Atoms
... •Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties, because they have the same number of protons and electrons. Isotopes are identified by mass number. Neutrons affect mass, so, isotopes with more neutrons ar ...
... •Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties, because they have the same number of protons and electrons. Isotopes are identified by mass number. Neutrons affect mass, so, isotopes with more neutrons ar ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... compound, the masses of one element combined with a fixed mass of the second are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Same elements to combine in different ratios to give different substances. ...
... compound, the masses of one element combined with a fixed mass of the second are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Same elements to combine in different ratios to give different substances. ...
Problem Set 4
... c. Different kinds of atoms have different sizes and shapes d. The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape and movement of atoms e. Apparent changes in matter result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not from changes in the atoms themselves. 6) What is wrong with Democritu ...
... c. Different kinds of atoms have different sizes and shapes d. The differing properties of matter are due to the size, shape and movement of atoms e. Apparent changes in matter result from changes in the groupings of atoms and not from changes in the atoms themselves. 6) What is wrong with Democritu ...
Notes 4.3 filled in
... MN is not indicated on the PT. To calculate the MN, simply add up #p+ and # no each having the mass of 1 amu. Q: an atom has 5 protons and 7 neutrons, calculate the MN. A: 5 amu + 7 amu = 12 amu Q: Which element is that? (Look in the PT) A: 5 protons, it’s Boron D. Isotopes Every element exist ...
... MN is not indicated on the PT. To calculate the MN, simply add up #p+ and # no each having the mass of 1 amu. Q: an atom has 5 protons and 7 neutrons, calculate the MN. A: 5 amu + 7 amu = 12 amu Q: Which element is that? (Look in the PT) A: 5 protons, it’s Boron D. Isotopes Every element exist ...
atoms - KMKunz
... of atoms. No atoms are created, destroyed, or broken apart in a chemical reaction ...
... of atoms. No atoms are created, destroyed, or broken apart in a chemical reaction ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Topic 2 Part 1 Slides - Coral Gables Senior High
... Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 19.0 is 55.0% abundant; the isotope with a mass number of 21.0 is 45.0% abundant. What is the relative atomic mass for element Z? You should always calculate RAM v ...
... Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 19.0 is 55.0% abundant; the isotope with a mass number of 21.0 is 45.0% abundant. What is the relative atomic mass for element Z? You should always calculate RAM v ...
The nucleus - VCE Chemistry
... • In 1913 Soddy explained these observations by introducing the idea of isotopes (from the Greek, meaning 'same place') as elements with the same chemical properties but containing atoms which differed in mass, physical properties and radioactive behaviour. • The relative atomic mass of such an elem ...
... • In 1913 Soddy explained these observations by introducing the idea of isotopes (from the Greek, meaning 'same place') as elements with the same chemical properties but containing atoms which differed in mass, physical properties and radioactive behaviour. • The relative atomic mass of such an elem ...
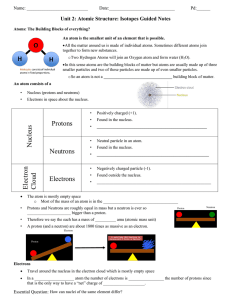
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
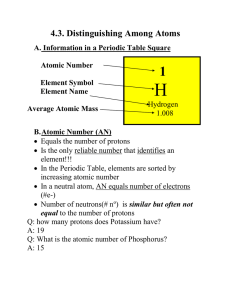
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
The nucleus Rutherford`s nuclear atom (1902
... introducing the idea of isotopes (from the Greek, meaning 'same place') as elements with the same chemical properties but containing atoms which differed in mass, physical properties and radioactive behaviour. • The relative atomic mass of such an element would therefore be an average according to t ...
... introducing the idea of isotopes (from the Greek, meaning 'same place') as elements with the same chemical properties but containing atoms which differed in mass, physical properties and radioactive behaviour. • The relative atomic mass of such an element would therefore be an average according to t ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... • A Proton and a Neutron have about the same mass (1 amu). • Electrons mass are around 2,000 times less than protons and neutrons. • Protons and Neutrons contribute to most of the atom’s mass. ...
... • A Proton and a Neutron have about the same mass (1 amu). • Electrons mass are around 2,000 times less than protons and neutrons. • Protons and Neutrons contribute to most of the atom’s mass. ...
ExamView - ev chap 4.tst
... 4. Which of the following is NOT a part of Dalton's atomic theory? A. Atoms that combine do so in simple whole-number ratios. B. Atoms are always in motion. C. All elements are composed of atoms. D. Atoms of the same element are identical. 5. Who conducted experiments to determine the quantity of ch ...
... 4. Which of the following is NOT a part of Dalton's atomic theory? A. Atoms that combine do so in simple whole-number ratios. B. Atoms are always in motion. C. All elements are composed of atoms. D. Atoms of the same element are identical. 5. Who conducted experiments to determine the quantity of ch ...
The Atom
... A. To find the number of neutrons an atom has 1. First you have to know the number of protons – that’s the atomic number 2. Then you have to know the atomic mass number 3. When you subtract the atomic number from the mass number rounded to nearest whole number 4. You get the number of neutrons Mass ...
... A. To find the number of neutrons an atom has 1. First you have to know the number of protons – that’s the atomic number 2. Then you have to know the atomic mass number 3. When you subtract the atomic number from the mass number rounded to nearest whole number 4. You get the number of neutrons Mass ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... table by increasing atomic number. 1. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. 2. In 1913, Henry G.J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
... table by increasing atomic number. 1. In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised the first periodic table based on atomic mass. 2. In 1913, Henry G.J. Moseley arranged the elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass. ...
7th Grade Atomic Structure and Periodic Table of Elements
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
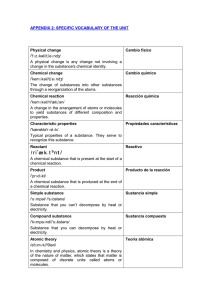
specific vocabulary of the unit
... Any of the elements of Group 18 (VIII, VIIIA), which includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and element 118. These elements are referred to as "inert" or "noble" because they do not easily form compounds with other elements. Transition elements /træn'zɪʃən//'eləmənts / A class of eleme ...
... Any of the elements of Group 18 (VIII, VIIIA), which includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and element 118. These elements are referred to as "inert" or "noble" because they do not easily form compounds with other elements. Transition elements /træn'zɪʃən//'eləmənts / A class of eleme ...
Note Packet for Students
... 3. The element lead consists of four naturally occurring isotopes with masses 203.97302, 205.97444, 206.97587 and 207.97663 amu. The relative abundances of these four isotopes are 1.4, 24.1, 22.1 and 52.4% respectively. From these data, calculate the average atomic mass of ...
... 3. The element lead consists of four naturally occurring isotopes with masses 203.97302, 205.97444, 206.97587 and 207.97663 amu. The relative abundances of these four isotopes are 1.4, 24.1, 22.1 and 52.4% respectively. From these data, calculate the average atomic mass of ...
Chemical Element
... Said another way, an "element" cannot be transformed into other chemical substances by chemical processes. In 1913, Henry Moseley discovered that the physical basis of the atomic number of the atom was its nuclear charge, which eventually led to the current definition. The current definition also av ...
... Said another way, an "element" cannot be transformed into other chemical substances by chemical processes. In 1913, Henry Moseley discovered that the physical basis of the atomic number of the atom was its nuclear charge, which eventually led to the current definition. The current definition also av ...
PS 2.3
... an advertisement poster on its everyday use. You want to make this poster as appealing as possible for your immediate classmates and school community, so that people will take the time to read and learn about the everyday use of several elements found on the Periodic Table Your poster needs to inclu ...
... an advertisement poster on its everyday use. You want to make this poster as appealing as possible for your immediate classmates and school community, so that people will take the time to read and learn about the everyday use of several elements found on the Periodic Table Your poster needs to inclu ...
Atom - Images
... (getting smaller) because the positive charge is greater than the smaller negative charges and pulls them in toward the nucleus. • More electrons than protons = radii increases (getting larger) because the electrons are farther away from the positive nucleus. • The Natural state of atoms has protons ...
... (getting smaller) because the positive charge is greater than the smaller negative charges and pulls them in toward the nucleus. • More electrons than protons = radii increases (getting larger) because the electrons are farther away from the positive nucleus. • The Natural state of atoms has protons ...
Slide 1
... • Mass number is used to describe the nuclear content of one isotope (usually the most abundant) of an element. • Atomic mass is the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element. • Atomic masses on the periodic table are not whole numbers because they contain the mass numbers all of the is ...
... • Mass number is used to describe the nuclear content of one isotope (usually the most abundant) of an element. • Atomic mass is the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element. • Atomic masses on the periodic table are not whole numbers because they contain the mass numbers all of the is ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
File
... X and Z because they have the same atomic number but different masses. 15. Atoms W, X, Y, and Z have the following nuclear compositions. Which two are isotopes? How do you know? ...
... X and Z because they have the same atomic number but different masses. 15. Atoms W, X, Y, and Z have the following nuclear compositions. Which two are isotopes? How do you know? ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.