World History Review - Bismarck Public Schools
... (5-1) What are the causes (legend and history) of the Trojan war and how did it end? (Three Points) How did the Persian War unify Greece? Focus on how city-states got along, why war started, and how the city-states worked together. Some of the city-states, such as Athens and Sparta, were rivals. Whe ...
... (5-1) What are the causes (legend and history) of the Trojan war and how did it end? (Three Points) How did the Persian War unify Greece? Focus on how city-states got along, why war started, and how the city-states worked together. Some of the city-states, such as Athens and Sparta, were rivals. Whe ...
Athens vs Sparta ASSIGNMENT
... 2- Explain what the Council of Five Hundred that Cleisthenes created was & did: ...
... 2- Explain what the Council of Five Hundred that Cleisthenes created was & did: ...
Ancient Greece Study Cards
... Encouraged the rebuilding of the acropolis after it had been destroyed in the Persian wars Patron of the arts and supported dramatists, painters, sculptors, and architects ...
... Encouraged the rebuilding of the acropolis after it had been destroyed in the Persian wars Patron of the arts and supported dramatists, painters, sculptors, and architects ...
SWC1_s6
... > Strategos Cimon leads to further victories against Persians at sea; > Athens coerces the subject poleis into the alliance; by force; exploitation; slave society; > Social unrest: more power to the thetes (people); > Pericles, 460, aristocrat & populist, enfranchisement of the people & its politica ...
... > Strategos Cimon leads to further victories against Persians at sea; > Athens coerces the subject poleis into the alliance; by force; exploitation; slave society; > Social unrest: more power to the thetes (people); > Pericles, 460, aristocrat & populist, enfranchisement of the people & its politica ...
Warring City
... no role in political life. Finally, many who lived in Athens were slaves who had no rights either. ...
... no role in political life. Finally, many who lived in Athens were slaves who had no rights either. ...
Greek Civilizations
... Peloponnesian War Causes 1. Rivalry between Athens & Sparta intensified 2. Sparta issued ultimatum to Athens “release all cities under its control or face war” 3. Athens refused & war begins in 431 BC The War 1. Lasts 27 years 2. Sparta had stronger army 3. Athens stronger navy 4. S ...
... Peloponnesian War Causes 1. Rivalry between Athens & Sparta intensified 2. Sparta issued ultimatum to Athens “release all cities under its control or face war” 3. Athens refused & war begins in 431 BC The War 1. Lasts 27 years 2. Sparta had stronger army 3. Athens stronger navy 4. S ...
Ancient Greece (Chapter 7)
... Aristotle taught Alexander literature, philosophy, and science Alexander’s role model was Achilles, the warrior and hero of the Iliad ...
... Aristotle taught Alexander literature, philosophy, and science Alexander’s role model was Achilles, the warrior and hero of the Iliad ...
Greece and Rome - 6th Grade History: Vinson Middle
... She hated Ares, god of war, often besting him in battle. ...
... She hated Ares, god of war, often besting him in battle. ...
Sparta vs ATHENS
... in all his body except in his heel, the legend tells that he died in a battle when being reached by a poisoned arrow in the heel. ...
... in all his body except in his heel, the legend tells that he died in a battle when being reached by a poisoned arrow in the heel. ...
File
... Early on, Greece became a powerful civilization because of its central trade position on the Mediterranean, Ionian, and Aegean Seas. Greek Legend: Trojan War In 1200 B.C. the Greeks fought against Troy, supposedly because a Trojan prince captured Queen Helen of Greece. Did they win because of a hors ...
... Early on, Greece became a powerful civilization because of its central trade position on the Mediterranean, Ionian, and Aegean Seas. Greek Legend: Trojan War In 1200 B.C. the Greeks fought against Troy, supposedly because a Trojan prince captured Queen Helen of Greece. Did they win because of a hors ...
Ancient Greece
... 3. as the Athenians were behind the city walls a ________________ a. _____________ of Athens population died 4. they did not have enough power to defeat the mighty Spartans 5. Sparta won and as a sign of the victory, forced the Athenians to _________________________ a. will this work?: 6. out of th ...
... 3. as the Athenians were behind the city walls a ________________ a. _____________ of Athens population died 4. they did not have enough power to defeat the mighty Spartans 5. Sparta won and as a sign of the victory, forced the Athenians to _________________________ a. will this work?: 6. out of th ...
The Persian Wars
... • Wars between Greeks and Persians in 5th century BC • Roughly from 492 – 448 BC • Two main invasions of Greece by Achaemenid kings of Persia • Herodotus – primary historian ...
... • Wars between Greeks and Persians in 5th century BC • Roughly from 492 – 448 BC • Two main invasions of Greece by Achaemenid kings of Persia • Herodotus – primary historian ...
Name: Mrs. S.S. Block 2 Date: Greece
... to allow all people to have the chance to be involved in government. Under Pericles, Athens also became a center of ___________ and the _______. Life in Athens Men in Athens worked as __________, artisans, and __________. Women in Athens worked in the __________ and worked to take care of __________ ...
... to allow all people to have the chance to be involved in government. Under Pericles, Athens also became a center of ___________ and the _______. Life in Athens Men in Athens worked as __________, artisans, and __________. Women in Athens worked in the __________ and worked to take care of __________ ...
Athenian Government: Spartan Government: Democracy Oligarchy
... When wealthy landowners are in power. Monarchy Under the rule of a single ruler, either a king or queen. ...
... When wealthy landowners are in power. Monarchy Under the rule of a single ruler, either a king or queen. ...
The Expansion of Greece: Persian Wars
... Persians invaded mainland Greece conquering Thrace and Macedonia. In 490 B.C. Persian went to war with the Athenians at the Battle of Marathon Even though the Athenians were outnumbered by the Persians, Athens defeated them in the Battle of Marathon. The Persians left leaving an uneasy peace ...
... Persians invaded mainland Greece conquering Thrace and Macedonia. In 490 B.C. Persian went to war with the Athenians at the Battle of Marathon Even though the Athenians were outnumbered by the Persians, Athens defeated them in the Battle of Marathon. The Persians left leaving an uneasy peace ...
490 BC - CAI Teachers
... Xerxes invasion of Greece is chronicled by Herodotus, the first historian, in his book ‘The Histories’. Herodotus is also known as the father of lies from his habit of reporting popular rumour as fact. Xerxes assembled what was, according to Herodotus, the largest army ever assembled. It was so larg ...
... Xerxes invasion of Greece is chronicled by Herodotus, the first historian, in his book ‘The Histories’. Herodotus is also known as the father of lies from his habit of reporting popular rumour as fact. Xerxes assembled what was, according to Herodotus, the largest army ever assembled. It was so larg ...
Sequencing events in the Peloponnesian War
... Below are a series of boxes that contain information about the Peloponnesian War. Re-arrange events so they are in chronological order. Thucydides begins to write a history of the Peloponnesian War. ...
... Below are a series of boxes that contain information about the Peloponnesian War. Re-arrange events so they are in chronological order. Thucydides begins to write a history of the Peloponnesian War. ...
Accommodated GCS
... trade. Sparta had only one goal – to be militarily strong. Athens Athenian nobles, merchants and manufacturers took over the government and made it an oligarchy – rule by a few. Solon prepared a constitution, a set of principles for governing. o He allowed more Athenians to take part in govern ...
... trade. Sparta had only one goal – to be militarily strong. Athens Athenian nobles, merchants and manufacturers took over the government and made it an oligarchy – rule by a few. Solon prepared a constitution, a set of principles for governing. o He allowed more Athenians to take part in govern ...
CHAPTER 11
... 4.) I can explain the reasons for war between Athens and Sparta. 1. Both city-states wanted to be the most powerful. 2. City-states feared Athens because of its grab for power and prestige. 3. The rise of Athens from a city-state into a naval empire. 4. Athenian settlers began to move into other ci ...
... 4.) I can explain the reasons for war between Athens and Sparta. 1. Both city-states wanted to be the most powerful. 2. City-states feared Athens because of its grab for power and prestige. 3. The rise of Athens from a city-state into a naval empire. 4. Athenian settlers began to move into other ci ...
Sparta
... –Five elected officials - carried out the laws, controlled education, and prosecuted court cases • Two kings ruled over the military ...
... –Five elected officials - carried out the laws, controlled education, and prosecuted court cases • Two kings ruled over the military ...
Part one: Reading and interpreting. (15pts) A. Comprehension ( 7pts)
... their might against the invading Persians. Athenian and Spartan fought side by side in the Battle of Plataea, which ended Persian invasions of Greece. One way that Athens and Sparta really differed was in their idea of getting along with the rest of the Greeks. Sparta seemed content to keep to itsel ...
... their might against the invading Persians. Athenian and Spartan fought side by side in the Battle of Plataea, which ended Persian invasions of Greece. One way that Athens and Sparta really differed was in their idea of getting along with the rest of the Greeks. Sparta seemed content to keep to itsel ...
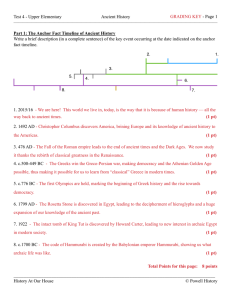
Test 4 - Upper Elementary
... After the Ionian Revolt, Darius commanded one of his slaves to whisper in his ear at every meal, “Master, Remember the Athenians.” He wanted to be kept angry so he would be inspired to seek revenge! (2 pts: 1 pt for the reminder; 1 pt for spelling and grammar) 11. How did the Athenians win the Battl ...
... After the Ionian Revolt, Darius commanded one of his slaves to whisper in his ear at every meal, “Master, Remember the Athenians.” He wanted to be kept angry so he would be inspired to seek revenge! (2 pts: 1 pt for the reminder; 1 pt for spelling and grammar) 11. How did the Athenians win the Battl ...
Thebes, Greece

Thebes (/ˈθiːbz/; Ancient Greek: Θῆβαι, Thēbai, Greek pronunciation: [tʰɛ̂ːbai̯]; Modern Greek: Θήβα, Thíva [ˈθiva]) is a city in Boeotia, central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age.Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes. Theban forces ended the power of Sparta at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC under the command of Epaminondas. The Sacred Band of Thebes (an elite military unit) famously fell at the battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC against Philip II and Alexander the Great. Prior to its destruction by Alexander in 335 BC, Thebes was a major force in Greek history, and was the most dominant city-state at the time of the Macedonian conquest of Greece. During the Byzantine period, the city was famous for its silks.The modern city contains an Archaeological Museum, the remains of the Cadmea (Bronze Age and forward citadel), and scattered ancient remains. Modern Thebes is the largest town of the regional unit of Boeotia.