Chapter 2- Genetics
... Free-floating nucleotides in cells are derived from the food one eats. ____ new strands of DNA are formed into the double helix. f) The genetic code With only 4 bases, billions of genes can be coded. Proteins are made from specific _______ __________________ called genes. A protein is a ch ...
... Free-floating nucleotides in cells are derived from the food one eats. ____ new strands of DNA are formed into the double helix. f) The genetic code With only 4 bases, billions of genes can be coded. Proteins are made from specific _______ __________________ called genes. A protein is a ch ...
Introductory Biology Primer
... • Why? Every cell has same DNA but each cell expresses different proteins. • Signal transduction: One signal converted to another – Cascade has “master regulators” turning on many proteins, which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
... • Why? Every cell has same DNA but each cell expresses different proteins. • Signal transduction: One signal converted to another – Cascade has “master regulators” turning on many proteins, which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
Lecture 6: Units of Selection cont`d
... • Proportion of variation in a phenotype in a population attributable to individual differences in genotype • Related to the genetic & phenotypic makeup of a population ...
... • Proportion of variation in a phenotype in a population attributable to individual differences in genotype • Related to the genetic & phenotypic makeup of a population ...
幻灯片 1 - TUST
... and discern patterns in function and regulation. The data also provide much information about microbial evolution, particularly with respect to phenomena such as horizontal gene transfer. The whole-genome sequence information provides an entirely new starting point for biological research. ...
... and discern patterns in function and regulation. The data also provide much information about microbial evolution, particularly with respect to phenomena such as horizontal gene transfer. The whole-genome sequence information provides an entirely new starting point for biological research. ...
MCA Review Part 3 File
... In addition to sexual reproduction, new, inheritable characteristics can occur from mutations that occur in genes of reproductive cells. (pg 238-241) Terms: Mutation: a change in an organism’s DNA Point Mutation: a mutation in which one nucleotide is substituted for another Frameshift Mutation: invo ...
... In addition to sexual reproduction, new, inheritable characteristics can occur from mutations that occur in genes of reproductive cells. (pg 238-241) Terms: Mutation: a change in an organism’s DNA Point Mutation: a mutation in which one nucleotide is substituted for another Frameshift Mutation: invo ...
Document
... sequence of nucleotides that forms part of a DNA molecule • Describe the way in which the nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in the polypeptide • Describe the effects of substitution, deletion, insertion, and frameshift mutations • Describe how the information is used during trans ...
... sequence of nucleotides that forms part of a DNA molecule • Describe the way in which the nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in the polypeptide • Describe the effects of substitution, deletion, insertion, and frameshift mutations • Describe how the information is used during trans ...
Chapter 14: Genes in Action
... Change • The change in the structure or amount of the genetic material of an organism ...
... Change • The change in the structure or amount of the genetic material of an organism ...
Class Presentation Questions 12
... 5. What must happen genetically for a female to be color blind? 6. The allele for colorblindness is ____________________ and located on the _____________ chromosome. 7. Alleles found on the same chromosome are “______________”. 8. _____________________ is another sex-linked disorder (more common in ...
... 5. What must happen genetically for a female to be color blind? 6. The allele for colorblindness is ____________________ and located on the _____________ chromosome. 7. Alleles found on the same chromosome are “______________”. 8. _____________________ is another sex-linked disorder (more common in ...
The purines In DNA, the pyrimidine bases are
... phosphodiester bridges (i.e., the 3'-OH group of the sugar of one is linked to the 5'-OH of the next sugar by a phosphate). The variable part of the DNA is the sequence of the bases, and the precise sequence of the purine and pyrimidine bases carry the genetic information to express the characterist ...
... phosphodiester bridges (i.e., the 3'-OH group of the sugar of one is linked to the 5'-OH of the next sugar by a phosphate). The variable part of the DNA is the sequence of the bases, and the precise sequence of the purine and pyrimidine bases carry the genetic information to express the characterist ...
presentation source
... prokaryotes, that do not have a cell nucleus, and eukaryotes, which do. Prokaryotes fall into two major groups: Eubacteria and Archaea. Phenotypically, eubacteria and archaea are very similar to each other. However, it has been demonstrated by using molecular data that archaea are more closely relat ...
... prokaryotes, that do not have a cell nucleus, and eukaryotes, which do. Prokaryotes fall into two major groups: Eubacteria and Archaea. Phenotypically, eubacteria and archaea are very similar to each other. However, it has been demonstrated by using molecular data that archaea are more closely relat ...
June-2015-Biology-Final-Exam-Review
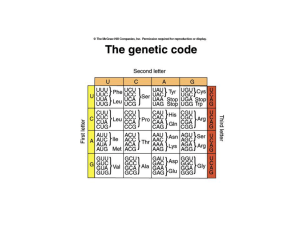
... 43. List the three types of RNA and their functions. (205) 44. How is RNA different from DNA? (205) 45. In RNA, Adenine base-pairs with _____________. (205) 46. Using the chart of codons on pg. 207, what would the sequence of amino acids be encoded by the following mRNA molecule: CUCAAGUGCUUC? (207) ...
... 43. List the three types of RNA and their functions. (205) 44. How is RNA different from DNA? (205) 45. In RNA, Adenine base-pairs with _____________. (205) 46. Using the chart of codons on pg. 207, what would the sequence of amino acids be encoded by the following mRNA molecule: CUCAAGUGCUUC? (207) ...
Indezine Template
... • Happens in the nucleus • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA), carries DNA message to ribosome • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA • Ribosomes are the sites of translation ...
... • Happens in the nucleus • Transcription produces messenger RNA (mRNA), carries DNA message to ribosome • Translation is the synthesis of a polypeptide, which occurs under the direction of mRNA • Ribosomes are the sites of translation ...
RNA
... 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA and unzips DNA beginning at the gene (one strand acts a template) 2. Free nucleotides pair with their complementary bases on the exposed DNA template 3. RNA polymerase continues until it reached the terminator sequence and stops 4. mRNA is released and goes to the ribo ...
... 1. RNA polymerase binds to DNA and unzips DNA beginning at the gene (one strand acts a template) 2. Free nucleotides pair with their complementary bases on the exposed DNA template 3. RNA polymerase continues until it reached the terminator sequence and stops 4. mRNA is released and goes to the ribo ...
Unit2Day5
... 169 different genes with expression differences between human and chimp in cortex Most genes were more highly expressed in human vs. chimp Caceres et al., 2003, PNAS, 100: 13030-13035 ...
... 169 different genes with expression differences between human and chimp in cortex Most genes were more highly expressed in human vs. chimp Caceres et al., 2003, PNAS, 100: 13030-13035 ...
src
... cDNAsarc corresponded to approximately 16 percent of the viral genome(1600 nucleotides out of a total genomic length of 10,000 nucleotides). This cDNA fragment hybridizes to DNA extracted from cells of a variety of avian species indicating that the cellular genomes of these birds contain a DNA seque ...
... cDNAsarc corresponded to approximately 16 percent of the viral genome(1600 nucleotides out of a total genomic length of 10,000 nucleotides). This cDNA fragment hybridizes to DNA extracted from cells of a variety of avian species indicating that the cellular genomes of these birds contain a DNA seque ...
Non-Mendellian Genetics Part II
... 332 expressing the phenotypes of the dominant Q and H alleles; 324 expressing phenotypes of the dominant Q and recessive h allele; 346 expressing the phenotypes of the recessive q and dominant H alleles; and no progeny expressing both recessive phenotypes. Does this follow the predicted pattern of i ...
... 332 expressing the phenotypes of the dominant Q and H alleles; 324 expressing phenotypes of the dominant Q and recessive h allele; 346 expressing the phenotypes of the recessive q and dominant H alleles; and no progeny expressing both recessive phenotypes. Does this follow the predicted pattern of i ...
Gene expression - El Camino College
... 10. Which of the following statements about transcription is FALSE? A. In RNA, U, rather than T, pairs with A B. The RNA molecule is built one nucleotide at a time ...
... 10. Which of the following statements about transcription is FALSE? A. In RNA, U, rather than T, pairs with A B. The RNA molecule is built one nucleotide at a time ...
August 31, 2016 - Iowa State University
... b. DNA contains Thymine; RNA contains Uracil c. DNA contains an extra hydroxyl group that RNA does not have d. DNA is much less reactive than RNA ...
... b. DNA contains Thymine; RNA contains Uracil c. DNA contains an extra hydroxyl group that RNA does not have d. DNA is much less reactive than RNA ...
Intro to Biotechnology
... working copy of the gene which codes for factor 8 into his liver cells so that his liver could then produce adequate levels of factor 8 ...
... working copy of the gene which codes for factor 8 into his liver cells so that his liver could then produce adequate levels of factor 8 ...
Features of the genetic code
... • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates a ...
... • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates a ...
New gene link to Glaucoma
... Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide, affecting more than 65 million people. Prof David Mackey, genetic researcher and Managing Director of the Lions Eye Institute, is a member of the consortium that have identified three new gene mutations associated with an increased s ...
... Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide, affecting more than 65 million people. Prof David Mackey, genetic researcher and Managing Director of the Lions Eye Institute, is a member of the consortium that have identified three new gene mutations associated with an increased s ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.