The Process of Chemical Reactions
... is so slow that most limestone formations remain unreacted for thousands of years. Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a mov ...
... is so slow that most limestone formations remain unreacted for thousands of years. Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a mov ...
Questions
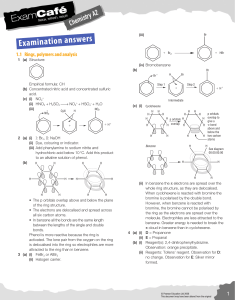
... These compounds can also be distinguished from one another by the use of concentrated sulphuric acid. (i) ...
... These compounds can also be distinguished from one another by the use of concentrated sulphuric acid. (i) ...
OCR answers to the examination questions File
... When cyclohexene is reacted with bromine the bromine is polarised by the double bond. However, when benzene is reacted with bromine, the bromine cannot be polarised by the ring as the electrons are spread over the molecule. Electrophiles are less attracted to the benzene. Greater energy is needed to ...
... When cyclohexene is reacted with bromine the bromine is polarised by the double bond. However, when benzene is reacted with bromine, the bromine cannot be polarised by the ring as the electrons are spread over the molecule. Electrophiles are less attracted to the benzene. Greater energy is needed to ...
Chemistry - Resonance
... (ii) Electronegativity and strength of bonds : The electronegativity of carbon (2.5) is close to a number of other elements like H (2.1) , N(3.0) , P (2.1), Cl (3.0) and O (3.5). So carbon forms strong covalent bonds with these elements. ...
... (ii) Electronegativity and strength of bonds : The electronegativity of carbon (2.5) is close to a number of other elements like H (2.1) , N(3.0) , P (2.1), Cl (3.0) and O (3.5). So carbon forms strong covalent bonds with these elements. ...
4U Chemistry Practice Exam - Coristines
... c. Amines always have a larger molecular weight than amides. d. Amines always have a nitrogen atom attached to two carbon atoms. e. Amines can be found in proteins, but amides can not. 5. Why does the boiling point of an alkane increase as its chain length increases? a. There is more hydrogen bondin ...
... c. Amines always have a larger molecular weight than amides. d. Amines always have a nitrogen atom attached to two carbon atoms. e. Amines can be found in proteins, but amides can not. 5. Why does the boiling point of an alkane increase as its chain length increases? a. There is more hydrogen bondin ...
visual problems - Western Oregon University
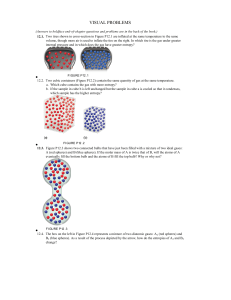
... 12.79. Lightbulb Filaments Tungsten (W) is the favored metal for lightbulb filaments, in part because of its high melting point of 3422°C. The enthalpy of fusion of tungsten is 35.4 kJ/mol. What is its entropy of fusion? 12.80. Making Methanol The element hydrogen (H2) is not abundant in nature, but ...
... 12.79. Lightbulb Filaments Tungsten (W) is the favored metal for lightbulb filaments, in part because of its high melting point of 3422°C. The enthalpy of fusion of tungsten is 35.4 kJ/mol. What is its entropy of fusion? 12.80. Making Methanol The element hydrogen (H2) is not abundant in nature, but ...
General Chemistry - Bioinorganic and Solution Chemistry Group
... The beginner’s course in inorganic and general chemistry is intended to teach the fundamental methods of chemical laboratory work to students of biology and pharmaceutical sciences and to make them familiar with the important reaction types in inorganic chemistry. Restrictions concerning the availab ...
... The beginner’s course in inorganic and general chemistry is intended to teach the fundamental methods of chemical laboratory work to students of biology and pharmaceutical sciences and to make them familiar with the important reaction types in inorganic chemistry. Restrictions concerning the availab ...
3 - LPS
... Identification. State whether each of the following is a physical or chemical change or property by writing an ”A” if it is a physical change, “B” if it is a physical property, “C” if it is a chemical change, or “D” if it is a chemical property. _______27. Melting butter ...
... Identification. State whether each of the following is a physical or chemical change or property by writing an ”A” if it is a physical change, “B” if it is a physical property, “C” if it is a chemical change, or “D” if it is a chemical property. _______27. Melting butter ...
APPLICATION OF IONIC LIQUIDS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
... Conventional organic solvents are used in a range of pharmaceutical and industrial applications. Ionic liquids have been gaining growing attention from synthetic organic chemists and practitioners in chemical industries in general. Ionic liquids are defined as containing organic cations and inorgani ...
... Conventional organic solvents are used in a range of pharmaceutical and industrial applications. Ionic liquids have been gaining growing attention from synthetic organic chemists and practitioners in chemical industries in general. Ionic liquids are defined as containing organic cations and inorgani ...
57 estonian national chemistry olympiad
... of B can be written as AX3. If gas B is heated in hydrogen atmosphere, elementary compound A If formed. A is also formed by thermal decomposition of iodide AI3 and in reaction of oxide A2O3 with magnesium. The second product in three given reactions of A formation are strong acid C, elementary subst ...
... of B can be written as AX3. If gas B is heated in hydrogen atmosphere, elementary compound A If formed. A is also formed by thermal decomposition of iodide AI3 and in reaction of oxide A2O3 with magnesium. The second product in three given reactions of A formation are strong acid C, elementary subst ...
Line 4: Equation
... Write the balanced equation between silver nitrate and a solution of sodium chloride. You begin with two compounds. This is a double replacement reaction. Double replacement reactions that occur in solution may also be called precipitation reactions. You will need to look at the solubility chart to ...
... Write the balanced equation between silver nitrate and a solution of sodium chloride. You begin with two compounds. This is a double replacement reaction. Double replacement reactions that occur in solution may also be called precipitation reactions. You will need to look at the solubility chart to ...
Stoichiometry - VernonScienceLSA
... amount of chemical #2 involved. A typical problem might be “How many grams of chemical #1 must be reacted to produce 25.0 g of chemical #2?” or “What volume of chemical #1 at STP will be produced when 15.0 g of chemical #2 is reacted?” In most cases, the quantities of the chemicals will be given in ...
... amount of chemical #2 involved. A typical problem might be “How many grams of chemical #1 must be reacted to produce 25.0 g of chemical #2?” or “What volume of chemical #1 at STP will be produced when 15.0 g of chemical #2 is reacted?” In most cases, the quantities of the chemicals will be given in ...
chemistry - Ethiopian Ministry of Education
... Chemistry is the science that deals with matter and the changes that it undergoes. It is a study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter and of the changes that occur in matter. Perhaps the only permanent thing in the world is change. Iron rusts, snow melts, paints peel off and firew ...
... Chemistry is the science that deals with matter and the changes that it undergoes. It is a study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter and of the changes that occur in matter. Perhaps the only permanent thing in the world is change. Iron rusts, snow melts, paints peel off and firew ...
as a PDF
... of irradiation pulses prevents this kind of redox process through electron transfer. It was shown that in the same mixed ion system the metal clusters obtained change with increasing dose rate from a bilayered core/shell structure to an alloyed structure or bimetallic solid solution.10 In the litera ...
... of irradiation pulses prevents this kind of redox process through electron transfer. It was shown that in the same mixed ion system the metal clusters obtained change with increasing dose rate from a bilayered core/shell structure to an alloyed structure or bimetallic solid solution.10 In the litera ...
CHEM 1411 – STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-2
... 56. During volcanic eruptions, hydrogen sulfide gas is given off and oxidized by air according to the following chemical equation: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the above reaction given: 3S(s) + 2H2O(g) 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) H° = 146.9 kJ/mol S(s) + O2 ...
... 56. During volcanic eruptions, hydrogen sulfide gas is given off and oxidized by air according to the following chemical equation: 2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the above reaction given: 3S(s) + 2H2O(g) 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) H° = 146.9 kJ/mol S(s) + O2 ...
PLACE LABEL HERE Tasmanian Certificate of Education
... Explain why this accident would contribute to an acidification of the local atmosphere around the sulfuric acid plant. Use a chemical equation to help explain your answer. ...
... Explain why this accident would contribute to an acidification of the local atmosphere around the sulfuric acid plant. Use a chemical equation to help explain your answer. ...
CHEM 1212 Principles of Chemistry II Course Study Guide
... on reserve at the library. ONLY use these to check problems you have already attempted. Reading the solutions will not help (See study tip #1). 3) Do not forget the “visual problems.” These are “conceptual” like your final and many test questions. 4) If you have the access code, you can also do the ...
... on reserve at the library. ONLY use these to check problems you have already attempted. Reading the solutions will not help (See study tip #1). 3) Do not forget the “visual problems.” These are “conceptual” like your final and many test questions. 4) If you have the access code, you can also do the ...
Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy and the Direction of
... (a) 1mol of SO2(g) or 1mol of SO3(g) (b) 1mol of CO2(s) or 1mol of CO2(g) (c) 3mol of oxygen gas (O2) or 2mol of ozone gas (O3) (d) 1mol of KBr(s) or 1mol of KBr(aq) (e) Seawater in midwinter at 20C or in midsummer at 230C (f) 1mol of CF4(g) or 1mol of CCl4(g) PLAN: In general less ordered systems h ...
... (a) 1mol of SO2(g) or 1mol of SO3(g) (b) 1mol of CO2(s) or 1mol of CO2(g) (c) 3mol of oxygen gas (O2) or 2mol of ozone gas (O3) (d) 1mol of KBr(s) or 1mol of KBr(aq) (e) Seawater in midwinter at 20C or in midsummer at 230C (f) 1mol of CF4(g) or 1mol of CCl4(g) PLAN: In general less ordered systems h ...
Chapter 23 + Practice Problems - Bloomsburg Area School District
... have a large amount of saturated fatty acids, fats are solids at room temperature. Oils have more unsaturated fatty acids than fats, and are liquids. Like other animals, humans make fat, which is stored in adipose tissue until it is needed as an energy source. Fat has about twice as much energy per ...
... have a large amount of saturated fatty acids, fats are solids at room temperature. Oils have more unsaturated fatty acids than fats, and are liquids. Like other animals, humans make fat, which is stored in adipose tissue until it is needed as an energy source. Fat has about twice as much energy per ...
Chemical Reactivity as Described by Quantum Chemical Methods
... pioneering work by Heitler and London [2] on the hydrogen molecule in 1928 providing insight into, to quote Pauling, the Nature of the Chemical Bond [3]. However Quantum Chemistry is, at least in our opinion, more than the mere application of quantum mechanical principles to molecules and their inte ...
... pioneering work by Heitler and London [2] on the hydrogen molecule in 1928 providing insight into, to quote Pauling, the Nature of the Chemical Bond [3]. However Quantum Chemistry is, at least in our opinion, more than the mere application of quantum mechanical principles to molecules and their inte ...
Follow Along Notes - Jackson County School System
... Calculations involving equilibrium How to solve Equilibrium Problems: 1. Start with a balanced Chemical Equation 2. Write down the amounts (either concentration or pressure units) in an ICE table. 3. Shift the equilibrium by subtracting and adding x to either side to the equation. 4. Solve for x us ...
... Calculations involving equilibrium How to solve Equilibrium Problems: 1. Start with a balanced Chemical Equation 2. Write down the amounts (either concentration or pressure units) in an ICE table. 3. Shift the equilibrium by subtracting and adding x to either side to the equation. 4. Solve for x us ...
Summer Study Assignment – Honors Chem 2/AP Chemistry
... 31. Write the electron configuration using the Noble Gas core method for californium. 32. Write a balanced equation for the following double replacement reactions: a. Calcium hydroxide (aq) + nitric acid (aq) b. Chromium (III) sulfite (aq) + sulfuric acid (aq) c. Zinc chloride (aq) + ammonium su ...
... 31. Write the electron configuration using the Noble Gas core method for californium. 32. Write a balanced equation for the following double replacement reactions: a. Calcium hydroxide (aq) + nitric acid (aq) b. Chromium (III) sulfite (aq) + sulfuric acid (aq) c. Zinc chloride (aq) + ammonium su ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.