atomic number.
... 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change at ...
... 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change at ...
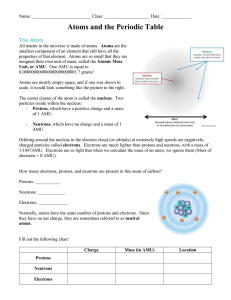
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
... 2 vocab words often confused, so here’s your warning: Ion and Isotope. Both have something the same, something different. Both start with the letter “i". Don’t confuse them! Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have identical numbers of protons (by definition!!) but different numbers of neutr ...
... 2 vocab words often confused, so here’s your warning: Ion and Isotope. Both have something the same, something different. Both start with the letter “i". Don’t confuse them! Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have identical numbers of protons (by definition!!) but different numbers of neutr ...
protons and neutrons
... Most of the particles passed right through A few particles were deflected VERY FEW were greatly deflected ...
... Most of the particles passed right through A few particles were deflected VERY FEW were greatly deflected ...
atomic number
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Oct 14th ,2015
... some ways you can separate assessment it? (Pick up periodic table up front) Objectives: St 4: Matter: Understand the structure of an atom in terms of its subatomic particles; isotopes and ions; differentiate between the classification and separation of matter (mixtures, pure substances…) ...
... some ways you can separate assessment it? (Pick up periodic table up front) Objectives: St 4: Matter: Understand the structure of an atom in terms of its subatomic particles; isotopes and ions; differentiate between the classification and separation of matter (mixtures, pure substances…) ...
File - Science by Shaw
... 3. An atom has 11 protons and 12 neutrons. a) What element is this? b) Write this isotope in hyphen notation c) Write this isotope in nuclear notation 4. STOTD ** You will need a calculator for today. ...
... 3. An atom has 11 protons and 12 neutrons. a) What element is this? b) Write this isotope in hyphen notation c) Write this isotope in nuclear notation 4. STOTD ** You will need a calculator for today. ...
Section 2 Powerpoint
... Reviewing Concepts • 1. Name three subatomic particles. • 2. Name three properties you could use to distinguish a proton from an electron. • 3. Which characteristic of an atom always varies among atoms of different elements? • 4. How are the isotopes of an element different from one another? • 5. W ...
... Reviewing Concepts • 1. Name three subatomic particles. • 2. Name three properties you could use to distinguish a proton from an electron. • 3. Which characteristic of an atom always varies among atoms of different elements? • 4. How are the isotopes of an element different from one another? • 5. W ...
Atomic terms Example: Helium has an atomic number of 2. Every
... - Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of previously unknown elements using his "periodic law" ...
... - Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of previously unknown elements using his "periodic law" ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
The Atom - VCE Chemistry
... country of her birth, Poland. • Its atomic number is 84 and was placed in the same group as tellurium (Group IV, atomic number 52) because of their similar chemical properties. ...
... country of her birth, Poland. • Its atomic number is 84 and was placed in the same group as tellurium (Group IV, atomic number 52) because of their similar chemical properties. ...
PreAP Chemistry
... 18. Boron (B) has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (abundance = 19.8%, mass = 10.013 amu) and boron-11 (abundance = 80.2%, mass = 11.009 amu). Calculate the atomic mass of boron. ...
... 18. Boron (B) has two naturally occurring isotopes: boron-10 (abundance = 19.8%, mass = 10.013 amu) and boron-11 (abundance = 80.2%, mass = 11.009 amu). Calculate the atomic mass of boron. ...
Document
... In figure 26, the blocks for most of the elements are _________________________. These elements are __________. The blocks for ______________ are ____________. Between the metals and the nonmetals are the _________________. These elements are represented by the _______________________________. Semim ...
... In figure 26, the blocks for most of the elements are _________________________. These elements are __________. The blocks for ______________ are ____________. Between the metals and the nonmetals are the _________________. These elements are represented by the _______________________________. Semim ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 1. amu appropriate unit for measuring the size of a particle 2. equals one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom C. Protons 1. number of protons is used to identify elements 2. each element has different number of protons 3. number of electrons equals the number of protons in an element ...
... 1. amu appropriate unit for measuring the size of a particle 2. equals one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom C. Protons 1. number of protons is used to identify elements 2. each element has different number of protons 3. number of electrons equals the number of protons in an element ...
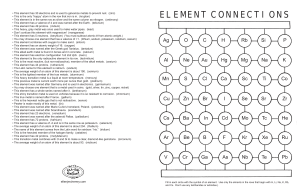
element connections
... • This element has 5 neutrons. (beryllium) (You must subtract atomic # from atomic weight.) • You may choose one element that has a valence of +1. (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium) • This element combines with oxygen to make sand. (silicon) • This element has an atomic weight of 16. (ox ...
... • This element has 5 neutrons. (beryllium) (You must subtract atomic # from atomic weight.) • You may choose one element that has a valence of +1. (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium) • This element combines with oxygen to make sand. (silicon) • This element has an atomic weight of 16. (ox ...
Atomic Mass
... same number of neutrons. •Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. •Isotope symbol: ...
... same number of neutrons. •Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. •Isotope symbol: ...
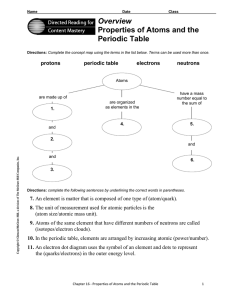
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
Masses of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
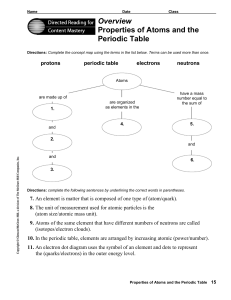
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
Notes matter energy
... lose electrons to become ions. Your periodic table gives some charges of ions that form from atoms. Ions can be indicated by a superscript in the upper right corner of the element box. For example Na+1 is a sodium ion that forms from a sodium atom losing one negatively charged electron. F−1 is a flu ...
... lose electrons to become ions. Your periodic table gives some charges of ions that form from atoms. Ions can be indicated by a superscript in the upper right corner of the element box. For example Na+1 is a sodium ion that forms from a sodium atom losing one negatively charged electron. F−1 is a flu ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.