Chemistry 106: General Chemistry
... I. Sodium (Na), has a larger atomic radius than Cesium (Cs). II. The first ionization energy of an atom generally increases moving left to right across a period because the effective nuclear charge, Zeff, increases in that direction. III. An atom of Phosphorus (P), releases more energy (becomes more ...
... I. Sodium (Na), has a larger atomic radius than Cesium (Cs). II. The first ionization energy of an atom generally increases moving left to right across a period because the effective nuclear charge, Zeff, increases in that direction. III. An atom of Phosphorus (P), releases more energy (becomes more ...
Chemistry of Life
... - Atom – smallest particle of matter that can exist and still have the properties of that particular kind of matter. - 3 Parts make up an atom 1. proton – positive charged particle Affects the IDENTITY of element 2. electron – negative charged particle affects reactivity 3. neutron – neutral/ no cha ...
... - Atom – smallest particle of matter that can exist and still have the properties of that particular kind of matter. - 3 Parts make up an atom 1. proton – positive charged particle Affects the IDENTITY of element 2. electron – negative charged particle affects reactivity 3. neutron – neutral/ no cha ...
Krebs Cycle Puzzle: Concept Map of Oxidation/Reduction Reactions:
... Krebs Cycle Puzzle: Concept Map of Oxidation/Reduction Reactions: Pyruvate is converted Acetyl CoA by the removal of one CO2 group. 1. The two carbon Acetyl CoA is added to a 4 carbon compound producing a 6 carbon compound called citric acid (citrate). A separate reaction isomerizes the citrate to i ...
... Krebs Cycle Puzzle: Concept Map of Oxidation/Reduction Reactions: Pyruvate is converted Acetyl CoA by the removal of one CO2 group. 1. The two carbon Acetyl CoA is added to a 4 carbon compound producing a 6 carbon compound called citric acid (citrate). A separate reaction isomerizes the citrate to i ...
Atomic Theory PPT
... Atomic Mass o The atomic mass of an element represents the average mass of all the isotopes found in nature. No element exists with only one possible isotope. Hydrogen has the smallest number of isotopes: 1H protium, 2H deuterium, 3H tritium. Its atomic mass is ...
... Atomic Mass o The atomic mass of an element represents the average mass of all the isotopes found in nature. No element exists with only one possible isotope. Hydrogen has the smallest number of isotopes: 1H protium, 2H deuterium, 3H tritium. Its atomic mass is ...
Section 1 - TeacherWeb
... FIGURE 10Isotopes Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain 6 protons and 6 electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon-12 is the most common isotope. An isotope is identified by its mass number, which is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most commo ...
... FIGURE 10Isotopes Atoms of all isotopes of carbon contain 6 protons and 6 electrons, but they differ in their number of neutrons. Carbon-12 is the most common isotope. An isotope is identified by its mass number, which is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The most commo ...
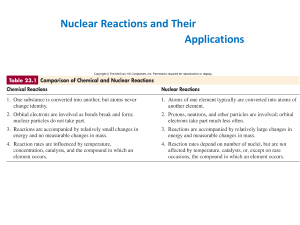
Nuclear Reactions and Their Applications
... Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable. Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special s ...
... Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable. Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special s ...
OC 583- ISOTOPE BIGEOCHEMISTRY
... equal number of neutrons and protons (e.g. 12C6, 14N7, 16O8, 32S16) (Fig. 6) -but not always: (e.g. 7Li3, 9Be4) 3. Since isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons this means isotopes have same chemical behavior, i.e., all isotopic species enter into same chemical reactions and form the ...
... equal number of neutrons and protons (e.g. 12C6, 14N7, 16O8, 32S16) (Fig. 6) -but not always: (e.g. 7Li3, 9Be4) 3. Since isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons this means isotopes have same chemical behavior, i.e., all isotopic species enter into same chemical reactions and form the ...
Addition Polymerisation - Dover College Science
... different types of nylon depending on the nature of those chains. Nylon-6,6 is made from two monomers each of which contain ___ carbon atoms . One of the monomers is a 6 carbon acid with a -COOH group at each end, __________ acid. The other monomer is a 6 carbon chain with an amino group, NH2, at ea ...
... different types of nylon depending on the nature of those chains. Nylon-6,6 is made from two monomers each of which contain ___ carbon atoms . One of the monomers is a 6 carbon acid with a -COOH group at each end, __________ acid. The other monomer is a 6 carbon chain with an amino group, NH2, at ea ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... terms of relative charge and mass. • Describe the structure of the atom, including the locations of the subatomic particles. ...
... terms of relative charge and mass. • Describe the structure of the atom, including the locations of the subatomic particles. ...
Grades 9-12 Chemistry California Content Standards
... b. the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions: change in mass (calculated by E=mc_) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. c. many naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioactive, as are isotopes formed i ...
... b. the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions: change in mass (calculated by E=mc_) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. c. many naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioactive, as are isotopes formed i ...
Chemistry - Gorman Learning Center
... e. the nucleus is much smaller in size than the atom yet contains most of its mass. f.* how to use the Periodic Table to identify the lanthanides and actinides, and transactinide elements, and know that the transuranium elements were man made. g.* how to relate the position of an element in the peri ...
... e. the nucleus is much smaller in size than the atom yet contains most of its mass. f.* how to use the Periodic Table to identify the lanthanides and actinides, and transactinide elements, and know that the transuranium elements were man made. g.* how to relate the position of an element in the peri ...
Summarised Notes
... (Molecules formed by the combination of two atoms are called di-atomic molecules, eg O2, N2, Cl2, CO. Molecules consisting of three atoms are called triatomic molecules, eg O3, CO2. Molecules consisting of four or more atoms are called polyatomic molecules, eg P4, S8, NH3) ...
... (Molecules formed by the combination of two atoms are called di-atomic molecules, eg O2, N2, Cl2, CO. Molecules consisting of three atoms are called triatomic molecules, eg O3, CO2. Molecules consisting of four or more atoms are called polyatomic molecules, eg P4, S8, NH3) ...
Matter Unit Study Guide Phases of Matter
... Compounds are substances made of two or more elements which combine in a chemical reaction. The smallest unit of a compound is a molecule Chemical formulas for used to show the different elements that make up a compound. The letters tell you which elements are in the compound. The numbers tell you h ...
... Compounds are substances made of two or more elements which combine in a chemical reaction. The smallest unit of a compound is a molecule Chemical formulas for used to show the different elements that make up a compound. The letters tell you which elements are in the compound. The numbers tell you h ...
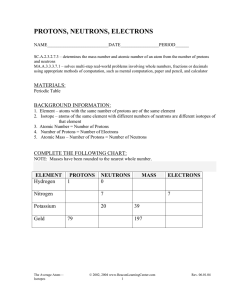
protons, neutrons, electrons
... 2. Place the 50 lima beans on the platform of the balance and determine the mass to the nearest tenth of a gram. 3. Record this mass on your Data Chart. (See below) 4. Now find the average mass of these 50 lima beans and record on the Data Chart. Average mass = mass of beans divided by number of bea ...
... 2. Place the 50 lima beans on the platform of the balance and determine the mass to the nearest tenth of a gram. 3. Record this mass on your Data Chart. (See below) 4. Now find the average mass of these 50 lima beans and record on the Data Chart. Average mass = mass of beans divided by number of bea ...
Project 2 - University of South Florida
... genetic content can lead to change from the action of several biochemical reactions. Mutation can lead to changes in enzyme expression. This may alter the mitochondrial function by changing fluxes of important metabolic reactions ...
... genetic content can lead to change from the action of several biochemical reactions. Mutation can lead to changes in enzyme expression. This may alter the mitochondrial function by changing fluxes of important metabolic reactions ...
A Mad Scientist`s Chemistry Presentation
... • A chemical change is also called a chemical reaction. • During a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds form. • However, the total amount of energy and matter does not change. • Scientists represent chemical reactions using equations like the one below: Reactants Product ...
... • A chemical change is also called a chemical reaction. • During a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds form. • However, the total amount of energy and matter does not change. • Scientists represent chemical reactions using equations like the one below: Reactants Product ...
Carbon Compounds In Living Organisms
... *How many water molecules were liberated by condensation to produce the shorter polypeptide strand? Answer: 20 (1 water molecule between each amino acid that is bonded) ...
... *How many water molecules were liberated by condensation to produce the shorter polypeptide strand? Answer: 20 (1 water molecule between each amino acid that is bonded) ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
CH. 3 - STOICHIOMETRY: CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS I. Molecular
... A. molecular mass - sum of masses of atoms represented in a molecular formula B. formula mass - sum of masses of atoms or ions present in a formula unit II. The Mole and Avogadro’s Number A. mole (mol) - amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 12g ...
... A. molecular mass - sum of masses of atoms represented in a molecular formula B. formula mass - sum of masses of atoms or ions present in a formula unit II. The Mole and Avogadro’s Number A. mole (mol) - amount of substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in exactly 12g ...
A New Deoxyisoaustamide Derivative from the Marine
... shift value of the methoxy group was far shifted to up-field (δH 1.44), whereas the carbon chemical shift value slightly up-field shifted (δC 47.5). The 1H and 13C NMR data of the diketopiperazine moiety of 3 were found to be similar with those of the similar partial structure, verpacamide D, except ...
... shift value of the methoxy group was far shifted to up-field (δH 1.44), whereas the carbon chemical shift value slightly up-field shifted (δC 47.5). The 1H and 13C NMR data of the diketopiperazine moiety of 3 were found to be similar with those of the similar partial structure, verpacamide D, except ...
Ch. 2 – Bio Chem
... http://thescienceofeating.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Book-Fats-Butter-Oils-2.jpg ...
... http://thescienceofeating.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Book-Fats-Butter-Oils-2.jpg ...
Atomic mass
... • Define isotope and nuclide • Use atomic number, mass number, and charge to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an isotope or ion • Identify carbon-12 as the standard atom for measuring relative atomic mass • Determine the process to calculate atomic mass of an element ...
... • Define isotope and nuclide • Use atomic number, mass number, and charge to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an isotope or ion • Identify carbon-12 as the standard atom for measuring relative atomic mass • Determine the process to calculate atomic mass of an element ...
Slide 1 - Mrs. Reed Science Classes
... For the reaction represented by the equation Mg + 2HCl H2 + MgCl2, calculate the percentage yield of magnesium chloride if 100. g of magnesium react with excess hydrochloric acid to yield 330. g of magnesium chloride. a. 71.8% c. 81.6% b. 74.3% d. 84.2% ...
... For the reaction represented by the equation Mg + 2HCl H2 + MgCl2, calculate the percentage yield of magnesium chloride if 100. g of magnesium react with excess hydrochloric acid to yield 330. g of magnesium chloride. a. 71.8% c. 81.6% b. 74.3% d. 84.2% ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.