Key Words Questions and Problems
... formed. The amount of product obtained in a reaction (the actual yield) may be less than the maximum possible amount (the theoretical yield). The ratio of the two multiplied by 100 percent is expressed as the percent yield. ...
... formed. The amount of product obtained in a reaction (the actual yield) may be less than the maximum possible amount (the theoretical yield). The ratio of the two multiplied by 100 percent is expressed as the percent yield. ...
Recycling and Chemical Mathematics
... vast majority of these atoms have existed as parts of our planet for billions of years. We can manipulate them physically and chemically to suit our needs, but what is already here is all that we can use. Materially, we have a virtually closed system, meaning one that does not receive matter from an ...
... vast majority of these atoms have existed as parts of our planet for billions of years. We can manipulate them physically and chemically to suit our needs, but what is already here is all that we can use. Materially, we have a virtually closed system, meaning one that does not receive matter from an ...
Sustainable Oxidation Catalysis for Synthesis
... i.e. sunlight as irradiation source for TiO2 photocatalysis and photo-Fenton. Therefore, low cost solar AOPs systems suitable to be combined with biological processes are innovative options in this area. The solar approach is a logical consequence for AOP cost saving to be applied especially in the ...
... i.e. sunlight as irradiation source for TiO2 photocatalysis and photo-Fenton. Therefore, low cost solar AOPs systems suitable to be combined with biological processes are innovative options in this area. The solar approach is a logical consequence for AOP cost saving to be applied especially in the ...
Word - icho39.chem.msu.ru
... Let nH 2 = nH2 H2 , where H 2 is the number of moles of hydrogen added to the system. Since H 2 is small, H2 ...
... Let nH 2 = nH2 H2 , where H 2 is the number of moles of hydrogen added to the system. Since H 2 is small, H2 ...
Lessons 9
... Surroundings: All matter around the system that is capable of absorbing or releasing thermal energy. Consider the following reaction taking place in your body cells: C6H12O6 + 6O2 Æ 6H2O +2CO2 + energy The molecules (glucose, oxygen, water, and carbon dioxide are the chemical system, while the surro ...
... Surroundings: All matter around the system that is capable of absorbing or releasing thermal energy. Consider the following reaction taking place in your body cells: C6H12O6 + 6O2 Æ 6H2O +2CO2 + energy The molecules (glucose, oxygen, water, and carbon dioxide are the chemical system, while the surro ...
Physical Chemistry 3: — Chemical Kinetics - Christian
... References to original publications and other recommended literature for further reading are given at the end of each Chapter. ...
... References to original publications and other recommended literature for further reading are given at the end of each Chapter. ...
enthalpy changes
... The amount of energy released from a chemical reaction is affected to the number of moles of reactant or product. If given the mass of reactant or product, the enthalpy change (∆H in kJ) ...
... The amount of energy released from a chemical reaction is affected to the number of moles of reactant or product. If given the mass of reactant or product, the enthalpy change (∆H in kJ) ...
Practice Exam I FR Answers and Explanations
... 7. Extra Practice Essay ---Electrochemistry—8 points total ...
... 7. Extra Practice Essay ---Electrochemistry—8 points total ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... In Aristotle's opinion, men were bigger and stronger than women; therefore, it was logical to him that men would have more teeth than women. Thus, Aristotle concluded it was a true fact that men had more teeth than women. Apparently, it never entered his mind to actually look into the mouths of both ...
... In Aristotle's opinion, men were bigger and stronger than women; therefore, it was logical to him that men would have more teeth than women. Thus, Aristotle concluded it was a true fact that men had more teeth than women. Apparently, it never entered his mind to actually look into the mouths of both ...
Syllabus Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level
... questions testing such skills may be based on information which is unfamiliar to the candidate. In answering such questions, candidates are required to use principles and concepts that are within the syllabus and apply them in a logical, reasoned or deductive manner to a novel situation. Questions t ...
... questions testing such skills may be based on information which is unfamiliar to the candidate. In answering such questions, candidates are required to use principles and concepts that are within the syllabus and apply them in a logical, reasoned or deductive manner to a novel situation. Questions t ...
Topic 5 Energetics File
... gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indicate a degree of covalent character. Electron affinity: Enthalpy change when an electron ...
... gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indicate a degree of covalent character. Electron affinity: Enthalpy change when an electron ...
Class XI Physical Chemistry Short note
... and protons. Since electrons have negligible mass, the entire mass of the atom was regarded as the mass of the proton only. Each proton has a mass of 1.67x 10-24 g which is taken as 1 unit mass. In 1920, Rutherford found that except for the hydrogen atom, the atomic masses of no other atom could be ...
... and protons. Since electrons have negligible mass, the entire mass of the atom was regarded as the mass of the proton only. Each proton has a mass of 1.67x 10-24 g which is taken as 1 unit mass. In 1920, Rutherford found that except for the hydrogen atom, the atomic masses of no other atom could be ...
Sample Exercise 19.1 Identifying Spontaneous Processes
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
exercise on Chapter 13 - Louisiana Tech University
... reactants cause the equilibrium to shift (right) to produce more products. 3) Removing reactants cause the equilibrium to shift (left) to produce more reactants. 4) Removing products cause the equilibrium to shift (right) to produce more products. 5) Increasing temperature of exothermic (Hrxn = neg ...
... reactants cause the equilibrium to shift (right) to produce more products. 3) Removing reactants cause the equilibrium to shift (left) to produce more reactants. 4) Removing products cause the equilibrium to shift (right) to produce more products. 5) Increasing temperature of exothermic (Hrxn = neg ...
19 BROWN Chemical Thermodynamics PPTSExercise
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
... Plan: In part (a) we can make this prediction by determining the sign of ΔS° for the reaction and then using that information to analyze Equation 19.12. In part (b) we need to calculate ΔH° and ΔS° for the reaction by using the data in Appendix C. We can then use Equation 19.12 to calculate ΔG°. Sol ...
Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective
... Ionic liquids are a new class of solvents entirely composed of ions. Their use as an environmentally friendly alternative for conventional solvents has gained much attention recently [12–14]. Esterification reactions have been extensively investigated in many ionic liquids so far, because of the imp ...
... Ionic liquids are a new class of solvents entirely composed of ions. Their use as an environmentally friendly alternative for conventional solvents has gained much attention recently [12–14]. Esterification reactions have been extensively investigated in many ionic liquids so far, because of the imp ...
How to Use Reaction Stoichiometry
... Figure 4.6 (a) When an octane molecule undergoes complete combustion, it forms carbon dioxide and water: one CO2 molecule is formed for each carbon atom present (yellow arrows). (b) However, in a limited supply of oxygen, some of the carbon atoms end up as carbon monoxide molecules, CO, so the yiel ...
... Figure 4.6 (a) When an octane molecule undergoes complete combustion, it forms carbon dioxide and water: one CO2 molecule is formed for each carbon atom present (yellow arrows). (b) However, in a limited supply of oxygen, some of the carbon atoms end up as carbon monoxide molecules, CO, so the yiel ...
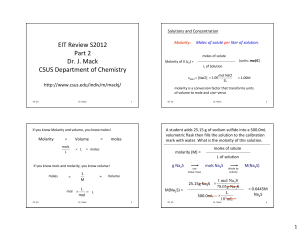
EIT Review S2012 Part 2 Dr. J. Mack CSUS Department of Chemistry
... absorbs 255 cal of energy. J The initial temperature of The specific heat ...
... absorbs 255 cal of energy. J The initial temperature of The specific heat ...
AP® Chemistry
... organizations. Each year, the College Board serves seven million students and their parents, 23,000 high schools, and 3,500 colleges through major programs and services in college admissions, guidance, assessment, financial aid, enrollment, and teaching and learning. Among its best-known programs ar ...
... organizations. Each year, the College Board serves seven million students and their parents, 23,000 high schools, and 3,500 colleges through major programs and services in college admissions, guidance, assessment, financial aid, enrollment, and teaching and learning. Among its best-known programs ar ...
AP® Chemistry
... organizations. Each year, the College Board serves seven million students and their parents, 23,000 high schools, and 3,500 colleges through major programs and services in college admissions, guidance, assessment, financial aid, enrollment, and teaching and learning. Among its best-known programs ar ...
... organizations. Each year, the College Board serves seven million students and their parents, 23,000 high schools, and 3,500 colleges through major programs and services in college admissions, guidance, assessment, financial aid, enrollment, and teaching and learning. Among its best-known programs ar ...
CHAPTER 20 METALLURGY AND THE CHEMISTRY OF METALS
... Table 19.1 of the text shows that Pb, Fe, Co, Zn are more easily oxidized (stronger reducing agents) than copper. The Ag, Au, and Pt are harder to oxidize and will not dissolve. Would you throw away the sludge if you were in charge of the copper refining plant? Why is it still profitable to manufact ...
... Table 19.1 of the text shows that Pb, Fe, Co, Zn are more easily oxidized (stronger reducing agents) than copper. The Ag, Au, and Pt are harder to oxidize and will not dissolve. Would you throw away the sludge if you were in charge of the copper refining plant? Why is it still profitable to manufact ...
EXAM IR - Academics
... CHEM 103 SEPTEMBER 26 2001 Page 6 of 14 8. If the nucleus of an atom were about the size of a softball, the electrons, proportionally, would likely be found: a) Within the softball b) Within a foot of the nucleus; c) Somewhere in this room;; d) Somewhere between here and Winooski (about 2-3 km). e) ...
... CHEM 103 SEPTEMBER 26 2001 Page 6 of 14 8. If the nucleus of an atom were about the size of a softball, the electrons, proportionally, would likely be found: a) Within the softball b) Within a foot of the nucleus; c) Somewhere in this room;; d) Somewhere between here and Winooski (about 2-3 km). e) ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.

















![Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017897985_1-047f9869d5604c115b21339541ccfffe-300x300.png)