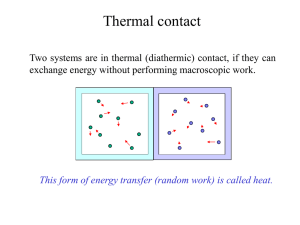
Overview
... 2. Use the dynamic interpretation of temperature to derive the internal energy of a two-dimensional monatomic gas. [ans U = nRT] Energy in Radiation Heated objects radiate energy in the form of electromagnetic waves so, for example, warmth from an oven can be felt at a distance because the energy is ...
... 2. Use the dynamic interpretation of temperature to derive the internal energy of a two-dimensional monatomic gas. [ans U = nRT] Energy in Radiation Heated objects radiate energy in the form of electromagnetic waves so, for example, warmth from an oven can be felt at a distance because the energy is ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... In a chemical reaction, substances that undergo chemical reactions, are called _________. Substances formed by chemical reactions, are called _________. CO2 + H20-----yields----H2CO3 (carbonic acid) is a sample chemical reaction in _________ things Reactants are on the left side of the equation, whi ...
... In a chemical reaction, substances that undergo chemical reactions, are called _________. Substances formed by chemical reactions, are called _________. CO2 + H20-----yields----H2CO3 (carbonic acid) is a sample chemical reaction in _________ things Reactants are on the left side of the equation, whi ...
Thermo Practice Test
... 26. T - F For the process in #25, we would expect S to decrease with increasing pressure. 27. T - F For the decomposition of water to the elements at standard conditions, G= +56.7 kcal. This means that at least 56.7 kcal of work (energy) has to be supplied to make this reaction go. ...
... 26. T - F For the process in #25, we would expect S to decrease with increasing pressure. 27. T - F For the decomposition of water to the elements at standard conditions, G= +56.7 kcal. This means that at least 56.7 kcal of work (energy) has to be supplied to make this reaction go. ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
... temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. QC QH ...
I PUC Chemistry Mock Paper
... 4. Write the IUPAC name of an element with atomic number 102. 5. Identify the type of redox reaction Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ----> ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s) 6. Name a compound in which oxidation number of oxygen is +1. 7. Which alkali metal is strongest reducing agent? 8. Name the catalyst used in Friedel Craft ...
... 4. Write the IUPAC name of an element with atomic number 102. 5. Identify the type of redox reaction Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ----> ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s) 6. Name a compound in which oxidation number of oxygen is +1. 7. Which alkali metal is strongest reducing agent? 8. Name the catalyst used in Friedel Craft ...
15-3 Constant Volume and Constant Pressure Processes
... Answer to Essential Question 15.2: An important distinction between work and the change in internal energy is that the work depends on the process involved in taking a system from one state to another, while the change in internal energy depends only on the initial and final states. Thus, if we do n ...
... Answer to Essential Question 15.2: An important distinction between work and the change in internal energy is that the work depends on the process involved in taking a system from one state to another, while the change in internal energy depends only on the initial and final states. Thus, if we do n ...
HONORS CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE Thermochemistry
... The total heat can then be determined by adding the heat associated with each temperature or phase change. Heat Curve for 1 mol of water (below): ...
... The total heat can then be determined by adding the heat associated with each temperature or phase change. Heat Curve for 1 mol of water (below): ...
Take notes on this document while you are watching the recorded
... Hydrolysis reactions are common decompositions reactions in biological systems: Water and another molecule react which breaks bonds in a molecule forming 2 molecules in which the HOH is added to them, usually H to one and OH to the other. ...
... Hydrolysis reactions are common decompositions reactions in biological systems: Water and another molecule react which breaks bonds in a molecule forming 2 molecules in which the HOH is added to them, usually H to one and OH to the other. ...
Chapters 6, 8
... Electronegativity and the Covalent Bond When non-metals react among themselves, the resulting compound is a molecular compound. Each reacting atom delivers its valence electrons to a pool of electrons, and the resulting compound is made by sharing these electrons among all atoms in the compound. Ea ...
... Electronegativity and the Covalent Bond When non-metals react among themselves, the resulting compound is a molecular compound. Each reacting atom delivers its valence electrons to a pool of electrons, and the resulting compound is made by sharing these electrons among all atoms in the compound. Ea ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Chemical Reactions • Key Concept 2: The process by which one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances is called a chemical reaction. What are some examples of evidence of a chemical reaction? ...
... Chemical Reactions • Key Concept 2: The process by which one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances is called a chemical reaction. What are some examples of evidence of a chemical reaction? ...
Chapter 1
... Path 1, in which there is free expansion against zero external pressure; Path 2, in which there is reversible, isothermal expansion. ...
... Path 1, in which there is free expansion against zero external pressure; Path 2, in which there is reversible, isothermal expansion. ...
States of matter - Tennessee State University
... There is such a function state U, called internal energy, that dU = dQ - dW where dQ is the heat delivered to the system and dW is the work performed by the system. Comment: On the microscopic scale, the internal energy of a system is the total mechanical energy of the system. ...
... There is such a function state U, called internal energy, that dU = dQ - dW where dQ is the heat delivered to the system and dW is the work performed by the system. Comment: On the microscopic scale, the internal energy of a system is the total mechanical energy of the system. ...
Ch 3 Matter & Change
... Each one has a unique name and symbol. In the symbol the first letter is always capitalized and the remaining letter(s) are lowercase. There are 91 naturally occurring elements Who was given credit for organizing them into a table? Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... Each one has a unique name and symbol. In the symbol the first letter is always capitalized and the remaining letter(s) are lowercase. There are 91 naturally occurring elements Who was given credit for organizing them into a table? Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Chemistry Definitions
... 2. Atomic number (Z): The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of an element 3. Mass number (A): Total number of neutrons and protons present in the nucleus if an atom of an element 4. Isotopes: Elements of the same atomic number but different number of neutrons. They have the same electron ...
... 2. Atomic number (Z): The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of an element 3. Mass number (A): Total number of neutrons and protons present in the nucleus if an atom of an element 4. Isotopes: Elements of the same atomic number but different number of neutrons. They have the same electron ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... 35. According to the zeroth law of thermodynamics: a) Energy is neither lost nor gained in any energy transformations. b) Two bodies in thermal equilibrium with a third, are in thermal equilibrium with each other c) Energy is conserved in quality but not in quantity. d) Energy is being created as ti ...
... 35. According to the zeroth law of thermodynamics: a) Energy is neither lost nor gained in any energy transformations. b) Two bodies in thermal equilibrium with a third, are in thermal equilibrium with each other c) Energy is conserved in quality but not in quantity. d) Energy is being created as ti ...
Chapter 18 Review 18.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation
... Corrosion- process of returning metals to their natural state Cathodic Protection- the connection of an active metal to another to prevent corrosion - corrosion involves the oxidation of metals - this process creates great economic lose - most metals produce a thin oxide coating, which protect their ...
... Corrosion- process of returning metals to their natural state Cathodic Protection- the connection of an active metal to another to prevent corrosion - corrosion involves the oxidation of metals - this process creates great economic lose - most metals produce a thin oxide coating, which protect their ...
The Atom Power point - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
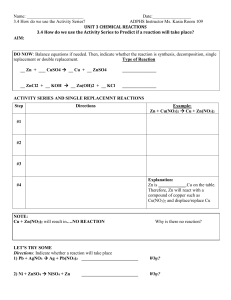
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
... F2 + 2NaCl Cl2 + 2NaF 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction ...
Slajd 1
... and final conditions are the same. Because we are dealing with changes in state functions, the net change is the same as the change we would have obtained hypothetically with T and P actually held constant. ...
... and final conditions are the same. Because we are dealing with changes in state functions, the net change is the same as the change we would have obtained hypothetically with T and P actually held constant. ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.