Lecture 14
... A compound is 24.27% C, 4.07% H, and 71.65% Cl. The molar mass is known to be 99.0 g. What are the empirical and molecular formulas? ...
... A compound is 24.27% C, 4.07% H, and 71.65% Cl. The molar mass is known to be 99.0 g. What are the empirical and molecular formulas? ...
Word
... reaction (A + B → C + D) is endothermic or exothermic: Since ΔHreverse = -10 kJ you can determine that ΔHforward = +10 kJ (same value, just change the sign). Since ΔHforward is positive you know that the forward direction of the reaction is endothermic. Begin by sketching a general endothermic poten ...
... reaction (A + B → C + D) is endothermic or exothermic: Since ΔHreverse = -10 kJ you can determine that ΔHforward = +10 kJ (same value, just change the sign). Since ΔHforward is positive you know that the forward direction of the reaction is endothermic. Begin by sketching a general endothermic poten ...
First law of thermodynamics
... Before look at the second law of thermodynamics, let us discuss where first law of thermodynamics fails. According to the first law of thermodynamics, whenever any process occurs, there may be either heat interaction or work interaction. But we cannot exactly tell by first law that in which directio ...
... Before look at the second law of thermodynamics, let us discuss where first law of thermodynamics fails. According to the first law of thermodynamics, whenever any process occurs, there may be either heat interaction or work interaction. But we cannot exactly tell by first law that in which directio ...
Thermodynamics - Deland High School
... Entropy is a thermodynamic measure of the randomness in the universe. As you have seen from the lab, it is a general rule of the universe that processes that produce randomness are favored over processes that decrease the amount of randomness in the universe. o The second law of thermodynamics: ...
... Entropy is a thermodynamic measure of the randomness in the universe. As you have seen from the lab, it is a general rule of the universe that processes that produce randomness are favored over processes that decrease the amount of randomness in the universe. o The second law of thermodynamics: ...
Energy & Power
... • Work can be changed into heat relatively easily – the reverse is a different challenge • From the second law of thermodynamics, we know that : – it is not possible to change completely into work, with no other change taking place ...
... • Work can be changed into heat relatively easily – the reverse is a different challenge • From the second law of thermodynamics, we know that : – it is not possible to change completely into work, with no other change taking place ...
Ionic Equations
... • A roller coaster at the top of a hill has a great amount of potential energy. • As the rollercoaster begins to speed down the hill, the potential energy is turned into kinetic energy ...
... • A roller coaster at the top of a hill has a great amount of potential energy. • As the rollercoaster begins to speed down the hill, the potential energy is turned into kinetic energy ...
The Laws of Thermodinamics
... Each way a gas can store energy is called a degree of freedom Each degree of freedom contributes ½ R to the molar specific heat See table 12.1 for some Cvvalues ...
... Each way a gas can store energy is called a degree of freedom Each degree of freedom contributes ½ R to the molar specific heat See table 12.1 for some Cvvalues ...
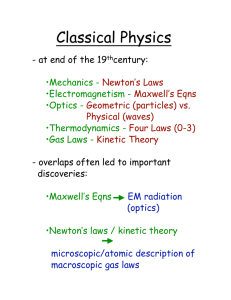
Classical Physics
... Heat DQ added to the system can have two effects: •Increase the internal energy of the system •Cause the gas to do work Conservation of Energy says: DQ = DU + DW where U is the internal energy of the system. fi 1st Law of Thermodynamics. ...
... Heat DQ added to the system can have two effects: •Increase the internal energy of the system •Cause the gas to do work Conservation of Energy says: DQ = DU + DW where U is the internal energy of the system. fi 1st Law of Thermodynamics. ...
Chapter 3
... -3 Important Prop of Solutions 1.part not large enough to be seen 2.part. are evenly spread out(all parts of sol are ident) 3.solution doesn’t settle out of time ...
... -3 Important Prop of Solutions 1.part not large enough to be seen 2.part. are evenly spread out(all parts of sol are ident) 3.solution doesn’t settle out of time ...
Chemical with Petro
... 3. Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry: First law-Internal Energy, Work and Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperatur ...
... 3. Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry: First law-Internal Energy, Work and Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperatur ...
UNIT-1 - Andhra University
... 3. Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry: First law-Internal Energy, Work and Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperatur ...
... 3. Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry: First law-Internal Energy, Work and Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperatur ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium Review Page 1
... B) greater than the rate of condensation C) equal to the rate of condensation D) equal to a zero rate of condensation 37. A liquid in a stoppered flask is allowed to stand at constant temperature until the liquid level in the flask remains constant. Which condition then exists in the flask? A) Only ...
... B) greater than the rate of condensation C) equal to the rate of condensation D) equal to a zero rate of condensation 37. A liquid in a stoppered flask is allowed to stand at constant temperature until the liquid level in the flask remains constant. Which condition then exists in the flask? A) Only ...
Name: 1) In a chemical reaction, the difference between the
... On the set of axes below, sketch the potential energy diagram for an endothermic chemical reaction that shows the activation energy and the potential energy of the reactants and the potential energy of the products. ...
... On the set of axes below, sketch the potential energy diagram for an endothermic chemical reaction that shows the activation energy and the potential energy of the reactants and the potential energy of the products. ...
Document
... The change in boiling point can be determined by the equation ΔTB.P.= i ·Kb ·m, where m is the molality of the solute(mol/kg), i is the Van 't Hoff factor (the number of dissolved particles the solute will create when dissolved), and Kb is the ebullioscopic constant unique to each solvent. Freezing- ...
... The change in boiling point can be determined by the equation ΔTB.P.= i ·Kb ·m, where m is the molality of the solute(mol/kg), i is the Van 't Hoff factor (the number of dissolved particles the solute will create when dissolved), and Kb is the ebullioscopic constant unique to each solvent. Freezing- ...
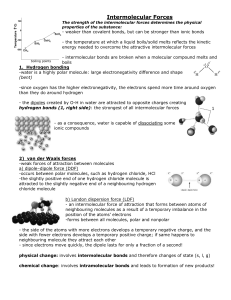
Intermolecular Forces
... position of the atoms’ electrons -forms between all molecules, polar and nonpolar - the side of the atoms with more electrons develops a temporary negative charge, and the side with fewer electrons develops a temporary positive charge; if same happens to neighbouring molecule they attract each other ...
... position of the atoms’ electrons -forms between all molecules, polar and nonpolar - the side of the atoms with more electrons develops a temporary negative charge, and the side with fewer electrons develops a temporary positive charge; if same happens to neighbouring molecule they attract each other ...
H = 890kJ - George Mason University
... energy transfer results in a temperature change. Chemical energy a form of potential energy. Energy is stored in chemical bonds and released when a compound reacts. During reaction, energy is usually transformed from chemical to thermal energy. First law can be written as: E=q+w where q = heat ...
... energy transfer results in a temperature change. Chemical energy a form of potential energy. Energy is stored in chemical bonds and released when a compound reacts. During reaction, energy is usually transformed from chemical to thermal energy. First law can be written as: E=q+w where q = heat ...
Thermochemistry
... • Constant volume ∆E = q + w = qv Energy released by reaction = temperature increase x heat capacity of calorimeter ...
... • Constant volume ∆E = q + w = qv Energy released by reaction = temperature increase x heat capacity of calorimeter ...
VCAA Study Design - Chemistry Education Association
... • (Chemical sciences) The atomic structure and properties of elements are used to organise them in the Periodic Table • (Chemical sciences) Different types of chemical reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates • (Earth sciences) Global systems, including the ...
... • (Chemical sciences) The atomic structure and properties of elements are used to organise them in the Periodic Table • (Chemical sciences) Different types of chemical reactions are used to produce a range of products and can occur at different rates • (Earth sciences) Global systems, including the ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.