CHM562 Natural Products Spring 2011 Meets MWF @ 9 AM, II-307B
... Some journal articles and other course materials will be distributed; others will be available in the library or through interlibrary loan. You will also have access to recent issues of Journal of Natural Products and Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry through our laboratory subscription, ca ...
... Some journal articles and other course materials will be distributed; others will be available in the library or through interlibrary loan. You will also have access to recent issues of Journal of Natural Products and Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry through our laboratory subscription, ca ...
Carbon Compounds 2-3 Foldable Instructions
... & lipids. It turns red in the presence of fats & lipids. Benedict’s solution is an indicator solution for simple sugars. It changes from blue to yellow, orange or red. Iodine solution is an indicator solution for complex sugars. It changes from brown to blue ...
... & lipids. It turns red in the presence of fats & lipids. Benedict’s solution is an indicator solution for simple sugars. It changes from blue to yellow, orange or red. Iodine solution is an indicator solution for complex sugars. It changes from brown to blue ...
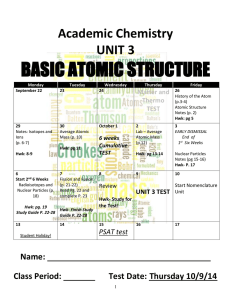
p Atomic Structure notes packet 14_15
... In nuclear fission reactions (also called radioactive decay), a neutron is aimed at the nucleus of a large, unstable atom, like uranium, thorium, or other radioactive elements. The extra mass of the neutron causes the radioactive nucleus to split apart, forming lighter elements, free neutrons, and g ...
... In nuclear fission reactions (also called radioactive decay), a neutron is aimed at the nucleus of a large, unstable atom, like uranium, thorium, or other radioactive elements. The extra mass of the neutron causes the radioactive nucleus to split apart, forming lighter elements, free neutrons, and g ...
Sample Exam #1 ( file)
... A. Unequal sharing of electrons leads to distinct areas of positive and negative charge in the molecule. B. Electrons are actually donated from one atom to another C. Transient attractions cause hydrophobic interactions D. More energy is used to make the bond, so there is more reduction ...
... A. Unequal sharing of electrons leads to distinct areas of positive and negative charge in the molecule. B. Electrons are actually donated from one atom to another C. Transient attractions cause hydrophobic interactions D. More energy is used to make the bond, so there is more reduction ...
ppt Sc10 Review Notes
... charges on the ions are the result of taking or giving eto go from formula to name: name of first ion, then brackets for charge if multivalent, then name for second ion i.e. first element ( ) second element-ide eg) AlCl3 = aluminum chloride ...
... charges on the ions are the result of taking or giving eto go from formula to name: name of first ion, then brackets for charge if multivalent, then name for second ion i.e. first element ( ) second element-ide eg) AlCl3 = aluminum chloride ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Using the periodic table on page 10 of this study guide, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? _______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius O or Ca? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius Ca or Ba? _____________ 4. Which elemen ...
... Using the periodic table on page 10 of this study guide, answer the following questions: 1. Which element stands alone in its family? _______________ 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius O or Ca? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius Ca or Ba? _____________ 4. Which elemen ...
Solutions - Dynamic Science
... The screws are too soft and will not support the window. Both the window frame and the screw will rust away. The screws will rust. The metal around the screw will corrode and the screw will fall out. ...
... The screws are too soft and will not support the window. Both the window frame and the screw will rust away. The screws will rust. The metal around the screw will corrode and the screw will fall out. ...
Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2220, Organic Chem II 1. Rank the
... 22. Which of these compounds best fits these data? It is soluble in water, and turns red litmus blue; has only one major IR band, at 2950 cm-1, and has the following 1H NMR spectrum: 2.7 ppm, 2H; 2.2 ppm, 6H; 1.0 ppm, 3H. A. N,N-dimethylethanamine B. propanoic acid C. 2-propanol D. 2-methylpropane ...
... 22. Which of these compounds best fits these data? It is soluble in water, and turns red litmus blue; has only one major IR band, at 2950 cm-1, and has the following 1H NMR spectrum: 2.7 ppm, 2H; 2.2 ppm, 6H; 1.0 ppm, 3H. A. N,N-dimethylethanamine B. propanoic acid C. 2-propanol D. 2-methylpropane ...
W. M. White Geochemistry Chapter 9: Stable Isotopes Chapter 9
... The elements interest in stable isotope geochemistry are H, Li, B, C, N, O, Si, S, and Cl. Of these, O, H, C and S are of the greatest interest. Most of these elements have several common characteristics: (1) They have low atomic mass. (2) The relative mass difference between their isotopes is large ...
... The elements interest in stable isotope geochemistry are H, Li, B, C, N, O, Si, S, and Cl. Of these, O, H, C and S are of the greatest interest. Most of these elements have several common characteristics: (1) They have low atomic mass. (2) The relative mass difference between their isotopes is large ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
Lecture note 3
... constitution as an element, compound, or mixture. Before we classify matter by its chemical constitution, we must first distinguish between physical and chemical change and between physical and chemical properties What is property? Any characteristic that can be used to describe or identify matter i ...
... constitution as an element, compound, or mixture. Before we classify matter by its chemical constitution, we must first distinguish between physical and chemical change and between physical and chemical properties What is property? Any characteristic that can be used to describe or identify matter i ...
Ex. 02 Answer
... d) Iron is an element. e) Nitrogen is an element. f) Concrete is a mixture of cement, stone chips, sand and water. 2 a) Sodium and chlorine are elements. Sodium chloride is a compound. b) Sodium chloride and sand are not chemically joined together. They can be separated by physical methods. Checkpoi ...
... d) Iron is an element. e) Nitrogen is an element. f) Concrete is a mixture of cement, stone chips, sand and water. 2 a) Sodium and chlorine are elements. Sodium chloride is a compound. b) Sodium chloride and sand are not chemically joined together. They can be separated by physical methods. Checkpoi ...
Dating Fossils and Rocks 5
... 1. How fast C-14 decays (measured in halflives - this is known: 5,730 years) 2. The starting amount of C-14 in the fossil We know number 1 How can we know how much C-14 was in an organism 5,000 years ago? ...
... 1. How fast C-14 decays (measured in halflives - this is known: 5,730 years) 2. The starting amount of C-14 in the fossil We know number 1 How can we know how much C-14 was in an organism 5,000 years ago? ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.1 - reich
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
... (g) means the substance is a gas (l) means the substance is a liquid (s) means the substance is a solid (aq) means the substance is aqueous Aqueous means dissolved in water, which does not necessarily mean the compound was a liquid. Ethanol and sugar both become aqueous, but only one of them was a s ...
Learning Outcomes for CHEM1001 in 2015
... 3. recognize that elements are labelled using their chemical symbol 4. explain the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures 5. explain the difference between allotropes and the physical state of an element 6. explain what atoms are and how they combine to form compounds 7. appreciate the ...
... 3. recognize that elements are labelled using their chemical symbol 4. explain the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures 5. explain the difference between allotropes and the physical state of an element 6. explain what atoms are and how they combine to form compounds 7. appreciate the ...
Unknown title - Sigma
... structural homogeneity and short-range order. In the next stage, 15N spectra and, in particular, (15N,13C) 2D data further report on molecular order and 1H bonding. In such correlation experiments, polarization transfer can either involve throughspace and through-bond interactions. The choice which ...
... structural homogeneity and short-range order. In the next stage, 15N spectra and, in particular, (15N,13C) 2D data further report on molecular order and 1H bonding. In such correlation experiments, polarization transfer can either involve throughspace and through-bond interactions. The choice which ...
Chapter 11 section 2 questions - the atom
... Electrons are the negatively charged particles found in the energy levels that surround the nucleus - this like the rings on a target! Electrons have a VERY small mass - almost inconsequential to the atomic mass. Electrons carry a negative charge and are held in place by the positively charged proto ...
... Electrons are the negatively charged particles found in the energy levels that surround the nucleus - this like the rings on a target! Electrons have a VERY small mass - almost inconsequential to the atomic mass. Electrons carry a negative charge and are held in place by the positively charged proto ...
2011-2012 Summer Packet - Tenafly Public Schools
... B Compounds: These are composed of two or more elements combined chemically in a very definite ratio (both by number of atoms and by mass of atoms). Compounds can be decomposed into simpler compounds or into elements, but this requires chemical methods such as reaction with acid, electrolysis, or th ...
... B Compounds: These are composed of two or more elements combined chemically in a very definite ratio (both by number of atoms and by mass of atoms). Compounds can be decomposed into simpler compounds or into elements, but this requires chemical methods such as reaction with acid, electrolysis, or th ...
MIDTERM REVIEW UNIT 1: Mass/Measurement
... 9. Each chemistry teacher provides 6 test tubes to each lab group. In each class there are 12 lab groups, and the teacher has four classes. There are a total of 5 chemistry teachers. ...
... 9. Each chemistry teacher provides 6 test tubes to each lab group. In each class there are 12 lab groups, and the teacher has four classes. There are a total of 5 chemistry teachers. ...
Metabolomics Research Core
... mathematical tools (e.g., Umetrics, Spotfire, SAS) to identify data trends that show the correlation of specific signals with the phenotypic response under investigation. Identified signals are mapped to biochemical pathways through the use of specialized software such as GeneGo, and expert biochemi ...
... mathematical tools (e.g., Umetrics, Spotfire, SAS) to identify data trends that show the correlation of specific signals with the phenotypic response under investigation. Identified signals are mapped to biochemical pathways through the use of specialized software such as GeneGo, and expert biochemi ...
Human Anatomy, Unit 1 Study Guide 1. Explain how anatomy and
... 12. Describe the physical basis and uses of the major medical imaging tools. 13. List the major energy forms and provide one example of how each energy form is used in the body. ...
... 12. Describe the physical basis and uses of the major medical imaging tools. 13. List the major energy forms and provide one example of how each energy form is used in the body. ...
Chemistry Chapter 4 (Due October 24) [Test
... c. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged. d. Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. ____ 38. Why do chemists use relative masses of atoms compared to a reference isotope rather than the actual masses of the atoms? a. The actual mass of an electron is very large compared to the actual ...
... c. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged. d. Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom. ____ 38. Why do chemists use relative masses of atoms compared to a reference isotope rather than the actual masses of the atoms? a. The actual mass of an electron is very large compared to the actual ...
chapter3 - AlvarezHChem
... a. sum all atoms of each type on a side, even if an element is in more than one substance b. work from left to right to stay organized c. if a polyatomic ion is present in the same form on both sides it can be counted as a unit rather than as individual elements d. look to balance H’s and O’s last i ...
... a. sum all atoms of each type on a side, even if an element is in more than one substance b. work from left to right to stay organized c. if a polyatomic ion is present in the same form on both sides it can be counted as a unit rather than as individual elements d. look to balance H’s and O’s last i ...
Nuclear Reactions - Kelso High School
... Mass number and atomic number are both conserved during this reaction. Even though the mass number is conserved, when the masses before and after the fission are compared accurately, there is a mass difference. The total mass before fission is greater than the total mass of the products. Einstein su ...
... Mass number and atomic number are both conserved during this reaction. Even though the mass number is conserved, when the masses before and after the fission are compared accurately, there is a mass difference. The total mass before fission is greater than the total mass of the products. Einstein su ...
Answer 2
... d) Iron is an element. e) Nitrogen is an element. f) Concrete is a mixture of cement, stone chips, sand and water. 2 a) Sodium and chlorine are elements. Sodium chloride is a compound. b) Sodium chloride and sand are not chemically joined together. They can be separated by physical methods. Checkpoi ...
... d) Iron is an element. e) Nitrogen is an element. f) Concrete is a mixture of cement, stone chips, sand and water. 2 a) Sodium and chlorine are elements. Sodium chloride is a compound. b) Sodium chloride and sand are not chemically joined together. They can be separated by physical methods. Checkpoi ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.