BIO113 Ex 3 sample Q → The questions are NOT comprehensive
... The questions are NOT comprehensive. Review the notes and corresponding textbook sections. These are for practice and are not actual exam questions. 1. DNA is composed of a. A single strand of nucleotides in a particular order b. 2 strands twisted around each other c. Amino acids that form a code ...
... The questions are NOT comprehensive. Review the notes and corresponding textbook sections. These are for practice and are not actual exam questions. 1. DNA is composed of a. A single strand of nucleotides in a particular order b. 2 strands twisted around each other c. Amino acids that form a code ...
A Gene Coexpression Network for Global Discovery of Conserved
... ► Would the multi-species network be as useful for species that are more closely related? ► Gene orthology is based on protein sequence similarity. Does sequence conservation equate to conserved function? ► Are 12 clusters of meta-genes sufficient to hypothesize function for 3416 metagenes? ► How ca ...
... ► Would the multi-species network be as useful for species that are more closely related? ► Gene orthology is based on protein sequence similarity. Does sequence conservation equate to conserved function? ► Are 12 clusters of meta-genes sufficient to hypothesize function for 3416 metagenes? ► How ca ...
document
... Gene is part of genome Genome =full set of genetic information encoded by the chromosomes of an organism ...
... Gene is part of genome Genome =full set of genetic information encoded by the chromosomes of an organism ...
genetics_4
... • Is the science of heredity. • Heredity is the transmission of genetic or physical traits from parent to offspring. ...
... • Is the science of heredity. • Heredity is the transmission of genetic or physical traits from parent to offspring. ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 18. What can be found in the promoter region of DNA? 19. What post-transcriptional modifications occur to an mRNA before it leaves the nucleus? 20. What are the three kinds of RNA, and what are their purposes? 21. What is aminoacl tRNA synthetase? 22. What is a stop codon? 23. When talking about the ...
... 18. What can be found in the promoter region of DNA? 19. What post-transcriptional modifications occur to an mRNA before it leaves the nucleus? 20. What are the three kinds of RNA, and what are their purposes? 21. What is aminoacl tRNA synthetase? 22. What is a stop codon? 23. When talking about the ...
Selection and Adaptation - WFSC 406 | Wildlife Habitat Management
... while a recessive allele is masked by a dominant allele. In most multi-cellular organisms, each individual cell contains 2 copies of each type of chromosome or alleles of a gene; 1 from the male and 1 from the female. 5. The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usu ...
... while a recessive allele is masked by a dominant allele. In most multi-cellular organisms, each individual cell contains 2 copies of each type of chromosome or alleles of a gene; 1 from the male and 1 from the female. 5. The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usu ...
DNA TESTING FOR INHERITED DISEASES IN DOGS The specific
... Health Trust, we have pioneered the application of cytogenetic techniques to canine chromosomes; techniques based on visualising DNA probes with fluorescent tags. We are using this approach to identify anchor points for the genetic map and to reveal regions of human chromosomes which match canine ch ...
... Health Trust, we have pioneered the application of cytogenetic techniques to canine chromosomes; techniques based on visualising DNA probes with fluorescent tags. We are using this approach to identify anchor points for the genetic map and to reveal regions of human chromosomes which match canine ch ...
9/20 Bacterial and viral genetics
... • Competent cells: cells that take up DNA • Transformants: cells that receive genetic material • Cotransformed: cells that are transformed by two or more genes ...
... • Competent cells: cells that take up DNA • Transformants: cells that receive genetic material • Cotransformed: cells that are transformed by two or more genes ...
DNA Packaging - kyoussef-mci
... circular molecule of naked DNA called a PLASMID DNA is readily available to RNA polymerase control of transcription by regulatory proteins (operon) most of DNA codes for protein or RNA no introns, small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences: promoters, operators ...
... circular molecule of naked DNA called a PLASMID DNA is readily available to RNA polymerase control of transcription by regulatory proteins (operon) most of DNA codes for protein or RNA no introns, small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences: promoters, operators ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... Definition: Basic, functional units of heredity, each occupying a specific place on a chromosome. Genes are represented by a pair of letters. Heterozygous or Homozygous Context: In 1909 a Danish botanist coined the term “genes” to describe Mendel’s factors in inherited traits. heredity Definition: G ...
... Definition: Basic, functional units of heredity, each occupying a specific place on a chromosome. Genes are represented by a pair of letters. Heterozygous or Homozygous Context: In 1909 a Danish botanist coined the term “genes” to describe Mendel’s factors in inherited traits. heredity Definition: G ...
Powerpoint slides - Berkeley Statistics
... • On average, 40% of our genes are expressed at any given time. ...
... • On average, 40% of our genes are expressed at any given time. ...
this certificate as PDF
... This certificate is issued based on tests performed on DNA samples to PiGen by accredited veterinarians and/or FCI officials appointed by the persons that confirmed, on the date of DNA sampling, to be the respective owners of the pigeons with the ringnumbers mentioned in this certificate. ...
... This certificate is issued based on tests performed on DNA samples to PiGen by accredited veterinarians and/or FCI officials appointed by the persons that confirmed, on the date of DNA sampling, to be the respective owners of the pigeons with the ringnumbers mentioned in this certificate. ...
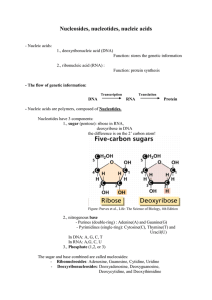
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
... Facilitate construction of other centromere binding proteins ...
... Facilitate construction of other centromere binding proteins ...
Insertional mutagenesis in zebrafish rapidly identifies genes
... • They suggest that genes required for protein synthesis, RNA processing, DNA replication and chromatin assembly give rise to non-specific mutations • Genes required for transcription factors, receptors and ligands give rise to mutants with specific developmental phenotypes • 20% of mutants give ris ...
... • They suggest that genes required for protein synthesis, RNA processing, DNA replication and chromatin assembly give rise to non-specific mutations • Genes required for transcription factors, receptors and ligands give rise to mutants with specific developmental phenotypes • 20% of mutants give ris ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... such beneficial mutations. The condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes is called polyploidy. Often larger and stronger than diploid plants, but not beneficial in animals. ...
... such beneficial mutations. The condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes is called polyploidy. Often larger and stronger than diploid plants, but not beneficial in animals. ...
STUDY GUIDE SEMESTER 2 EXAM 4 Dr. Marks Name: Class
... Refer to the illustration above. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for thi ...
... Refer to the illustration above. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for thi ...
finalexamcrib201213NED 33.5 KB
... 44) Chargaff’s pair rules and prediction of nucleotide composition of ds DNA 45) Key experiments of Griffith, Chargaff, Meselsohn, Beadle, Jacob, McLeod, etc. 46) Watson and Crick’s rationale and conclusions based on Chargaff and Franklin 47) Key diffs between proke and euk genome size, txn, tln, po ...
... 44) Chargaff’s pair rules and prediction of nucleotide composition of ds DNA 45) Key experiments of Griffith, Chargaff, Meselsohn, Beadle, Jacob, McLeod, etc. 46) Watson and Crick’s rationale and conclusions based on Chargaff and Franklin 47) Key diffs between proke and euk genome size, txn, tln, po ...
Protein Synthesis Practice
... Now that you’re experts on the process of DNA replication and protein synthesis, let’s put it to the test! You’re ready to become a professional DNA/RNA code breaker. Write the complimentary base pairs for the segments of DNA or RNA below. DNA Replication REMEMBER: DNA copies itself using DNA polyme ...
... Now that you’re experts on the process of DNA replication and protein synthesis, let’s put it to the test! You’re ready to become a professional DNA/RNA code breaker. Write the complimentary base pairs for the segments of DNA or RNA below. DNA Replication REMEMBER: DNA copies itself using DNA polyme ...
Chapter 5 PPT Review
... The way an organism looks and behaves as a result of its genetic makeup is called its _____. ...
... The way an organism looks and behaves as a result of its genetic makeup is called its _____. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.