Cyanide Destruction with Chlorine Dioxide
... treatment of cyanides in wastewater. Oxidation should be considered when levels of oxidizable cyanide are too high to be processed by a biological treatment system. Chlorine dioxide Chlorine dioxide is unique in its ability to be used at moderately basic pH's. All other oxidants require pH's greater ...
... treatment of cyanides in wastewater. Oxidation should be considered when levels of oxidizable cyanide are too high to be processed by a biological treatment system. Chlorine dioxide Chlorine dioxide is unique in its ability to be used at moderately basic pH's. All other oxidants require pH's greater ...
Test 4: Equations and Math of Equations Review Name: Tuesday
... Acid rain is a problem in industrialized countries around the world. Oxides of sulfur and nitrogen are formed when various fuels are burned. These oxides dissolve in atmospheric water droplets that fall to earth as acid rain or acid snow. While normal rain has a pH between 5.0 and 6.0 due to the pre ...
... Acid rain is a problem in industrialized countries around the world. Oxides of sulfur and nitrogen are formed when various fuels are burned. These oxides dissolve in atmospheric water droplets that fall to earth as acid rain or acid snow. While normal rain has a pH between 5.0 and 6.0 due to the pre ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
... 1. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and the ammonium ion are soluble. 2. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO4-, ClO3-, and C2H3O2- anions are soluble. 3. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag +, Pb2+, or Hg2+. 4. All sulfates are soluble except those ...
Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form unstable
... But aniline does not undergo H−bonding with water to a very large extent due to the presence of a large hydrophobic −C6H5 group. Hence, aniline is insoluble in water. (iii) Methylamine in water reacts with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric ...
... But aniline does not undergo H−bonding with water to a very large extent due to the presence of a large hydrophobic −C6H5 group. Hence, aniline is insoluble in water. (iii) Methylamine in water reacts with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric ...
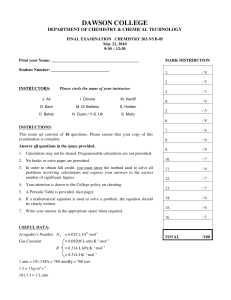
Final Exam - Dawson College
... Toluene, C7H8 is a component of gasoline (octane, C8H18). It is present in gasoline as an octane booster at concentrations between 3 to 5% by mass (25% in racing cars gasoline). Consider a solution of octane with 20.% by mass of toluene at 20°C a. Calculate the total vapor pressure of this solution ...
... Toluene, C7H8 is a component of gasoline (octane, C8H18). It is present in gasoline as an octane booster at concentrations between 3 to 5% by mass (25% in racing cars gasoline). Consider a solution of octane with 20.% by mass of toluene at 20°C a. Calculate the total vapor pressure of this solution ...
Reaction Rates/Chemical Kinetics
... Plan: We can determine the starting concentration of each species in the reaction mixture. We can then substitute the starting concentrations into the equilibrium-constant expression to calculate the reaction quotient, Qc. Comparing the magnitudes of the equilibrium constant, which is given, and the ...
... Plan: We can determine the starting concentration of each species in the reaction mixture. We can then substitute the starting concentrations into the equilibrium-constant expression to calculate the reaction quotient, Qc. Comparing the magnitudes of the equilibrium constant, which is given, and the ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical explanations
... selectively, so that the transmitted light has a different spectrum from that of sunlight; but a chemist would answer that it is because ordinary glass contains ferrous ions. This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In the present case all answers are releva ...
... selectively, so that the transmitted light has a different spectrum from that of sunlight; but a chemist would answer that it is because ordinary glass contains ferrous ions. This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In the present case all answers are releva ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... time is the instantaneous speed. It's the speed that is reported by a police radar gun at the split second the officer points the device at your car. It is possible to get a speeding ticket for going 80 miles / hour even when the average speed for your journey is only 40 miles / hour. Likewise, when ...
... time is the instantaneous speed. It's the speed that is reported by a police radar gun at the split second the officer points the device at your car. It is possible to get a speeding ticket for going 80 miles / hour even when the average speed for your journey is only 40 miles / hour. Likewise, when ...
幻灯片 1
... way different orbitals are filled is controlled by their energies (and hence their An atom consists of a very small positively charged nucleus, Electron and Nuclei different screening by other electrons) and by the Pauli exclusion principle. surrounded by negative electrons held by electrostatic att ...
... way different orbitals are filled is controlled by their energies (and hence their An atom consists of a very small positively charged nucleus, Electron and Nuclei different screening by other electrons) and by the Pauli exclusion principle. surrounded by negative electrons held by electrostatic att ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
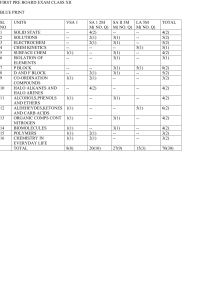
... 2. Question nos. 1 to 8 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each. 3. Question nos. 9 to 18 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each. 4. Question nos. 19 to 27 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each 5. Question nos. 28 to 30 are long answer questions and carry 5 ...
... 2. Question nos. 1 to 8 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each. 3. Question nos. 9 to 18 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each. 4. Question nos. 19 to 27 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each 5. Question nos. 28 to 30 are long answer questions and carry 5 ...
KCET – CHEMISTRY – 2016 - Medicine.careers360.com
... 12. Replacement of Cl of Chlorobenzene to give phenol requires drastic conditions, but Cl of 2, 4dinitro chlorobenene is readily replaced. This is because 1) –NO2 group makes the ring electron rich at ortho and para positions ...
... 12. Replacement of Cl of Chlorobenzene to give phenol requires drastic conditions, but Cl of 2, 4dinitro chlorobenene is readily replaced. This is because 1) –NO2 group makes the ring electron rich at ortho and para positions ...
Appendices - Mattson Creighton
... 1. A precipitate is an insoluble solid substance that is formed from an aqueous solution. Usually, precipitates are noticed as a cloudiness in the solution or as suspended particles. Eventually they settle to the bottom. 2. Limewater is a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2(aq) 3. Carbo ...
... 1. A precipitate is an insoluble solid substance that is formed from an aqueous solution. Usually, precipitates are noticed as a cloudiness in the solution or as suspended particles. Eventually they settle to the bottom. 2. Limewater is a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2(aq) 3. Carbo ...
Chemistry Transition Information
... b) strontium chloride c) caesium selenide d) calcium astatide e) radium polonide f) gallium fluoride g) scandium (III) bromide h) chromium (III) oxide i) strontium iodide j) lithium arsenide ...
... b) strontium chloride c) caesium selenide d) calcium astatide e) radium polonide f) gallium fluoride g) scandium (III) bromide h) chromium (III) oxide i) strontium iodide j) lithium arsenide ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Request a Spot account
... number of sandwiches, slices of bread, and slices of cheese were not changing (macroscopic); however, you would still be breaking apart sandwiches as fast as you were making sandwiches (molecular). This constant action on the molecular level is the reason chemical equilibrium is frequently referred ...
... number of sandwiches, slices of bread, and slices of cheese were not changing (macroscopic); however, you would still be breaking apart sandwiches as fast as you were making sandwiches (molecular). This constant action on the molecular level is the reason chemical equilibrium is frequently referred ...
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
... only six valence electrons and elemental Cl has seven valence electrons. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... only six valence electrons and elemental Cl has seven valence electrons. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
G o rxn
... Stability of particular substances The Spontaneity of a chemical reaction Equilibrium constant (Keq) of a chemical reaction Predict the proportions of products and reactants at ...
... Stability of particular substances The Spontaneity of a chemical reaction Equilibrium constant (Keq) of a chemical reaction Predict the proportions of products and reactants at ...
Support Material
... Examples are O 2, Cu2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ which are paramagnetic due to the presence of unpaired one or more electrons. They lose their magnetism in the absence of magnetic field. ...
... Examples are O 2, Cu2+, Fe3+, Cr3+ which are paramagnetic due to the presence of unpaired one or more electrons. They lose their magnetism in the absence of magnetic field. ...
CH 13
... b) Solid catalyst is easily poisoned, foreign material deposited on the surface during reaction reduce or destroy its effectiveness. ...
... b) Solid catalyst is easily poisoned, foreign material deposited on the surface during reaction reduce or destroy its effectiveness. ...
Stoichiometry: Predicting Amounts in Reactions
... dioxide are formed, how many moles of propane were burned? ...
... dioxide are formed, how many moles of propane were burned? ...
here
... Now let’s consider the law of definite proportions. Dalton’s theory assumes that atoms can join together to make compounds only in simple, whole–number ratios. In other words, a compound might have 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms, while another compound might have 1 carbon atom and 1 oxygen atom. A ...
... Now let’s consider the law of definite proportions. Dalton’s theory assumes that atoms can join together to make compounds only in simple, whole–number ratios. In other words, a compound might have 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms, while another compound might have 1 carbon atom and 1 oxygen atom. A ...
Answers - Pearson
... lighter gas. Its particles have greater velocity than the particles of Y at the same temperature. (Note though that they will both have the same ...
... lighter gas. Its particles have greater velocity than the particles of Y at the same temperature. (Note though that they will both have the same ...
Introduction to Kinetics and Equilibrium
... ‐ e. g. combustion reactions (like the balloon e g combustion reactions (like the balloon demo) or establish a chemical equilibrium (some reactants, some products) ...
... ‐ e. g. combustion reactions (like the balloon e g combustion reactions (like the balloon demo) or establish a chemical equilibrium (some reactants, some products) ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.