Ch 2 Bio All
... In nature, most elements are found combined with other elements in compounds. Defined: A chemical compound is a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. The physical and chemical properties of a compound are different from the elements from which ...
... In nature, most elements are found combined with other elements in compounds. Defined: A chemical compound is a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. The physical and chemical properties of a compound are different from the elements from which ...
chapter2
... • An example of an isotope symbol is 28 Ni. This symbol represents an isotope of nickel that contains 28 protons and 32 neutrons in the nucleus. • Isotopes are also represented by the notation: Name-A, where Name is the name of the element and A is the mass number of the isotope. • An example of thi ...
... • An example of an isotope symbol is 28 Ni. This symbol represents an isotope of nickel that contains 28 protons and 32 neutrons in the nucleus. • Isotopes are also represented by the notation: Name-A, where Name is the name of the element and A is the mass number of the isotope. • An example of thi ...
CHAPTER 3 - THE ATOM
... and the Law of Definite composition could only be explained if atoms existed. Wrote Dalton’s Atomic Theory, which was mostly right. 1. Matter is composed extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and ch ...
... and the Law of Definite composition could only be explained if atoms existed. Wrote Dalton’s Atomic Theory, which was mostly right. 1. Matter is composed extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible 3. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and ch ...
The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass ...
... No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: Relative atomic mass (Ar) is the average of the mass ...
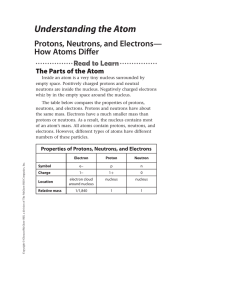
Understanding the Atom
... mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons You can determine any one of these three quantities if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example, to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. The mass numbe ...
... mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons You can determine any one of these three quantities if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example, to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. The mass numbe ...
Chemical Stoichiometry
... of the values. 4. Multiply each number by an integer to obtain all whole numbers. Copyright©2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
... of the values. 4. Multiply each number by an integer to obtain all whole numbers. Copyright©2000 by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. ...
Name_________________________ Date________
... The world population is currently 7 x 10 9people There are 3 x 1012 (3 000 000 000 000) many atoms in the small coin as there are people on the planet. 10 000 000 (1x 107) copper atoms lined up side by side would only be 1 cm. long. Individual atoms have been observed using scanning electron m ...
... The world population is currently 7 x 10 9people There are 3 x 1012 (3 000 000 000 000) many atoms in the small coin as there are people on the planet. 10 000 000 (1x 107) copper atoms lined up side by side would only be 1 cm. long. Individual atoms have been observed using scanning electron m ...
Matter Key
... chemical formula 3X Subscript : number of atoms of the element BEFORE it X2 Homogeneous Mixture vs. Heterogeneous Mixture – Homogeneous is spread evenly throughout, it is a mixture composed of more than one substance uniformly mixed (cake batter), while a heterogeneous mixture A mixture composed of ...
... chemical formula 3X Subscript : number of atoms of the element BEFORE it X2 Homogeneous Mixture vs. Heterogeneous Mixture – Homogeneous is spread evenly throughout, it is a mixture composed of more than one substance uniformly mixed (cake batter), while a heterogeneous mixture A mixture composed of ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table 2014
... Are these isotopes? If the blue spheres are the neutrons and the burgundy spheres are the protons, are these three items isotopes of an element? By the way, how many electrons does this atom have? ...
... Are these isotopes? If the blue spheres are the neutrons and the burgundy spheres are the protons, are these three items isotopes of an element? By the way, how many electrons does this atom have? ...
Is Mass Conserved?
... Mass of flask Mass of 50 ml of vinegar Mass of balloon Mass of 20 ml of baking soda Sum of all reactants before experiment After Experiment Mass of flask, balloon, and products after experiment (when you dump the baking soda into the flask and les the reaction happen, weigh what is left over.) ...
... Mass of flask Mass of 50 ml of vinegar Mass of balloon Mass of 20 ml of baking soda Sum of all reactants before experiment After Experiment Mass of flask, balloon, and products after experiment (when you dump the baking soda into the flask and les the reaction happen, weigh what is left over.) ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter
... Test-Taking Tip: Anticipate the Answer When you take a test, read the question slowly. Don’t look at the answer choices. Try to think of a possible answer for the question. Once you’ve thought of an answer, look at your choices. Do you see a match? Read the following question. Do not read the answer ...
... Test-Taking Tip: Anticipate the Answer When you take a test, read the question slowly. Don’t look at the answer choices. Try to think of a possible answer for the question. Once you’ve thought of an answer, look at your choices. Do you see a match? Read the following question. Do not read the answer ...
www.studyguide.pk
... Structural formulae do not show all of the isomers that may exist for a given molecular formula. Which two compounds each show different types of isomerism and what type of isomerism does each compound show? Identify each compound ...
... Structural formulae do not show all of the isomers that may exist for a given molecular formula. Which two compounds each show different types of isomerism and what type of isomerism does each compound show? Identify each compound ...
Biochemistry
... Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
... Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
Chemistry Topic III – The Atom
... d. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. e. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are ____________________, ____________________ or ______________________. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into ...
... d. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. e. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are ____________________, ____________________ or ______________________. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy
... the intensity of the transmitted beam is detected and recorded. Frequencies that are absorbed by the sample appear as peaks deviating from a baseline value. ...
... the intensity of the transmitted beam is detected and recorded. Frequencies that are absorbed by the sample appear as peaks deviating from a baseline value. ...
Document
... Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line. _____ 1. A physical property of zinc metal is a. its color ...
... Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line. _____ 1. A physical property of zinc metal is a. its color ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... terms of relative charge and mass. • Describe the structure of the atom, including the locations of the subatomic particles. ...
... terms of relative charge and mass. • Describe the structure of the atom, including the locations of the subatomic particles. ...
chemistry - billpalmer
... 1) Matter is composed of small particles called atoms 2) All atoms of the same element are identical; different atoms are different 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4) atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds 5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combi ...
... 1) Matter is composed of small particles called atoms 2) All atoms of the same element are identical; different atoms are different 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4) atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds 5) In chemical reactions, atoms are combi ...
Matter – Properties and Changes
... throughout and always has a single phase; also called a solution. Ex: salt water • Heterogeneous mixture: one that does not have a uniform composition and in which the individual substances remain present in more than one physical state. Ex: sand in water • Intensive property: a physical property th ...
... throughout and always has a single phase; also called a solution. Ex: salt water • Heterogeneous mixture: one that does not have a uniform composition and in which the individual substances remain present in more than one physical state. Ex: sand in water • Intensive property: a physical property th ...
Chemical digestion
... Isotopes have a different # of neutrons. Isotopes have the same number of electrons and behave the same way chemically. ...
... Isotopes have a different # of neutrons. Isotopes have the same number of electrons and behave the same way chemically. ...
Glossary - WordPress.com
... The formula of a compound which shows the minimum ratio present between the atoms. Electron Affinity The amount of energy given out when an electron is absorbed in the outermost electronic shell of all isolated gaseous atom. Its units are KJ/mol. Electro-Negativity It is the power of an atom to attr ...
... The formula of a compound which shows the minimum ratio present between the atoms. Electron Affinity The amount of energy given out when an electron is absorbed in the outermost electronic shell of all isolated gaseous atom. Its units are KJ/mol. Electro-Negativity It is the power of an atom to attr ...
UNIVERSITY REVISION GURU Covalent Bonds • Covalent bonds
... A common example of this is oil. Oil and water do not mix, since oil is nonpolar, demonstrated by the separation of the two when attempted to be mixed. This is known as the ‘Hydrophobic effect’. ...
... A common example of this is oil. Oil and water do not mix, since oil is nonpolar, demonstrated by the separation of the two when attempted to be mixed. This is known as the ‘Hydrophobic effect’. ...
hydrosulfuric
... NonNon-metal with a nonnon-metal When non-metals combine, they form molecules. They may do so in multiple forms: ...
... NonNon-metal with a nonnon-metal When non-metals combine, they form molecules. They may do so in multiple forms: ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.