IPS Unit 8 – Periodic Table Review Worksheet
... 10. What are the four block of the periodic table in order and give the group numbers for each block. ...
... 10. What are the four block of the periodic table in order and give the group numbers for each block. ...
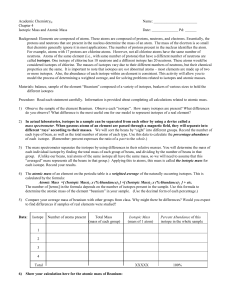
In actual laboratories, isotopes in a sample can be
... Background: Elements are composed of atoms. These atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Essentially, the protons and neutrons that are present in the nucleus determine the mass of an atom. The mass of the electron is so small that chemists generally ignore it in most applications. ...
... Background: Elements are composed of atoms. These atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Essentially, the protons and neutrons that are present in the nucleus determine the mass of an atom. The mass of the electron is so small that chemists generally ignore it in most applications. ...
1 - VCE Chemistry
... 4. A group in the periodic table is identified as: A) Elements with the same electronegativity B) A column of the periodic table C) A row of the periodic table D) Elements with different numbers of valence electrons E) Elements with identical electronic configurations 5. Bromine and iodine are in th ...
... 4. A group in the periodic table is identified as: A) Elements with the same electronegativity B) A column of the periodic table C) A row of the periodic table D) Elements with different numbers of valence electrons E) Elements with identical electronic configurations 5. Bromine and iodine are in th ...
gp - fc2009goran
... iodine also has 53 protons (this is what makes it behave chemically as iodine) but four extra neutrons, for a total atomic weight of 131 (53 protons and 78 neutrons). With "too many" neutrons in its nucleus, it is unstable and radioactive, with a half-life of eight days. Because it behaves chemicall ...
... iodine also has 53 protons (this is what makes it behave chemically as iodine) but four extra neutrons, for a total atomic weight of 131 (53 protons and 78 neutrons). With "too many" neutrons in its nucleus, it is unstable and radioactive, with a half-life of eight days. Because it behaves chemicall ...
Step 1 Lesson Plan
... Each atom has a charged substructure consisting of a nucleus, which is made of protons and neutrons, which are surrounded by electrons. (HS-PS1-1) The periodic table orders elements horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus and places those with similar chemical properties in colum ...
... Each atom has a charged substructure consisting of a nucleus, which is made of protons and neutrons, which are surrounded by electrons. (HS-PS1-1) The periodic table orders elements horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus and places those with similar chemical properties in colum ...
Answer on Question #47967 - Chemistry – Other
... c. The neutron was discovered by Chadwick in 1932. d. The electron was discovered by Goldstein in 1886. e. Canal rays were found to be made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 6. Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element are identical. We know that__________. a. A ...
... c. The neutron was discovered by Chadwick in 1932. d. The electron was discovered by Goldstein in 1886. e. Canal rays were found to be made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 6. Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element are identical. We know that__________. a. A ...
Atomic Masses
... Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify the parts of an atom, their location, charge, and relative mass. Determine the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom. ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify the parts of an atom, their location, charge, and relative mass. Determine the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom. ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... Based on his experimental evidence: The atom is mostly empty space All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occu ...
... Based on his experimental evidence: The atom is mostly empty space All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occu ...
Atomic Structure Notes file
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
HighFour Chemistry Round 1 Category C: Grades 9 – 10 Thursday
... To balance the 8 H atoms on the right side, 8 moles of HNO3 is required. To finalize the balancing, 2 moles of NO is required to balance out the O and N atoms. The balanced chemical reaction is therefore: ...
... To balance the 8 H atoms on the right side, 8 moles of HNO3 is required. To finalize the balancing, 2 moles of NO is required to balance out the O and N atoms. The balanced chemical reaction is therefore: ...
Year 9 Science revison _15-16_ end of year CHEM
... it has 1 electron in the outer shell. It loses that electron (in a chemical reaction) to have a full outer shell and become “stable” like the noble gases. You know that it loses 1 electron…..because it’s in group 1. ii) what is the charge on a rubidium ion ? ...
... it has 1 electron in the outer shell. It loses that electron (in a chemical reaction) to have a full outer shell and become “stable” like the noble gases. You know that it loses 1 electron…..because it’s in group 1. ii) what is the charge on a rubidium ion ? ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, elements are composed of tiny particles called ________________(1). Atoms of each element are ________________(2) from the atoms of all other elements. Atoms of different elements can form ________________(3) by combining in whole-number ratios. Chemical reaction ...
... According to Dalton’s atomic theory, elements are composed of tiny particles called ________________(1). Atoms of each element are ________________(2) from the atoms of all other elements. Atoms of different elements can form ________________(3) by combining in whole-number ratios. Chemical reaction ...
Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... found and how they are named. Describe atomic structure and how that structure determines an elements identity. Identify number of proton, electrons, and neutrons using a periodic table. Interpret information about an element using a periodic table. Evaluate and calculate the number of atomic partic ...
... found and how they are named. Describe atomic structure and how that structure determines an elements identity. Identify number of proton, electrons, and neutrons using a periodic table. Interpret information about an element using a periodic table. Evaluate and calculate the number of atomic partic ...
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses due to different numbers of neutrons. See the example below for two isotopes of oxygen. One has 8 neutrons while the other has 10 neutrons. Therefore, the masses are 16 amu and 18 amu respectively. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses due to different numbers of neutrons. See the example below for two isotopes of oxygen. One has 8 neutrons while the other has 10 neutrons. Therefore, the masses are 16 amu and 18 amu respectively. ...
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number (A) of the atom (remember A for “all”): Mass Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons Protons attract the electrons because they have opposite charges. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is ...
... The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number (A) of the atom (remember A for “all”): Mass Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons Protons attract the electrons because they have opposite charges. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is ...
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number (A) of the atom (remember A for “all”): Mass Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons Protons attract the electrons because they have opposite charges. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is ...
... The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number (A) of the atom (remember A for “all”): Mass Number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons Protons attract the electrons because they have opposite charges. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is ...
No Slide Title
... • This term describes a metal that can be pounded or rolled into shape. • What is malleable. ...
... • This term describes a metal that can be pounded or rolled into shape. • What is malleable. ...
4.1Atoms and Isotopes
... The mass reported on the periodic table is actually a weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of an element. Most hydrogen is Hydrogen – 1, therefore the average mass is very close to 1 (1.0079). For most atoms, one isotope is much more common than the other(s). ...
... The mass reported on the periodic table is actually a weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of an element. Most hydrogen is Hydrogen – 1, therefore the average mass is very close to 1 (1.0079). For most atoms, one isotope is much more common than the other(s). ...
Atoms - Peoria Public Schools
... • In 1808 John Dalton proposed an explanation that included all three laws • Dalton’s atomic theory has five points: – All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. – Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, ...
... • In 1808 John Dalton proposed an explanation that included all three laws • Dalton’s atomic theory has five points: – All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. – Atoms of an element are identical in size, mass and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, ...
Structures of Matter
... Two parts of an atom have an electrical charge; they are protons (positive) and electrons (negative). Protons and electrons usually are equal which makes them a neutral atom. However, sometimes you can add or remove an electron, which changes the electrical charge of the atom. ...
... Two parts of an atom have an electrical charge; they are protons (positive) and electrons (negative). Protons and electrons usually are equal which makes them a neutral atom. However, sometimes you can add or remove an electron, which changes the electrical charge of the atom. ...
Atomic Structure and Isotopes
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory: > All elements are composed of atoms. > Atoms of the same elements are the same. > Atoms of different elements can combine together to make compounds. > Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory: > All elements are composed of atoms. > Atoms of the same elements are the same. > Atoms of different elements can combine together to make compounds. > Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1. Which of the following
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1.
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
isotopes and average atomic mass
... The atomic mass of an element is the sum of all the masses of the sub-atomic particles which comprise the atom. The mass in grams of these particles (protons, neutrons, electrons, et al) are exceptionally small. The mass of the proton is 1.67 X 10-23 grams. The neutron is slightly larger and the ele ...
... The atomic mass of an element is the sum of all the masses of the sub-atomic particles which comprise the atom. The mass in grams of these particles (protons, neutrons, electrons, et al) are exceptionally small. The mass of the proton is 1.67 X 10-23 grams. The neutron is slightly larger and the ele ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.