AQA Core Science Final Test - Atoms and Chemical equations
... The equation shows the same number of atoms go into the reaction as come out. This is known as conservation of mass. There is one Calcium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms in this reaction. (6 marks) ...
... The equation shows the same number of atoms go into the reaction as come out. This is known as conservation of mass. There is one Calcium atom, one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms in this reaction. (6 marks) ...
std 8 9 reviewanswers
... A The larger the amount of activation energy, the more unstable the transition state is B The activation energy is the difference energy between the products and the transition state C A catalyst works by lowering the activation energy for the reaction 9. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process at ...
... A The larger the amount of activation energy, the more unstable the transition state is B The activation energy is the difference energy between the products and the transition state C A catalyst works by lowering the activation energy for the reaction 9. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process at ...
Calorimetry Notes
... can be written as either a reactant or a product A thermochemical equation includes the enthalpy change The heat of reaction is the enthalpy change for the chemical equation exactly as it is written The heat of combustion is the heat of reaction for the complete burning of one mole of a substa ...
... can be written as either a reactant or a product A thermochemical equation includes the enthalpy change The heat of reaction is the enthalpy change for the chemical equation exactly as it is written The heat of combustion is the heat of reaction for the complete burning of one mole of a substa ...
Lecture 5 – Chemical Reactions
... needed to react with on molecule of O2 to produce two molecules of H2O. b. The letters in parentheses are used to indicate that state of the reactant or the product i. (s) for solid ii. (l) for liquid iii. (g) for gas iv. (aq) for aqueous solution (dissolved in water) Chemical equations embody a fun ...
... needed to react with on molecule of O2 to produce two molecules of H2O. b. The letters in parentheses are used to indicate that state of the reactant or the product i. (s) for solid ii. (l) for liquid iii. (g) for gas iv. (aq) for aqueous solution (dissolved in water) Chemical equations embody a fun ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OBJECTIVES 1. To study reactions
... When two ionic solutions are mixed and there is not an ion combination that is insoluble or gaseous, no reaction will be observed. For example, no reaction occurs between NaCl and KNO3 because all ionic combinations are soluble compounds. Part II. Exothermic and endothermic reactions Reactions that ...
... When two ionic solutions are mixed and there is not an ion combination that is insoluble or gaseous, no reaction will be observed. For example, no reaction occurs between NaCl and KNO3 because all ionic combinations are soluble compounds. Part II. Exothermic and endothermic reactions Reactions that ...
Heat
... o NH4NO3 dissolves in water, causing a drop in temperature. Write the reaction: o NH4NO3 + H2O + Heat →NH41+ (aq) + NO31- (aq) o NH4NO3 is used in cold packs for sports injuries. o ENDOTHERMIC Reaction o Note: NH4NO3 can also undergo an EXOTHERMIC reaction when it explodes, hence its use as a blasti ...
... o NH4NO3 dissolves in water, causing a drop in temperature. Write the reaction: o NH4NO3 + H2O + Heat →NH41+ (aq) + NO31- (aq) o NH4NO3 is used in cold packs for sports injuries. o ENDOTHERMIC Reaction o Note: NH4NO3 can also undergo an EXOTHERMIC reaction when it explodes, hence its use as a blasti ...
BR. HMWK 2012-03-07 11052
... 3. A spring scale calibrate in kg is used to determine the density of a rock specimen. The reading on the spring scale is 0.45 kg when the specimen is suspended in air and 0.36 kg when the specimen is fully submerged in water. If the density of water is 1000 kg/m3, the density of the rock specimen ...
... 3. A spring scale calibrate in kg is used to determine the density of a rock specimen. The reading on the spring scale is 0.45 kg when the specimen is suspended in air and 0.36 kg when the specimen is fully submerged in water. If the density of water is 1000 kg/m3, the density of the rock specimen ...
Science Outline NHPS: Chemistry
... formulas for molecular interpret phase compounds formulas for change graphs. using ratios compounds. and ion charts. Describe the Calculate factors that Identify names masses and effect phase and formulas yields of changes. and uses for reactants and common products in a Describe the compounds react ...
... formulas for molecular interpret phase compounds formulas for change graphs. using ratios compounds. and ion charts. Describe the Calculate factors that Identify names masses and effect phase and formulas yields of changes. and uses for reactants and common products in a Describe the compounds react ...
Quiz Review Name Period 1. What is the equation that
... 12. Identify the name of the phase change. a. Br2 (l) Br2 (s) b. NH3 (l) NH3 (g) c. H2O (s) H2O (l) d. I2 (s) I2 (g) e. H2O (g) H2O (l) f. CO2 (g) CO2 (s) 13. Which phase change results in release of energy? a. Br2 (l) Br2 (s) b. I2 (s) I2 (g) c. H2O (s) H2O (l) d. NH3 (l) NH3 ( ...
... 12. Identify the name of the phase change. a. Br2 (l) Br2 (s) b. NH3 (l) NH3 (g) c. H2O (s) H2O (l) d. I2 (s) I2 (g) e. H2O (g) H2O (l) f. CO2 (g) CO2 (s) 13. Which phase change results in release of energy? a. Br2 (l) Br2 (s) b. I2 (s) I2 (g) c. H2O (s) H2O (l) d. NH3 (l) NH3 ( ...
12. THE LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS Key Words
... We must be careful and consistent in sign conventions for Q and W . If work is done by the system W 0 . If work is done on the system W 0 . If heat is added to the system Q 0 . If heat leaves the system Q 0 . The internal energy of any thermodynamic system depends only on the initial and final stat ...
... We must be careful and consistent in sign conventions for Q and W . If work is done by the system W 0 . If work is done on the system W 0 . If heat is added to the system Q 0 . If heat leaves the system Q 0 . The internal energy of any thermodynamic system depends only on the initial and final stat ...
Visualizing the Transition State and
... HOW THE DEMONSTRATION ADDRESSES THE CHEMICAL CONCEPTS Transition state theory (TST), also called activated complex theory, is often introduced in general chemistry courses when discussing kinetics. A reaction energy diagram is used to follow the progress of the reaction from reactants through a tran ...
... HOW THE DEMONSTRATION ADDRESSES THE CHEMICAL CONCEPTS Transition state theory (TST), also called activated complex theory, is often introduced in general chemistry courses when discussing kinetics. A reaction energy diagram is used to follow the progress of the reaction from reactants through a tran ...
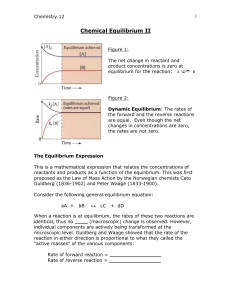
Chemical Equilibrium II
... Where ____ is known as the ___________ ___________ Note that the equilibrium expression can be expressed by concentrations in terms of _________ for aqueous solutions or _________________ for gases (although for the purposes of Chemistry 12, we will not be using partial pressures) Some rules to foll ...
... Where ____ is known as the ___________ ___________ Note that the equilibrium expression can be expressed by concentrations in terms of _________ for aqueous solutions or _________________ for gases (although for the purposes of Chemistry 12, we will not be using partial pressures) Some rules to foll ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Explain the relationship between vapor pressure, volatility, boiling point, and the strength of the forces holding particles together. Define the molar heat of vaporization and molar heat of fusion. Calculate the amount of heat energy absorbed or released when a given quantity of substance cha ...
... Explain the relationship between vapor pressure, volatility, boiling point, and the strength of the forces holding particles together. Define the molar heat of vaporization and molar heat of fusion. Calculate the amount of heat energy absorbed or released when a given quantity of substance cha ...
Chemical Context of Life
... Electrons may move from one energy level to another. In the process, they gain or lose energy equal to the difference in potential energy between the old and new energy level. ...
... Electrons may move from one energy level to another. In the process, they gain or lose energy equal to the difference in potential energy between the old and new energy level. ...
EOC Review - Dorman Freshman Campus
... • You have to have equal amounts of each element on the reactant and product side of the equation • This is why the equation must be BALANCED ...
... • You have to have equal amounts of each element on the reactant and product side of the equation • This is why the equation must be BALANCED ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.