Here
... (iii) electrons are set free within a lattice of positive ions A chemical reaction of oxygen requires breaking the oxygen‐oxygen double bond, and generally forming other bonds. As such, the propensity of oxygen to react depends on the strength of the O=O bond, as well as the strength of bonds ...
... (iii) electrons are set free within a lattice of positive ions A chemical reaction of oxygen requires breaking the oxygen‐oxygen double bond, and generally forming other bonds. As such, the propensity of oxygen to react depends on the strength of the O=O bond, as well as the strength of bonds ...
CHAPTER 19 TRANSITION METALS AND COORDINATION
... Test tube 1: Added Cl− reacts with Ag+ to form a silver chloride precipitate. The net ionic equation is Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq) → AgCl(s). Test tube 2: Added NH3 reacts with Ag+ ions to form a soluble complex ion Ag(NH3)2+. As this complex ion forms, Ag+ is removed from solution, which causes the AgCl(s) ...
... Test tube 1: Added Cl− reacts with Ag+ to form a silver chloride precipitate. The net ionic equation is Ag+(aq) + Cl−(aq) → AgCl(s). Test tube 2: Added NH3 reacts with Ag+ ions to form a soluble complex ion Ag(NH3)2+. As this complex ion forms, Ag+ is removed from solution, which causes the AgCl(s) ...
Nature of Materials in Serum That Interfere inthe Glucose Oxidase
... To test Mode 3, we increased the amount of peroxidase-o- dianisidine reagent in a series of solutions, uric acid and H202 being held constant. The resulting absorbance increased correspondingly, as shown in the second column of Table 2, indicating that uric acid interferes by Mode 3. The nonlinear i ...
... To test Mode 3, we increased the amount of peroxidase-o- dianisidine reagent in a series of solutions, uric acid and H202 being held constant. The resulting absorbance increased correspondingly, as shown in the second column of Table 2, indicating that uric acid interferes by Mode 3. The nonlinear i ...
Ch 16 Power Point
... combustion of one mole of a substance is called the enthalpy of combustion of the substance. • Enthalpy of combustion is defined in terms of one mole of reactant, whereas the enthalpy of formation is defined in terms of one mole of product. • ∆H with a subscripted c, ∆Hc, refers specifically to enth ...
... combustion of one mole of a substance is called the enthalpy of combustion of the substance. • Enthalpy of combustion is defined in terms of one mole of reactant, whereas the enthalpy of formation is defined in terms of one mole of product. • ∆H with a subscripted c, ∆Hc, refers specifically to enth ...
chemistry sp.indd
... syllabus that will be examined in 2010, 2011 and 2012. The purpose of these materials is to provide Centres with a reasonable idea of the general shape and character of the planned question papers in advance of the first operational examination. If there are any changes to the syllabus CIE will writ ...
... syllabus that will be examined in 2010, 2011 and 2012. The purpose of these materials is to provide Centres with a reasonable idea of the general shape and character of the planned question papers in advance of the first operational examination. If there are any changes to the syllabus CIE will writ ...
Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic
... products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative electrochemical cells have reaction times of tens of ...
... products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative electrochemical cells have reaction times of tens of ...
Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic
... products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative electrochemical cells have reaction times of tens of ...
... products in briefer reaction times, and at higher concentrations, when compared with electrolytic preparations. Except for thin-layer electrochemical cells,7a,b which are very limited in the quantities of reagent that can be produced, preparative electrochemical cells have reaction times of tens of ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions 1
... 103. One way of obtaining pure sodium carbonate is through the decomposition of the mineral trona, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O(s) → 5Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) When 1.00 metric ton (1 × 103 kg) of trona is decomposed, 0.74 metric ton of Na2CO3 is recovered. What is the percent yield ...
... 103. One way of obtaining pure sodium carbonate is through the decomposition of the mineral trona, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O(s) → 5Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) When 1.00 metric ton (1 × 103 kg) of trona is decomposed, 0.74 metric ton of Na2CO3 is recovered. What is the percent yield ...
Contents - MCAT Prep Course
... Reducing agent undergoes oxidation (most easily oxidized = strongest reducing agent) From A+ + B → A + B+ B can oxidize to B+, ∴ B is a stronger reducing agent than A. From A+ + C → no reaction C cannot oxidize to C+ ∴ A is a stronger reducing agent than C. From 2 B+ + D → 2B + D2+ D can oxidize to ...
... Reducing agent undergoes oxidation (most easily oxidized = strongest reducing agent) From A+ + B → A + B+ B can oxidize to B+, ∴ B is a stronger reducing agent than A. From A+ + C → no reaction C cannot oxidize to C+ ∴ A is a stronger reducing agent than C. From 2 B+ + D → 2B + D2+ D can oxidize to ...
CHM203 - National Open University of Nigeria
... organic compounds and for making the general assessment of the purity of these compounds. Pure crystalline solids have sharp melting points and they melt over a temperature range of 1o or less. In contrast to this, impure crystalline solids melt over wider ranges of temperatures. In a crystalline so ...
... organic compounds and for making the general assessment of the purity of these compounds. Pure crystalline solids have sharp melting points and they melt over a temperature range of 1o or less. In contrast to this, impure crystalline solids melt over wider ranges of temperatures. In a crystalline so ...
Problem 28. TUNNELING IN CHEMISTRY
... » in the «Journal of the Russian Chemical Society». In that article Mendeleev described in detail the properties of three unknown elements that were ekaboron (Eb), ekaaluminum (Ea), and ekasilicon (Es). All of them were discovered in the next 15 years. ...
... » in the «Journal of the Russian Chemical Society». In that article Mendeleev described in detail the properties of three unknown elements that were ekaboron (Eb), ekaaluminum (Ea), and ekasilicon (Es). All of them were discovered in the next 15 years. ...
File
... 1. All graphs should have a descriptive title (“Graph” is not a title) and a label. e.g. – Graph A: Density of Solutions with Varying Sugar Concentrations. 2. Both the vertical and horizontal axes should both have labels and units clearly marked. Use a ruler to draw the axes. 3. The scales chosen sh ...
... 1. All graphs should have a descriptive title (“Graph” is not a title) and a label. e.g. – Graph A: Density of Solutions with Varying Sugar Concentrations. 2. Both the vertical and horizontal axes should both have labels and units clearly marked. Use a ruler to draw the axes. 3. The scales chosen sh ...
2 - mrs. leinweber`s wiki
... There are scientific rules for putting elements together just as there are spelling rules for putting letters together. There are rules for how compounds may react just as there are grammatical rules for how words interact ...
... There are scientific rules for putting elements together just as there are spelling rules for putting letters together. There are rules for how compounds may react just as there are grammatical rules for how words interact ...
AP Chemistry Lab Manual
... 1. All graphs should have a descriptive title (“Graph” is not a title) and a label. e.g. – Graph A: Density of Solutions with Varying Sugar Concentrations. 2. Both the vertical and horizontal axes should both have labels and units clearly marked. Use a ruler to draw the axes. 3. The scales chosen sh ...
... 1. All graphs should have a descriptive title (“Graph” is not a title) and a label. e.g. – Graph A: Density of Solutions with Varying Sugar Concentrations. 2. Both the vertical and horizontal axes should both have labels and units clearly marked. Use a ruler to draw the axes. 3. The scales chosen sh ...
WJEC Eduqas A Level Chemistry specification
... that learners must demonstrate a holistic understanding of the links between different areas of content. In practice this means that questions set in any component may require learners to draw upon knowledge from other parts of the specification. Each topic area includes an overview outlining the co ...
... that learners must demonstrate a holistic understanding of the links between different areas of content. In practice this means that questions set in any component may require learners to draw upon knowledge from other parts of the specification. Each topic area includes an overview outlining the co ...
9.5. Combined Methods: Electrochemical
... There are other examples in which analytical determinations have been enhanced with the use of the electrochemically oxidized surface: 1) the determination of chlorophenols (63); and the determination of sulfur-containing organic compounds (64, 65). In the latter case, the negatively charged surface ...
... There are other examples in which analytical determinations have been enhanced with the use of the electrochemically oxidized surface: 1) the determination of chlorophenols (63); and the determination of sulfur-containing organic compounds (64, 65). In the latter case, the negatively charged surface ...
19_Worked_Examples
... (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transferred from the hotter object to the colder one. (Section 5.1) Thus, heat is transferred from the hot metal to the cooler water. The final temperature, after the metal and water ach ...
... (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transferred from the hotter object to the colder one. (Section 5.1) Thus, heat is transferred from the hot metal to the cooler water. The final temperature, after the metal and water ach ...
Order date : 24-07-2010
... Dissymmetry, asymmetry and chirality- simple and alternating axis of symmetry- Conditions for optical activity, Isotopic asymmetric variation and specific rotation of the same compound in sign and magnitude under different conditions. Relative and absolute configurations. Sequence rule– R and S nota ...
... Dissymmetry, asymmetry and chirality- simple and alternating axis of symmetry- Conditions for optical activity, Isotopic asymmetric variation and specific rotation of the same compound in sign and magnitude under different conditions. Relative and absolute configurations. Sequence rule– R and S nota ...
noble gases
... 32. Cuprous and cupric oxides find use in the manufacture of a. Paints b. medicinal preparations c Special steels d. c. d coloured glasses Ans : d Cuprous oxides provides red colour and cupric oxide provides blue green colour to glass Vikasana - CET 2012 ...
... 32. Cuprous and cupric oxides find use in the manufacture of a. Paints b. medicinal preparations c Special steels d. c. d coloured glasses Ans : d Cuprous oxides provides red colour and cupric oxide provides blue green colour to glass Vikasana - CET 2012 ...
chapter twenty-one transition metals and coordination chemistry
... different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 21.27 for the tetrahedral crystal field diagram. Notice that the orbitals are reverse of that i ...
... different. The tetrahedrally oriented ligands point differently in relationship to the d-orbitals than do the octahedrally oriented ligands. Plus, we have more ligands in an octahedral complex. See Figure 21.27 for the tetrahedral crystal field diagram. Notice that the orbitals are reverse of that i ...
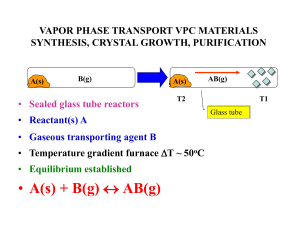
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... • Exothermic • W(s) + 2H2O(g) + 3I2(g) (T2 1000oC) (T1 800oC) WO2I2 (g) + 4HI(g) • The antithetical nature of these two reactions allows W/WO2 mixtures which often form together to be separated at different ends of the gradient reactor using H2O/I2 as the VPT reagents ...
... • Exothermic • W(s) + 2H2O(g) + 3I2(g) (T2 1000oC) (T1 800oC) WO2I2 (g) + 4HI(g) • The antithetical nature of these two reactions allows W/WO2 mixtures which often form together to be separated at different ends of the gradient reactor using H2O/I2 as the VPT reagents ...
chap-4-atomic-weights
... The problem with using the above method to determine the relative weights of atoms was that there was no way to tell if water was really HO or H2O or HO2. Dalton claimed that the tendency of things to vaporize probably meant that atoms repelled each other - so no more would stick together than were ...
... The problem with using the above method to determine the relative weights of atoms was that there was no way to tell if water was really HO or H2O or HO2. Dalton claimed that the tendency of things to vaporize probably meant that atoms repelled each other - so no more would stick together than were ...
379 - FTP
... Formula: H2S; MW 34.08 Synonyms: sulfur hydride; sulfureted hydrogen Occurrence and Uses Hydrogen sulfide occurs in natural gas. It also is found in many sewer gases. It is a by-product of many industrial processes. Trace amounts of dissolved H2S are found in wastewaters in equilibrium with dissolve ...
... Formula: H2S; MW 34.08 Synonyms: sulfur hydride; sulfureted hydrogen Occurrence and Uses Hydrogen sulfide occurs in natural gas. It also is found in many sewer gases. It is a by-product of many industrial processes. Trace amounts of dissolved H2S are found in wastewaters in equilibrium with dissolve ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.