Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
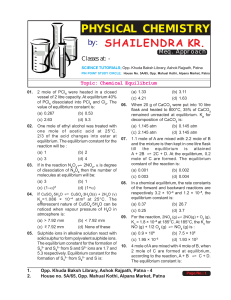
Chemical Equilibrium - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... For an equilibrium change involving gaseous phase, the forward reaction is first order while the reverse reaction is second order. The unit of Kp for the forward equilibrium is : ...
... For an equilibrium change involving gaseous phase, the forward reaction is first order while the reverse reaction is second order. The unit of Kp for the forward equilibrium is : ...
paper - American Society for Engineering Education
... instructor then asks students to evaluate each property to see if it is known or unknown. Maybe the property is clearly given in the problem statement, or it may be determinable from the information given in the problem statement. Students are encouraged to find two properties that are either known ...
... instructor then asks students to evaluate each property to see if it is known or unknown. Maybe the property is clearly given in the problem statement, or it may be determinable from the information given in the problem statement. Students are encouraged to find two properties that are either known ...
Principles of Reactivity: Chemical Equilibria
... When the stoichiometric coefficients of a balanced equation are multiplied by some factor, the equilibrium constant for the new equation (Knew) is the old equilibrium constant (Kold) raised to the power of the multiplication factor. The equilibrium constants for a reaction and its reverse are the re ...
... When the stoichiometric coefficients of a balanced equation are multiplied by some factor, the equilibrium constant for the new equation (Knew) is the old equilibrium constant (Kold) raised to the power of the multiplication factor. The equilibrium constants for a reaction and its reverse are the re ...
Analytical Chemistry
... side. The increase in pressure always affects the side that has more volume. Hence, increase in pressure shifts the equilibrium from left to right. The Dressure has no effect ...
... side. The increase in pressure always affects the side that has more volume. Hence, increase in pressure shifts the equilibrium from left to right. The Dressure has no effect ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier
... whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our p ...
... whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our p ...
International Student Guide 2014
... development and design of new, sustainable chemical industrial processes as well as on the improvement of existing ones. This is done to ensure high quality, reliable and safe production that takes into account criteria of the economy, efficiency and environmental protection. In addition, students o ...
... development and design of new, sustainable chemical industrial processes as well as on the improvement of existing ones. This is done to ensure high quality, reliable and safe production that takes into account criteria of the economy, efficiency and environmental protection. In addition, students o ...
Mechanical Engineering and Aeronautics
... In general, hydrocarbons with 5 or more carbon atoms in the basic molecule are liquids at normal atmospheric conditions, while those with less than 5 atoms in the molecule are gaseous. Alcohols are an exception to the above rule. All alcohols are liquids at normal atmospheric conditions. ...
... In general, hydrocarbons with 5 or more carbon atoms in the basic molecule are liquids at normal atmospheric conditions, while those with less than 5 atoms in the molecule are gaseous. Alcohols are an exception to the above rule. All alcohols are liquids at normal atmospheric conditions. ...
Calorimetry - NC State University
... The enthalpy change DH is the change in energy at constant pressure. When a change takes place in a system that is open to the atmosphere, the volume of the system changes, but the pressure remains constant. In any chemical reactions that involve the creation or consumption of molecules in the vapor ...
... The enthalpy change DH is the change in energy at constant pressure. When a change takes place in a system that is open to the atmosphere, the volume of the system changes, but the pressure remains constant. In any chemical reactions that involve the creation or consumption of molecules in the vapor ...
Heat of Reaction
... All reactions and changes in state involve the release or absorption of heat ...
... All reactions and changes in state involve the release or absorption of heat ...
Description of liquid–gas phase transition in the frame of continuum
... That means that the Eqs. (5), (10) define not only the temperature and entropy, but also the internal energy. These three quantities are always interdependent, and they should be defined simultaneously. With other words, it is not possible to introduce at first the internal energy and then the tempe ...
... That means that the Eqs. (5), (10) define not only the temperature and entropy, but also the internal energy. These three quantities are always interdependent, and they should be defined simultaneously. With other words, it is not possible to introduce at first the internal energy and then the tempe ...
Minimum Learning Competencies - Ministry of Education, Ethiopia
... • Explain what an Electro chemistry is • Define electrical conductivity and differentiate ...
... • Explain what an Electro chemistry is • Define electrical conductivity and differentiate ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... Explain the term isotopes as atoms of an element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses. State that 12C is used as the standard measurement of ...
... Explain the term isotopes as atoms of an element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses. State that 12C is used as the standard measurement of ...
3.1.1.2 Mass number and isotopes
... indicates how far reactions will go. Le Chatelier’s principle can be used to predict the effects of changes in temperature, pressure and concentration on the yield of a reversible reaction. This has important consequences for many industrial processes. The further study of the equilibrium constant, ...
... indicates how far reactions will go. Le Chatelier’s principle can be used to predict the effects of changes in temperature, pressure and concentration on the yield of a reversible reaction. This has important consequences for many industrial processes. The further study of the equilibrium constant, ...
Practice Test 2
... Vinegar contains a weak acid, acetic acid (HC2H3O2), which is responsible for its acidity. In one analysis of a commercial vinegar brand, a 15.0 mL sample was titrated with 0.4500 M NaOH. It required 30.50 mL of this NaOH solution to neutralize the acid in the vinegar sample. What is the molar conce ...
... Vinegar contains a weak acid, acetic acid (HC2H3O2), which is responsible for its acidity. In one analysis of a commercial vinegar brand, a 15.0 mL sample was titrated with 0.4500 M NaOH. It required 30.50 mL of this NaOH solution to neutralize the acid in the vinegar sample. What is the molar conce ...
AP Chemistry 2015-‐‑2016 Name: Chapter 5: Thermodynamics
... 16) A gas is confined to a cylinder with a piston under constant atmospheric pressure (fig. 5.3). When the gas reacts, it releases 79 kJ of heat to its surroundings and does 18 kJ of P-‐ ...
... 16) A gas is confined to a cylinder with a piston under constant atmospheric pressure (fig. 5.3). When the gas reacts, it releases 79 kJ of heat to its surroundings and does 18 kJ of P-‐ ...
Paired with Lecture
... • These phase diagrams are based on the concept of Gibbs Free Energy, DG, which we have briefly introduced before: DG is the thermodynamic driving force for a reaction If DG is negative then there is a probability that a reaction will occur. The more negative DG becomes, the more driving force ...
... • These phase diagrams are based on the concept of Gibbs Free Energy, DG, which we have briefly introduced before: DG is the thermodynamic driving force for a reaction If DG is negative then there is a probability that a reaction will occur. The more negative DG becomes, the more driving force ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... surroundings. Reversible heat transfer from the heat source at TH to the gas which is also at TH. 2‐3 Reversible adiabatic expansion: The cylinder‐piston is now insulated (adiabatic) and gas continues to expand reversibly (slowly). So, the gas is doing work on the surroundings, and as ...
... surroundings. Reversible heat transfer from the heat source at TH to the gas which is also at TH. 2‐3 Reversible adiabatic expansion: The cylinder‐piston is now insulated (adiabatic) and gas continues to expand reversibly (slowly). So, the gas is doing work on the surroundings, and as ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.