Η - Knockhardy
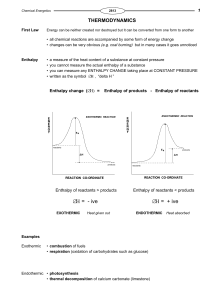
... as the strength of a bond also depends on its environment, MEAN values are quoted making a bond is an exothermic process as it is the opposite of breaking a bond for diatomic gases, the bond enthalpy is twice the enthalpy of atomisation the smaller the bond enthalpy, the weaker the bond and the easi ...
... as the strength of a bond also depends on its environment, MEAN values are quoted making a bond is an exothermic process as it is the opposite of breaking a bond for diatomic gases, the bond enthalpy is twice the enthalpy of atomisation the smaller the bond enthalpy, the weaker the bond and the easi ...
LaBrake, Fundamentals Diagnostic Questions
... 18. All of the following are statements from Dalton’s atomic hypothesis, except: a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. (correct) d) A compound is a specific combinati ...
... 18. All of the following are statements from Dalton’s atomic hypothesis, except: a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. (correct) d) A compound is a specific combinati ...
orange review book_2014_key
... compounds is that both (1) are heterogeneous (2) consist of two or more substances (3) are homogeneous (4) are heterogeneous 20. A dilute, aqueous potassium nitrate solution is best classified as a (1) homogeneous compound (2) homogeneous mixture (3) heterogeneous compound (4) heterogeneou ...
... compounds is that both (1) are heterogeneous (2) consist of two or more substances (3) are homogeneous (4) are heterogeneous 20. A dilute, aqueous potassium nitrate solution is best classified as a (1) homogeneous compound (2) homogeneous mixture (3) heterogeneous compound (4) heterogeneou ...
REVIEW and answers
... melting point (bottom right hand side of transition metals). As electrons become less delocalized the metals become harder, more brittle and conduct less well, but their melting and boiling points increase (top left hand side of transition metals). ...
... melting point (bottom right hand side of transition metals). As electrons become less delocalized the metals become harder, more brittle and conduct less well, but their melting and boiling points increase (top left hand side of transition metals). ...
semester i - Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University
... Spectroscopic ground states, Correlation, Orgel and Tanabe-Sugano diagrams for transition metal complexes (d1-d9 states), Selection rules, mechanism for break down of the selection rules, intensity of absorption, band width, spectra of d-d metal complexes of the type [M (H2O)] n+, spin free and spin ...
... Spectroscopic ground states, Correlation, Orgel and Tanabe-Sugano diagrams for transition metal complexes (d1-d9 states), Selection rules, mechanism for break down of the selection rules, intensity of absorption, band width, spectra of d-d metal complexes of the type [M (H2O)] n+, spin free and spin ...
Exam
... B) NaOH, strong base C) HCl, weak acid D) H2 CO3 , strong acid E) Ca(OH)2 , weak base 10) Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because A) it is a dilute solution. B) it is only slightly soluble in water. C) it cannot hold on to its hydroxide ions. D) it dissociates only slightly in water. E) it is comp ...
... B) NaOH, strong base C) HCl, weak acid D) H2 CO3 , strong acid E) Ca(OH)2 , weak base 10) Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because A) it is a dilute solution. B) it is only slightly soluble in water. C) it cannot hold on to its hydroxide ions. D) it dissociates only slightly in water. E) it is comp ...
Chemistry Worksheets
... These elements are rare, have high densities, and are used for various industrial purposes. __________________________ ...
... These elements are rare, have high densities, and are used for various industrial purposes. __________________________ ...
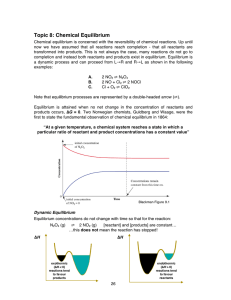
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... now we have assumed that all reactions reach completion - that all reactants are transformed into products. This is not always the case, many reactions do not go to completion and instead both reactants and products exist in equilibrium. Equilibrium is a dynamic process and can proceed from L→R and ...
... now we have assumed that all reactions reach completion - that all reactants are transformed into products. This is not always the case, many reactions do not go to completion and instead both reactants and products exist in equilibrium. Equilibrium is a dynamic process and can proceed from L→R and ...
G - Senger Science
... NO as a Catalyst for Ozone Destruction Explain why NO is a catalyst in the following two-step process that results in the depletion of ozone in the stratosphere: (1) NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) (2) O(g) + NO2(g) → NO(g) + O2(g) ...
... NO as a Catalyst for Ozone Destruction Explain why NO is a catalyst in the following two-step process that results in the depletion of ozone in the stratosphere: (1) NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) (2) O(g) + NO2(g) → NO(g) + O2(g) ...
Common Curriculum Map Discipline: Science Course: Chemistry
... - Lewis dot diagrams to show the creation of molecules - Monatomic vs polyatmoic ions - The criss-cross method to determine chemical formulas - Covalent bonds (single, double, and triple) - Polar vs nonpolar covalent bonds - Using electronegativities to determine the type of bond (ionic, polar coval ...
... - Lewis dot diagrams to show the creation of molecules - Monatomic vs polyatmoic ions - The criss-cross method to determine chemical formulas - Covalent bonds (single, double, and triple) - Polar vs nonpolar covalent bonds - Using electronegativities to determine the type of bond (ionic, polar coval ...
PDF File
... constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the pH (38). The affinity of S or P for the ribozyme is very high (see Figure 2B and Results), such that nonspecific losses to the tube walls are observed at the low ribozym ...
... constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the pH (38). The affinity of S or P for the ribozyme is very high (see Figure 2B and Results), such that nonspecific losses to the tube walls are observed at the low ribozym ...
2008 FALL Semester Midterm Examination For
... (e) In aqueous solution near-neutral pH, most of Glycine exists as a zwitterion as a result of an internal proton transfer. The very small K b arises from protonation of the carboxylate anion of the zwitterions, rather than the amine group, which is already protonated. ...
... (e) In aqueous solution near-neutral pH, most of Glycine exists as a zwitterion as a result of an internal proton transfer. The very small K b arises from protonation of the carboxylate anion of the zwitterions, rather than the amine group, which is already protonated. ...
1 - A-Level Chemistry
... no lone / spare / non-bonded pair of electrons only score M2 if M1 correct or give ‘H’ in M1 ...
... no lone / spare / non-bonded pair of electrons only score M2 if M1 correct or give ‘H’ in M1 ...
Integrated Chemical Systems
... 1B). The line shape and gvalue (1.9682) in the dry film are very similar to those observed with an immobilized Ti(II1)-porphyrin (Ti(F)(TPP)) crystal: Ti(II1) in MgO,Io or Ti(II1) in C H 3 0 D at low temperature." The variation in the line shape and in the intensity with the state of solvation indic ...
... 1B). The line shape and gvalue (1.9682) in the dry film are very similar to those observed with an immobilized Ti(II1)-porphyrin (Ti(F)(TPP)) crystal: Ti(II1) in MgO,Io or Ti(II1) in C H 3 0 D at low temperature." The variation in the line shape and in the intensity with the state of solvation indic ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Course Book for M.Sc. in Chemistry
... Objective: The objective of the course is to cater the need of R&D division of various chemical and pharmaceutical industries, by imparting detailed knowledge of important name reactions, oxidizing-reducing agents, selective organometalic reagents used in organic synthesis and their industrial appli ...
... Objective: The objective of the course is to cater the need of R&D division of various chemical and pharmaceutical industries, by imparting detailed knowledge of important name reactions, oxidizing-reducing agents, selective organometalic reagents used in organic synthesis and their industrial appli ...
Chap 3 - HCC Learning Web
... when the question is given as a description. For instance, the above question can be given as “Balance the equation when butane gas reacts with oxygen gas (combustion or burning)” or “write a balanced chemical equation when butane reacts with oxygen”. Balancing equation is a very, very important qu ...
... when the question is given as a description. For instance, the above question can be given as “Balance the equation when butane gas reacts with oxygen gas (combustion or burning)” or “write a balanced chemical equation when butane reacts with oxygen”. Balancing equation is a very, very important qu ...
Chemical Reaction Equations
... Predicted value: 2AgNO3(aq) + Na2CrO7(aq) Ag2CrO7(s) +2NaNO3(aq) ...
... Predicted value: 2AgNO3(aq) + Na2CrO7(aq) Ag2CrO7(s) +2NaNO3(aq) ...
Word Pro
... This is the contents of a Quiz 1 from a few years ago in the days of Chemistry 1000. (It has been reformatted to save paper) Answer ALL of the questions in the spaces provided. The mark that you obtain for this test will be used in calculating your final grade for the course. 1. Name the following c ...
... This is the contents of a Quiz 1 from a few years ago in the days of Chemistry 1000. (It has been reformatted to save paper) Answer ALL of the questions in the spaces provided. The mark that you obtain for this test will be used in calculating your final grade for the course. 1. Name the following c ...
Chemistry – 5071
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
... on the understanding and application of scientific concepts and principles. This approach has been adopted in recognition of the need of students to develop skills that will be of long term value in an increasing technological world rather than focusing on large quantities of actual material which m ...
Kinetics Simulations of the Neutralizing Capacity of Silicate Minerals
... of silicate mineral dissolution relative to rates of abiotic pyrite oxidation by dissolved O2 the extent to which standard silicate rock types could potentially provide acid neutralization. Biotic processes involved in pyrite oxidation were not considered because they become important primarily in s ...
... of silicate mineral dissolution relative to rates of abiotic pyrite oxidation by dissolved O2 the extent to which standard silicate rock types could potentially provide acid neutralization. Biotic processes involved in pyrite oxidation were not considered because they become important primarily in s ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... Chemistry comprises two related but distinct activities: (i) the quest for an understanding of matter and material change, (ii) the utilization of material change for human ends. Ideally, the first activity provides the necessary know-how for the pursuit of the second, but in practice, the help it c ...
... Chemistry comprises two related but distinct activities: (i) the quest for an understanding of matter and material change, (ii) the utilization of material change for human ends. Ideally, the first activity provides the necessary know-how for the pursuit of the second, but in practice, the help it c ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... is so slow that most limestone formations remain unreacted for thousands of years. Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a mov ...
... is so slow that most limestone formations remain unreacted for thousands of years. Why, then, does it take place rapidly at 1200 °C? Similarly, why does the combustion of gasoline take place more quickly when the fuel air mixture in a cylinder of your car is compressed into a smaller volume by a mov ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
... a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: ...
... a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.