Document
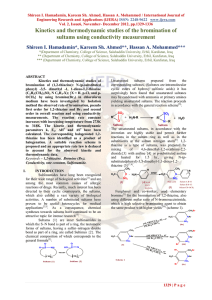
... Where Q1 and Q2 are the charges on the particles, d is the distance between their centers, and k is a constant. ...
... Where Q1 and Q2 are the charges on the particles, d is the distance between their centers, and k is a constant. ...
Lab announcements – 2 lab quiz week before spring break
... Most chemical reactions do not go to completion. chemical equilibrium – two opposing reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate ‘equilibrium’ doesn’t necessarily mean ‘equal’ amounts of reactants and products – in fact, it usually doesn’t. Equilibrium constant – measure of this balance aA + Kc ...
... Most chemical reactions do not go to completion. chemical equilibrium – two opposing reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate ‘equilibrium’ doesn’t necessarily mean ‘equal’ amounts of reactants and products – in fact, it usually doesn’t. Equilibrium constant – measure of this balance aA + Kc ...
chapter 8
... equations. As you can see, some things can be shown in different ways. For example, sometimes a gaseous product is indicated by an arrow pointing upward,↑, instead of (g). A downward arrow, ↓, is often used to show the formation of a precipitate during a reaction in solution. The conditions under wh ...
... equations. As you can see, some things can be shown in different ways. For example, sometimes a gaseous product is indicated by an arrow pointing upward,↑, instead of (g). A downward arrow, ↓, is often used to show the formation of a precipitate during a reaction in solution. The conditions under wh ...
Chapter 11 Homework
... heat is a form of energy (thermal energy) that flows between objects at different temperatures. heat is different than temperature, which is a measure of average kinetic energy. chemical potential energy is a form of energy stored within a substance, depending on the types of atoms, bonds, and ...
... heat is a form of energy (thermal energy) that flows between objects at different temperatures. heat is different than temperature, which is a measure of average kinetic energy. chemical potential energy is a form of energy stored within a substance, depending on the types of atoms, bonds, and ...
File
... Iodine is a black, shiny, non-metallic solid and a member of Group VII. It sublimes easily on heating to give a purple vapour. A sample of iodine vapour of mass 6.35 g has a volume of 1.247 dm3 when maintained at constant temperature and a pressure of 1.00 × 105 Pa. If iodine vapour acts as an ideal ...
... Iodine is a black, shiny, non-metallic solid and a member of Group VII. It sublimes easily on heating to give a purple vapour. A sample of iodine vapour of mass 6.35 g has a volume of 1.247 dm3 when maintained at constant temperature and a pressure of 1.00 × 105 Pa. If iodine vapour acts as an ideal ...
Energy and Matter in Chemical Change Science 10
... flowing (dependent variable) changes in response--you observe that the water flow increases. The number of dependent variables in an experiment varies, but there is often more than one. ...
... flowing (dependent variable) changes in response--you observe that the water flow increases. The number of dependent variables in an experiment varies, but there is often more than one. ...
Naming Binary Molecular Compounds
... Which elements do not have a specific rule? Neither N nor S has a specific rule. You must break the compound into the individual ions that are present and then use rule 9 to find the oxidation numbers of N and S. Notice that if you try to use rule 8, you end up with one equation with two unknowns: 2 ...
... Which elements do not have a specific rule? Neither N nor S has a specific rule. You must break the compound into the individual ions that are present and then use rule 9 to find the oxidation numbers of N and S. Notice that if you try to use rule 8, you end up with one equation with two unknowns: 2 ...
Theoretical Competition - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... 2.1. What is the element A? 2.2. Give the formula and the name of complex K1. 2.3. Draw the occupation of the d-orbitals for K1 and verify it by comparing the calculated and the measured magnetic moment. 2.4. Calculate the ligand energy splitting ∆ (in kJ/mol) for K1. 2.5. In case of the same centra ...
... 2.1. What is the element A? 2.2. Give the formula and the name of complex K1. 2.3. Draw the occupation of the d-orbitals for K1 and verify it by comparing the calculated and the measured magnetic moment. 2.4. Calculate the ligand energy splitting ∆ (in kJ/mol) for K1. 2.5. In case of the same centra ...
Calometric Measurement of Saponification Reaction
... The enthalpy of formation of the soap product is calculated using Power Compensation Calorimetery (PCC). This is achieved through the control and online monitoring of the power applied through the compensation heating rod (which is inserted directly into the reaction-content) and control of the temp ...
... The enthalpy of formation of the soap product is calculated using Power Compensation Calorimetery (PCC). This is achieved through the control and online monitoring of the power applied through the compensation heating rod (which is inserted directly into the reaction-content) and control of the temp ...
Document
... • Use the principle of conservation of energy — the experimental observation that energy can be neither created nor destroyed — to assess the energy changes that accompany physical and chemical processes • The means by which a system can exchange energy with its surroundings in terms of the work it ...
... • Use the principle of conservation of energy — the experimental observation that energy can be neither created nor destroyed — to assess the energy changes that accompany physical and chemical processes • The means by which a system can exchange energy with its surroundings in terms of the work it ...
PPT
... Solubilization of IB in 8 M urea or 6 M GuHCl Overnight binding to Ni-NTA (Qiagen) Column wash with urea buffer and 20 mM imidazole ...
... Solubilization of IB in 8 M urea or 6 M GuHCl Overnight binding to Ni-NTA (Qiagen) Column wash with urea buffer and 20 mM imidazole ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... Reactions are described by balanced equations because all the atoms of the reactants must be accounted for in the reaction products. An equation with all correct chemical formulas can be balanced by a number of methods, the simplest being by inspection. Given an unbalanced equation, students can do ...
... Reactions are described by balanced equations because all the atoms of the reactants must be accounted for in the reaction products. An equation with all correct chemical formulas can be balanced by a number of methods, the simplest being by inspection. Given an unbalanced equation, students can do ...
Lecture08
... – Sun is steadily losing energy at its surface (it’s shining!); it is trying to “cool off” – Heat from the Sun’s interior slowly diffuses toward the surface – This lost heat can be replenished by slow gravitational contraction (whenever a gas is compressed, its temperature rises); this is referred t ...
... – Sun is steadily losing energy at its surface (it’s shining!); it is trying to “cool off” – Heat from the Sun’s interior slowly diffuses toward the surface – This lost heat can be replenished by slow gravitational contraction (whenever a gas is compressed, its temperature rises); this is referred t ...
Catalytic Synthesis of Organophosphorus Compounds from
... H 2 O (4-6 %) promotes the formation of di(hydroxyaryl)phosphite: ...
... H 2 O (4-6 %) promotes the formation of di(hydroxyaryl)phosphite: ...
Introduction to Organic Synthesis
... simpler molecules by means of DISCONNECTIONS and/or FUNCTIONAL GROUP INTERCONVERSIONS that correspond to known reactions. When you've got to a simple enough starting material (like something you can buy [and usually is cheap]) then the synthetic plan is simply the reverse of the analysis. The design ...
... simpler molecules by means of DISCONNECTIONS and/or FUNCTIONAL GROUP INTERCONVERSIONS that correspond to known reactions. When you've got to a simple enough starting material (like something you can buy [and usually is cheap]) then the synthetic plan is simply the reverse of the analysis. The design ...
CHEMISTRY Academic Standards Statement
... v. Separation methods and sample preparation may be required prior to determination of structure. 2.1.3 Properties of matter in relation to structure i. The size and location of the constituent atoms within a chemical species influences the shape and hence the chemical and physical properties of tha ...
... v. Separation methods and sample preparation may be required prior to determination of structure. 2.1.3 Properties of matter in relation to structure i. The size and location of the constituent atoms within a chemical species influences the shape and hence the chemical and physical properties of tha ...
C6_rev - boswellsrcd
... (eg could get too hot if exothermic; gas could be produced to quickly and pressure build up) If it is too slow, then product would be made too slowly, and yield low, so profit too low. (economic factors) ...
... (eg could get too hot if exothermic; gas could be produced to quickly and pressure build up) If it is too slow, then product would be made too slowly, and yield low, so profit too low. (economic factors) ...
two stroke engines
... Eg: Study of Atomic Structure in nuclear physics. Macroscopic Analysis : Behavior of more number of molecules is taken into account. It is also known as Engineering Thermodynamics. Eg : Force on a given area can be measured by Pressure gauge, Measurement of pressure, volume and temperature. ...
... Eg: Study of Atomic Structure in nuclear physics. Macroscopic Analysis : Behavior of more number of molecules is taken into account. It is also known as Engineering Thermodynamics. Eg : Force on a given area can be measured by Pressure gauge, Measurement of pressure, volume and temperature. ...
GQ2613291336
... was fitted with a rubber stopper and the conductivity readings from conductivity meter (C) were recorded (the conductivity of distilled water as a blank was excluded). The other neck of the flask (A) connected by a rubber tube to the flask (I) which contains 10ml distilled water and indicator, the c ...
... was fitted with a rubber stopper and the conductivity readings from conductivity meter (C) were recorded (the conductivity of distilled water as a blank was excluded). The other neck of the flask (A) connected by a rubber tube to the flask (I) which contains 10ml distilled water and indicator, the c ...
Notes - Text
... • At room temperature, it decomposes to brown NO2. N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g) • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the concentrations of all species are constant. • Assume that both the forward and reverse reactions are e ...
... • At room temperature, it decomposes to brown NO2. N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g) • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the concentrations of all species are constant. • Assume that both the forward and reverse reactions are e ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.