils at 882.8°C, what is its physical state at 80°C? At 250°C? 6. What is a pure substance made up of more than one kind of atom called? 7. Describe the difference between a compound and an element. Give two examples of each. 8. How can a solution be distinguished ...
... 5. If sodium melts at 97.72° C and boils at 882.8°C, what is its physical state at 80°C? At 250°C? 6. What is a pure substance made up of more than one kind of atom called? 7. Describe the difference between a compound and an element. Give two examples of each. 8. How can a solution be distinguished ...
Answers
... (c) Lithium would float on water, [1] producing gas steadily. [1] (d) Potassium would melt to a silvery ball [1] which moves about very quickly on the water surface, [1] producing a hissing sound, [1] burning spontaneously with a lilac flame [1] before finally disappearing completely. [1] (e) It wou ...
... (c) Lithium would float on water, [1] producing gas steadily. [1] (d) Potassium would melt to a silvery ball [1] which moves about very quickly on the water surface, [1] producing a hissing sound, [1] burning spontaneously with a lilac flame [1] before finally disappearing completely. [1] (e) It wou ...
The Basics of Atomic Structure
... • An element will always have the same number of protons regardless of the number of neutrons and electrons. An element can be identified by its Atomic Number. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different but th ...
... • An element will always have the same number of protons regardless of the number of neutrons and electrons. An element can be identified by its Atomic Number. • Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons; therefore, the mass number will be different but th ...
Matter Unit Study Guide Phases of Matter
... Chemical formulas for used to show the different elements that make up a compound. The letters tell you which elements are in the compound. The numbers tell you how many atoms of each element are in one molecule of the compound. Complete the chart with the element name and number of atoms for each e ...
... Chemical formulas for used to show the different elements that make up a compound. The letters tell you which elements are in the compound. The numbers tell you how many atoms of each element are in one molecule of the compound. Complete the chart with the element name and number of atoms for each e ...
AP Semester I Review: Free Response Questions
... that represents the different particles present in the solution. Base the particles in your drawing on the particles shown in the representations above. Include only one formula unit of LiCl and no more than ten molecules of water. ...
... that represents the different particles present in the solution. Base the particles in your drawing on the particles shown in the representations above. Include only one formula unit of LiCl and no more than ten molecules of water. ...
Unit 2 - Chapter 3 Elements, Atoms, Ions The elements Can we
... Subatomic particle, so the atom was made of smaller particles ...
... Subatomic particle, so the atom was made of smaller particles ...
Chapter 5 - Effingham County Schools
... nucleus, called the atomic number. For example, a hydrogen atom has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is called its atomic mass number. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. Ions are formed whe ...
... nucleus, called the atomic number. For example, a hydrogen atom has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus is called its atomic mass number. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons. Ions are formed whe ...
Atom, Ion, Isotope Notes from 10/5 and 10/6
... a good estimation for finding the most common stable isotope of an atom. HOWEVER, it is not a perfect method. Look at Ag for example. It’s atomic mass is 107.87 amu, which would round to 108 amu. This is actually NOT a stable isotope of Ag (only 107 amu and 109 amu are). If you really wanted to know ...
... a good estimation for finding the most common stable isotope of an atom. HOWEVER, it is not a perfect method. Look at Ag for example. It’s atomic mass is 107.87 amu, which would round to 108 amu. This is actually NOT a stable isotope of Ag (only 107 amu and 109 amu are). If you really wanted to know ...
Sem 1 Final
... • In two isotopes of the same element, which of the following would be the same and which would be different? – Atomic number – Number of protons – Number of neutrons – Number of electrons – Element symbol – Atomic mass ...
... • In two isotopes of the same element, which of the following would be the same and which would be different? – Atomic number – Number of protons – Number of neutrons – Number of electrons – Element symbol – Atomic mass ...
UNIT 5 REVIEW PROBLEMS
... higher electronegativities and lower ionization energies higher electronegativities and higher ionization energies lower electronegativities and lower ionization energies lower electronegativities and higher ionization energies ...
... higher electronegativities and lower ionization energies higher electronegativities and higher ionization energies lower electronegativities and lower ionization energies lower electronegativities and higher ionization energies ...
Chapter 4
... who came up with the concept of the atom. He said that everything was made up of extremely small particles that could not be cut into anything smaller. ...
... who came up with the concept of the atom. He said that everything was made up of extremely small particles that could not be cut into anything smaller. ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
File
... • The atomic number, Z, represents the number of protons, p+, in the nucleus of an atom. • The atomic number is usually the biggest number listed in the box for each element (look at periodic table). • The atomic number (or number of protons) identifies an element. • The modern periodic table orders ...
... • The atomic number, Z, represents the number of protons, p+, in the nucleus of an atom. • The atomic number is usually the biggest number listed in the box for each element (look at periodic table). • The atomic number (or number of protons) identifies an element. • The modern periodic table orders ...
2 C Atomic Number Mass Number Atomic Mass and Isotopes
... Atoms have no overall electrical charge so, an atom must have as many electrons as there are ...
... Atoms have no overall electrical charge so, an atom must have as many electrons as there are ...
EXPERIMENT
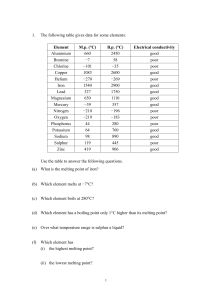
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
... In this experiment, you will be looking at some elements in the laboratory display. Some look different from each other, while others look similar. Elements can be categorized in several ways. In this experiment, you are going to group elements by similarities in their physical properties. Elements ...
Atomic mass - cloudfront.net
... The meaning of the terms "atom" and "element" can be confusing because they are often used as if they are the same thing. They are related to one another but they are not the same. An atom is the smallest particle or "building block" of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same ...
... The meaning of the terms "atom" and "element" can be confusing because they are often used as if they are the same thing. They are related to one another but they are not the same. An atom is the smallest particle or "building block" of a substance. An element is a substance made up of all the same ...
Chem 200 Dr. Saidane
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.