AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam, Also Data Base of MC
... When the concentration of substance B in the reaction above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) the order of the reaction with respect to substance B is 1 (B) su ...
... When the concentration of substance B in the reaction above is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) the order of the reaction with respect to substance B is 1 (B) su ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Reactions and Solution
... net ionic chemical equations. This will require you to be disciplined, committing yourself to memorizing certain information and doing much practice. To be successful you must develop the ability to recognize an acid, a base and an ionic compound from their formulas. An understanding of the nature o ...
... net ionic chemical equations. This will require you to be disciplined, committing yourself to memorizing certain information and doing much practice. To be successful you must develop the ability to recognize an acid, a base and an ionic compound from their formulas. An understanding of the nature o ...
Slide 2.1 - Cloudfront.net
... • Can be separated by physical means • Evaporation, filtration, distillation, centrifugation, etc. ...
... • Can be separated by physical means • Evaporation, filtration, distillation, centrifugation, etc. ...
measures of amount or size
... • Temperature, pressure, specific volume, and density are examples of intensive properties. • Mass and total volume are examples of extensive properties. ...
... • Temperature, pressure, specific volume, and density are examples of intensive properties. • Mass and total volume are examples of extensive properties. ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review
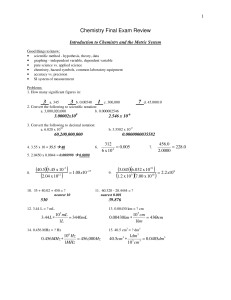
... 3. If you have a 2.75dm3 balloon under 455kPa of pressure at 100oC, what will the volume be at STP? ...
... 3. If you have a 2.75dm3 balloon under 455kPa of pressure at 100oC, what will the volume be at STP? ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... moving and far apart; aqueous (dissolved in water): particles moving and far. 5. chemical: Chlorine reacts with sodium to form NaCl. You could also list the formula of any ionic compound chlorine forms, such as MgCl2, CaCl2, etc. physical: Chlorine is a pale green gas at room temperature. It’s a non ...
... moving and far apart; aqueous (dissolved in water): particles moving and far. 5. chemical: Chlorine reacts with sodium to form NaCl. You could also list the formula of any ionic compound chlorine forms, such as MgCl2, CaCl2, etc. physical: Chlorine is a pale green gas at room temperature. It’s a non ...
Physical Chemistry Problems. ©Mike Lyons 2009
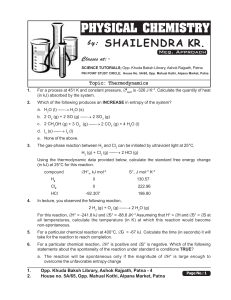
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
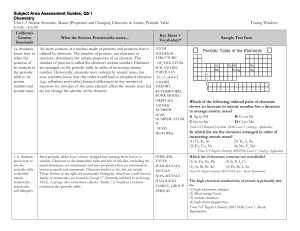
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... Reactions are described by balanced equations because all the atoms of the reactants must be accounted for in the reaction products. An equation with all correct chemical formulas can be balanced by a number of methods, the simplest being by inspection. Given an unbalanced equation, students can do ...
... Reactions are described by balanced equations because all the atoms of the reactants must be accounted for in the reaction products. An equation with all correct chemical formulas can be balanced by a number of methods, the simplest being by inspection. Given an unbalanced equation, students can do ...
Molecular and Empirical Formulas
... 2. Find the number of atoms for each element on the left side. Compare those against the number of the atoms of the same element on the right side. 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in o ...
... 2. Find the number of atoms for each element on the left side. Compare those against the number of the atoms of the same element on the right side. 3. Determine where to place coefficients in front of formulas so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in o ...
Chemical Kinetics
... Stability of Pharmaceuticals Decomposition and Stabilization of Medicinal Agents Pharmaceutical decomposition can be classified as hydrolysis, oxidation, isomerization, epimerization, and photolysis, and these processes may affect the stability of drugs in liquid, solid, and semisolid products. Mol ...
... Stability of Pharmaceuticals Decomposition and Stabilization of Medicinal Agents Pharmaceutical decomposition can be classified as hydrolysis, oxidation, isomerization, epimerization, and photolysis, and these processes may affect the stability of drugs in liquid, solid, and semisolid products. Mol ...
Chemical Dynamics at Surfaces
... One of the most important discoveries in the field of chemistry in the last 100 years N2+ 3H2→2NH3 ...
... One of the most important discoveries in the field of chemistry in the last 100 years N2+ 3H2→2NH3 ...
Chemical Stability
... of the atoms are about the same, they share equally and form a Non-Polar compound. • If the electronegativity of one type of atom is greater than the other, the electrons are not shared equally and a Polar compound is formed. ...
... of the atoms are about the same, they share equally and form a Non-Polar compound. • If the electronegativity of one type of atom is greater than the other, the electrons are not shared equally and a Polar compound is formed. ...
equilibrium - TeacherWeb
... The equilibrium constant expression for a reaction written in one direction is the reciprocal of the one for the reaction in the reverse direction. The equilibrium constant allows you: 1. to predict the direction in which a reaction mixture will proceed to achieve equilibrium. 2. to calculate the co ...
... The equilibrium constant expression for a reaction written in one direction is the reciprocal of the one for the reaction in the reverse direction. The equilibrium constant allows you: 1. to predict the direction in which a reaction mixture will proceed to achieve equilibrium. 2. to calculate the co ...
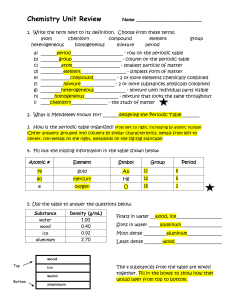
Classification of
... e) ______heterogeneous_________________ - mixture with individual parts visible f) _______states of matter_______________________ - solid, liquid, gas g) ___________solid___________________ - definite volume and shape h) ____________liquid__________________ - definite volume, changeable shape i) ___ ...
... e) ______heterogeneous_________________ - mixture with individual parts visible f) _______states of matter_______________________ - solid, liquid, gas g) ___________solid___________________ - definite volume and shape h) ____________liquid__________________ - definite volume, changeable shape i) ___ ...
BONUS: Which line in the above graph represents G for the reaction
... which change will cause an increase in the pressure of CO2(g) when equilibrium is re-established? (A) ...
... which change will cause an increase in the pressure of CO2(g) when equilibrium is re-established? (A) ...
Chapter 4
... Consider the following arguments for each answer and vote again: A. Until sufficient phosphorus is added to achieve the correct molar ratio of phosphorus to oxygen (2:5), no reaction will occur, after which P4O10 will form as more phosphorus is added. B. The amount of P4O10 product will accumulate ...
... Consider the following arguments for each answer and vote again: A. Until sufficient phosphorus is added to achieve the correct molar ratio of phosphorus to oxygen (2:5), no reaction will occur, after which P4O10 will form as more phosphorus is added. B. The amount of P4O10 product will accumulate ...
LN_ch06
... In solving chemical-equation-based problems, the only “transitions” allowed are those between quantities (boxes) connected by arrows. Chapter 6 | Slide 37 ...
... In solving chemical-equation-based problems, the only “transitions” allowed are those between quantities (boxes) connected by arrows. Chapter 6 | Slide 37 ...
Chemical Reactions
... shift. This is because the addition of a non-reactive gas does not change the partial pressures of the other gases in the container. While it is true that the total pressure of the system increases, the total pressure does not have any effect on the equilibrium constant; rather, it is a change in pa ...
... shift. This is because the addition of a non-reactive gas does not change the partial pressures of the other gases in the container. While it is true that the total pressure of the system increases, the total pressure does not have any effect on the equilibrium constant; rather, it is a change in pa ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.