Masses of Atoms
... Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? ...
... Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? ...
Practice Packet
... amounts of energy and move in areas called orbitals Developed after the famous discovery that energy can behave as both waves & particles ...
... amounts of energy and move in areas called orbitals Developed after the famous discovery that energy can behave as both waves & particles ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
... _____ 55) How do the isotopes Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 differ? a. Carbon-12 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. b. Carbon-12 has 12 neutrons; carbon-13 has 13 neutrons c. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12 d. Carbon-13 has one more proton that carbon-12 _____ 56) The atomic mass of an ...
Chemistry Unit 2 - Finding Patterns
... The periodic table, arranged by atomic number, reveals a tendency for properties to repeat in a periodic pattern (periodicity), and can be used to predict the properties and uses of an element. These periodic trends exist for many properties of the elements including atomic radii, ionization energy, ...
... The periodic table, arranged by atomic number, reveals a tendency for properties to repeat in a periodic pattern (periodicity), and can be used to predict the properties and uses of an element. These periodic trends exist for many properties of the elements including atomic radii, ionization energy, ...
2.1 Elements
... B. Electron-Dot Symbols • Dots representing valence electrons are placed on the four sides of an element symbol. • Each dot represents one valence electron. • For 1 to 4 valence electrons, single dots are used. With more than 4 valence electrons, the dots are paired. ...
... B. Electron-Dot Symbols • Dots representing valence electrons are placed on the four sides of an element symbol. • Each dot represents one valence electron. • For 1 to 4 valence electrons, single dots are used. With more than 4 valence electrons, the dots are paired. ...
Elements and Compounds
... • Atoms of the same element can have different masses. • They always have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. • The difference in the number of neutrons accounts for the difference in ...
... • Atoms of the same element can have different masses. • They always have the same number of protons, but they can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. • The difference in the number of neutrons accounts for the difference in ...
Name ____ Date
... 3. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 4. Correlate atomic structure and the physical and chemical properties of an element to the position of the element on the periodic table. 5. Compare the dif ...
... 3. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 4. Correlate atomic structure and the physical and chemical properties of an element to the position of the element on the periodic table. 5. Compare the dif ...
Chapter 2 - WordPress.com
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Do Now - March [4-2], 2009 - stroh
... • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means – An element is made of only one type of atom ...
... • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means – An element is made of only one type of atom ...
Name Honors Chemistry ___/___/___ Subatomic Particles Atomic
... and electrons have a -1 charge, in a neutral atom the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Thus, in a neutral atom, the atomic number also indicates the number of electrons in an atom. (For now, assume all atoms are neutral. We will discuss charged atoms later this year.) Summary: ...
... and electrons have a -1 charge, in a neutral atom the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Thus, in a neutral atom, the atomic number also indicates the number of electrons in an atom. (For now, assume all atoms are neutral. We will discuss charged atoms later this year.) Summary: ...
Counting Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... From the periodic table, the atomic number of chlorine is 17. Mass # - atomic # = # of neutrons 37 – 17 = 20 An atom of chlorine-37 is made up of 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 20 neutrons. ...
... From the periodic table, the atomic number of chlorine is 17. Mass # - atomic # = # of neutrons 37 – 17 = 20 An atom of chlorine-37 is made up of 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 20 neutrons. ...
Element - Faculty
... 6. If the molecular mass of acetic acid is 60.00 g/mol, and methane gas is 16.00 g/mol, what is the?: a) molecular formula of acetic acid; and ...
... 6. If the molecular mass of acetic acid is 60.00 g/mol, and methane gas is 16.00 g/mol, what is the?: a) molecular formula of acetic acid; and ...
Atomic Structure 3: ISOTOPES
... element have the same number of protons, as given by the atomic number. You also know that the number of electrons in an uncharged atom equals the number of protons. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is not so predictable. The periodic table helps us out, though, by giving the atomic ...
... element have the same number of protons, as given by the atomic number. You also know that the number of electrons in an uncharged atom equals the number of protons. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is not so predictable. The periodic table helps us out, though, by giving the atomic ...
The Chemistry of Life
... • Atoms of the same element, however, may have a different number of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... • Atoms of the same element, however, may have a different number of neutrons. • Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table 16
... Not all atoms of an element have the same number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. For example, boron atoms can have mass numbers of 10 or 11. To find the number of neutrons in an isotope, you can use the formula above. Look at the ta ...
... Not all atoms of an element have the same number of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. For example, boron atoms can have mass numbers of 10 or 11. To find the number of neutrons in an isotope, you can use the formula above. Look at the ta ...
Atoms, Isotopes and Relative Atomic Masses
... The Group 7 element bromine was discovered by Balard in 1826. Bromine gets its name from the Greek bromos meaning stench. Bromine consists of a mixture of two isotopes, 79Br and 81Br. ...
... The Group 7 element bromine was discovered by Balard in 1826. Bromine gets its name from the Greek bromos meaning stench. Bromine consists of a mixture of two isotopes, 79Br and 81Br. ...
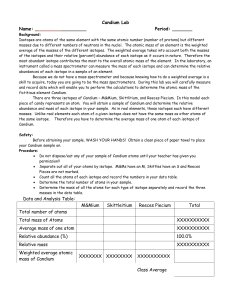
Candium Lab - OCPS TeacherPress
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number (number of protons) but different masses due to different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of the different isotopes. The weighted average takes into account both ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number (number of protons) but different masses due to different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of the different isotopes. The weighted average takes into account both ...
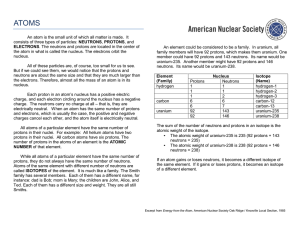
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called ...
... All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called ...
An atom is the small unit of which all matter is made. It consists of
... ELECTRONS. The neutrons and protons are located in the center of the atom in what is called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. All of these particles are, of course, too small for us to see. But if we could see them, we would notice that the protons and neutrons are about the same size an ...
... ELECTRONS. The neutrons and protons are located in the center of the atom in what is called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. All of these particles are, of course, too small for us to see. But if we could see them, we would notice that the protons and neutrons are about the same size an ...
Unit 2- The Atom
... on the blank side. Record the number of “S.” To flip the skittles, shake the bag containing the skittles and pour the contents out on the paper towel. The skittles that have landed on the blank side have decayed and may be consumed. 2. Flip the skittles that landed on the “S” and separate as ...
... on the blank side. Record the number of “S.” To flip the skittles, shake the bag containing the skittles and pour the contents out on the paper towel. The skittles that have landed on the blank side have decayed and may be consumed. 2. Flip the skittles that landed on the “S” and separate as ...
Reading 2.1 A Return to Isotopes
... This whole discussion of isotopes brings us back to Dalton’s atomic theory. According to Dalton, atoms of a given element are identical. But if atoms of a given element can have different numbers of neutrons, then they can have different masses as well. How did Dalton miss this? It turns out that el ...
... This whole discussion of isotopes brings us back to Dalton’s atomic theory. According to Dalton, atoms of a given element are identical. But if atoms of a given element can have different numbers of neutrons, then they can have different masses as well. How did Dalton miss this? It turns out that el ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... actinide series. One element of the lanthanide series and most of the elements in the actinide series are called trans-uranium, which means synthetic or man-made. ...
... actinide series. One element of the lanthanide series and most of the elements in the actinide series are called trans-uranium, which means synthetic or man-made. ...
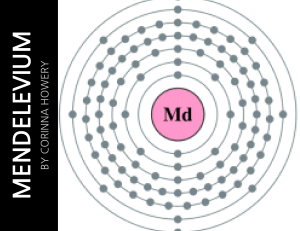
Mendelevium
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
Lawrencium

Lawrencium is a synthetic chemical element with chemical symbol Lr (formerly Lw) and atomic number 103. It is named in honor of Ernest Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron, a device that was used to discover many artificial radioactive elements. A radioactive metal, lawrencium is the eleventh transuranic element and is also the final member of the actinide series. Like all elements with atomic number over 100, lawrencium can only be produced in particle accelerators by bombarding lighter elements with charged particles. Twelve isotopes of lawrencium are currently known; the most stable is 266Lr with a half-life of 11 hours, but the shorter-lived 260Lr (half-life 2.7 minutes) is most commonly used in chemistry because it can be produced on a larger scale.Chemistry experiments have confirmed that lawrencium indeed behaves as a heavier homolog to lutetium in the periodic table, and is a trivalent element. It thus could also be classified as the first of the 7th-period transition metals: however, its electron configuration is anomalous for its position in the periodic table, having an s2p configuration instead of the s2d configuration of its homolog lutetium. This means that lawrencium may be less volatile than expected for its position in the periodic table and have a volatility comparable to that of lead.In the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s, many claims of the synthesis of lawrencium of varying quality were made from laboratories in the Soviet Union and the United States. The priority of the discovery and therefore the naming of the element was disputed between Soviet and American scientists, and while the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) established lawrencium as the official name for the element and gave the American team credit for the discovery, this was reevaluated in 1997, giving both teams shared credit for the discovery but not changing the element's name.






![Do Now - March [4-2], 2009 - stroh](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008519532_1-cab23fd6aae248311f653b62e7fe2161-300x300.png)