Answers for Quiz #4
... Two imp. Theban generals, Epaminondas & _Pelopidas__ used new tactics, giving Thebes pwr until 362 B.C. at B. of _Mantinea_. The 3 most influential ppl in Alex. the Great's life were: _his father Philip II_; his teacher -=_Aristotle_; & his mother =_Olympias_ who gave him idea of his divine birth. P ...
... Two imp. Theban generals, Epaminondas & _Pelopidas__ used new tactics, giving Thebes pwr until 362 B.C. at B. of _Mantinea_. The 3 most influential ppl in Alex. the Great's life were: _his father Philip II_; his teacher -=_Aristotle_; & his mother =_Olympias_ who gave him idea of his divine birth. P ...
Ancient Greece
... • Athenians used a water clock to time speakers at city council meeting. • In Athens, people used coins as a standardized currency. ...
... • Athenians used a water clock to time speakers at city council meeting. • In Athens, people used coins as a standardized currency. ...
Ancient Greece Military Battles Powerpoint
... Sparta attacked Athens and Persia attacked Athens (revenge from Persian Wars) 405 BCE- Athenian navy destroyed in a surprise attack 404 BCE- Athens totally surrendered to Sparta who installed oligarchic government Age of Athens, Age of Pericles, the Classical Age and the Athenian Empire- came to and ...
... Sparta attacked Athens and Persia attacked Athens (revenge from Persian Wars) 405 BCE- Athenian navy destroyed in a surprise attack 404 BCE- Athens totally surrendered to Sparta who installed oligarchic government Age of Athens, Age of Pericles, the Classical Age and the Athenian Empire- came to and ...
Forms of - Ancient Greece
... Based on principle that all citizens of the city-state of Athens had right to attend and speak at assembly (women, slaves & metics were not ...
... Based on principle that all citizens of the city-state of Athens had right to attend and speak at assembly (women, slaves & metics were not ...
MS Word - Ancient Greece
... Based on principle that all citizens of the city-state of Athens had right to attend and speak at assembly (women, slaves & metics were not ...
... Based on principle that all citizens of the city-state of Athens had right to attend and speak at assembly (women, slaves & metics were not ...
File
... In 431BC the _________________ War broke out between Athens and Sparta. The war was inconclusive until a _____________ broke out in Athens destroying nearly _______ of its population. The weakening of the Greek city-states allowed the ______________ under __________ to conquer Greece. His son, ____ ...
... In 431BC the _________________ War broke out between Athens and Sparta. The war was inconclusive until a _____________ broke out in Athens destroying nearly _______ of its population. The weakening of the Greek city-states allowed the ______________ under __________ to conquer Greece. His son, ____ ...
Ancient Greece Test Review
... 24. What do Spartan men spend all of their time doing? ____________________________________________________ 25. Describe what happens to boys when they are born in Sparta? What if they don’t make the cut? ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
... 24. What do Spartan men spend all of their time doing? ____________________________________________________ 25. Describe what happens to boys when they are born in Sparta? What if they don’t make the cut? ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
The House of Atreus Period 6
... • Polyneices took refuge in the city of Argo, and did everything he could to form an army to march against Thebes. • Oedipus and Antigone eventually settled in Colonus, a spot near Athens. They felt safe there, and that was where Oedipus shortly after, died. As he was dying, the oracle who once spo ...
... • Polyneices took refuge in the city of Argo, and did everything he could to form an army to march against Thebes. • Oedipus and Antigone eventually settled in Colonus, a spot near Athens. They felt safe there, and that was where Oedipus shortly after, died. As he was dying, the oracle who once spo ...
King Philip II: United the Greek city states under his leadership after
... Barbarian - a non-Greek who was thought to be wild and uncivilized Alexandria - ancient city in Egypt founded by Alexander the Great Peninsula - a piece of land surrounded by water on 3 sides Epic - a long poem that tells a story Assassinate - to take another’s life for political reasons Agora - a p ...
... Barbarian - a non-Greek who was thought to be wild and uncivilized Alexandria - ancient city in Egypt founded by Alexander the Great Peninsula - a piece of land surrounded by water on 3 sides Epic - a long poem that tells a story Assassinate - to take another’s life for political reasons Agora - a p ...
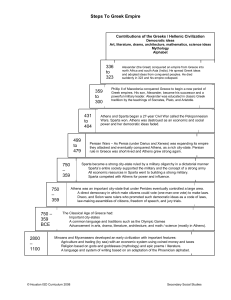
Steps To Greek Empire 2800
... Persian Wars – As Persia (under Darius and Xerxes) was expanding its empire they attacked and eventually conquered Athens, as a rich city-state. Persian rule in Greece was short-lived and Athens grew strong again. ...
... Persian Wars – As Persia (under Darius and Xerxes) was expanding its empire they attacked and eventually conquered Athens, as a rich city-state. Persian rule in Greece was short-lived and Athens grew strong again. ...
Greece – Persian and Peloponnesian Wars
... Darius’ son, Xerxes, picked up where his father left off and decided to try to take over Greece one more time. The Greeks got word of the pending invasion. ...
... Darius’ son, Xerxes, picked up where his father left off and decided to try to take over Greece one more time. The Greeks got word of the pending invasion. ...
Chapter 7 - Greece Outline
... Delian League - naval compact between Greek city-states in event of further Persian attacks Golden Age of Greece - otherwise known as the Age of Pericles 50 years (480 - 430 BC) when Athens reached its zenith culturally Most of the great men of Greece came from this time period Peloponnesian W ...
... Delian League - naval compact between Greek city-states in event of further Persian attacks Golden Age of Greece - otherwise known as the Age of Pericles 50 years (480 - 430 BC) when Athens reached its zenith culturally Most of the great men of Greece came from this time period Peloponnesian W ...
Oedipus Lecture Kerr
... Platea that was disastrous but Platea suspected more invasions so called on Athens for assistance – Athens as ever acquiesced. Thebes turned to Sparta… ...
... Platea that was disastrous but Platea suspected more invasions so called on Athens for assistance – Athens as ever acquiesced. Thebes turned to Sparta… ...
Military Battles of Ancient Greece
... Age of Athens, Age of Pericles, the Classical Age and the Athenian Empire- came to and end ...
... Age of Athens, Age of Pericles, the Classical Age and the Athenian Empire- came to and end ...
Unit 6ана Classical Greece
... 1. the Greeks used an alphabet B. OLYMPICS 1. held among all of the Greek citystates to determine the best athletes of Greece C. Religion 1. Polytheistic 2. the King of the gods was ZEUS followed by other gods/goddesses ...
... 1. the Greeks used an alphabet B. OLYMPICS 1. held among all of the Greek citystates to determine the best athletes of Greece C. Religion 1. Polytheistic 2. the King of the gods was ZEUS followed by other gods/goddesses ...
Military & Battles
... Age of Athens, Age of Pericles, the Classical Age and the Athenian Empire- came to and end ...
... Age of Athens, Age of Pericles, the Classical Age and the Athenian Empire- came to and end ...
ANCIENT GREECE II For use with the Britannica Student
... 2. _______ Athenian slaves were never allowed to become educated or buy their freedom. 3. _______ Athenian women were only seen in public at the theater and religious festivals. 4. _______ “The golden mean” meant a life with “nothing to excess.” ...
... 2. _______ Athenian slaves were never allowed to become educated or buy their freedom. 3. _______ Athenian women were only seen in public at the theater and religious festivals. 4. _______ “The golden mean” meant a life with “nothing to excess.” ...
Peloponnesian War - Mr. Reustle's Social Studies
... Created after the Persian Wars Greek city-states unite 200 city-states join (Sparta says no) Defensive alliance Athens becomes leader Used the navy to control the Aegean Sea ...
... Created after the Persian Wars Greek city-states unite 200 city-states join (Sparta says no) Defensive alliance Athens becomes leader Used the navy to control the Aegean Sea ...
CLAS 201 (Hellenism and Philosophy)
... and its allies, Corinth and its allies etc) that had formed against its rule and influence; at the same time such dominance was artificial because its own military strength was being overdrawn. Battle of Leuctra (371) In the aftermath of the Corinthian War, there was more infighting among the poleis ...
... and its allies, Corinth and its allies etc) that had formed against its rule and influence; at the same time such dominance was artificial because its own military strength was being overdrawn. Battle of Leuctra (371) In the aftermath of the Corinthian War, there was more infighting among the poleis ...
Classical Greece 477
... an expression of civic pride and a tribute to the gods Wealthy citizens bore the cost of producing the plays What types of modern entertainment can you think of that serve the purpose of Athenian drama’s? ...
... an expression of civic pride and a tribute to the gods Wealthy citizens bore the cost of producing the plays What types of modern entertainment can you think of that serve the purpose of Athenian drama’s? ...
Chapter 9, Section 2 Student Note Form
... 4. The money was kept on the island of _____________, historians called the alliance the ___________ League. 5. ______________ was the strongest member of the league. 6. They began to treat the other league members as ________________. 7. The refused to let members _____________ the league and _____ ...
... 4. The money was kept on the island of _____________, historians called the alliance the ___________ League. 5. ______________ was the strongest member of the league. 6. They began to treat the other league members as ________________. 7. The refused to let members _____________ the league and _____ ...
Chapter 5 Study Guide Questions
... What was the purpose of the Olympic Games? Who is the earliest known Greek civilization? How did Sparta win the Peloponnesian War? How did Pericles anger other members of the Delian League? What navy defeated the Persian Navy at Salamis Straight? Describe the Spartan half-citizen. What is the role o ...
... What was the purpose of the Olympic Games? Who is the earliest known Greek civilization? How did Sparta win the Peloponnesian War? How did Pericles anger other members of the Delian League? What navy defeated the Persian Navy at Salamis Straight? Describe the Spartan half-citizen. What is the role o ...
Ch1_Notes_-_Greece
... like this... • This would be written to the RIGHT side of your paper, under your main idea. ...
... like this... • This would be written to the RIGHT side of your paper, under your main idea. ...
Thebes, Greece

Thebes (/ˈθiːbz/; Ancient Greek: Θῆβαι, Thēbai, Greek pronunciation: [tʰɛ̂ːbai̯]; Modern Greek: Θήβα, Thíva [ˈθiva]) is a city in Boeotia, central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age.Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes. Theban forces ended the power of Sparta at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC under the command of Epaminondas. The Sacred Band of Thebes (an elite military unit) famously fell at the battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC against Philip II and Alexander the Great. Prior to its destruction by Alexander in 335 BC, Thebes was a major force in Greek history, and was the most dominant city-state at the time of the Macedonian conquest of Greece. During the Byzantine period, the city was famous for its silks.The modern city contains an Archaeological Museum, the remains of the Cadmea (Bronze Age and forward citadel), and scattered ancient remains. Modern Thebes is the largest town of the regional unit of Boeotia.