CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
... __ Na2S + __ AgNO3 _ NaNO3 + _ Ag2S ___ Mg + ___ HCl ___ H2 + ___ MgCl2 ...
Chapter 2 Law of Conservation of Mass Law of Conservation of Mass
... • states that all samples of the same compound always contain the same proportions by mass of the component elements – For example, water is always composed of oxygen and hydrogen in a mass ratio of 8:1 (or 16:2). ...
... • states that all samples of the same compound always contain the same proportions by mass of the component elements – For example, water is always composed of oxygen and hydrogen in a mass ratio of 8:1 (or 16:2). ...
ATOMIC STRUacad test
... 11. Atomic mass is a relative scale based on which of the following nuclides? A. carbon-12 B. oxygen-16 C. nitrogen-14 D. hydrogen-1 12. What is the mass number of an atom that has 8 protons, 9 neutrons, and 8 electrons? A. 8 B. 17 C. 16 D. 25 13. The Avogadro constant is ________ A. 2.998 X 108 B. ...
... 11. Atomic mass is a relative scale based on which of the following nuclides? A. carbon-12 B. oxygen-16 C. nitrogen-14 D. hydrogen-1 12. What is the mass number of an atom that has 8 protons, 9 neutrons, and 8 electrons? A. 8 B. 17 C. 16 D. 25 13. The Avogadro constant is ________ A. 2.998 X 108 B. ...
1 - PTO
... 10. In terms of subatomic particles, how does one isotope of hydrogen differ from another isotope of hydrogen? How does one isotope of carbon differ from another isotope of carbon? ...
... 10. In terms of subatomic particles, how does one isotope of hydrogen differ from another isotope of hydrogen? How does one isotope of carbon differ from another isotope of carbon? ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... erase pen, and tissue for erasing. • The teacher will ask you a question about atomic structure, you will write your answer and hold up your board. ...
... erase pen, and tissue for erasing. • The teacher will ask you a question about atomic structure, you will write your answer and hold up your board. ...
Chemistry - StudyTime NZ
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
... From this informa>on, we can tell that Magnesium has three electron shells, the last of which contains 2 electrons. We can assume that the first two electron shells are full with 2 electrons and 8 ...
Phy. Sci Mid-term review
... substance reacts or relates to other substances. Ex: Flammable, reacts with acids, decomposes … 6. Explain how to find the density of an object or a liquid. D = mass/volume 7. A piece of wood has a mass of 2.0 grams and a volume of 6 cm3. What is the density of the wood? Will the wood float on top o ...
... substance reacts or relates to other substances. Ex: Flammable, reacts with acids, decomposes … 6. Explain how to find the density of an object or a liquid. D = mass/volume 7. A piece of wood has a mass of 2.0 grams and a volume of 6 cm3. What is the density of the wood? Will the wood float on top o ...
Chapter 28
... of a beta particle is 0. For the atomic number, we say that it is “-1.” We say it’s -1, because losing a beta particle causes the nucleus to GAIN a proton. We’ll see how in a little bit. Yes, it’s in German. Not all the best stuff is in English. Notice that an electron is “produced” when a neutron ...
... of a beta particle is 0. For the atomic number, we say that it is “-1.” We say it’s -1, because losing a beta particle causes the nucleus to GAIN a proton. We’ll see how in a little bit. Yes, it’s in German. Not all the best stuff is in English. Notice that an electron is “produced” when a neutron ...
IB 1 CHEMISTRY
... There is large intermolecular distance between the molecules in a gas = a gas is mainly empty space. The gas molecules are free to move randomly in all directions. The molecules travel in a straight line until they collide with other gas molecules or with the walls of the container. ...
... There is large intermolecular distance between the molecules in a gas = a gas is mainly empty space. The gas molecules are free to move randomly in all directions. The molecules travel in a straight line until they collide with other gas molecules or with the walls of the container. ...
COMPOUNDS Chapter 2 : Preliminary course Chemistry 2
... Law of Multiple proportions The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine with a fixed weight of the other are in a simple whole number ratio. Example: N20 NO N2O3 ...
... Law of Multiple proportions The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine with a fixed weight of the other are in a simple whole number ratio. Example: N20 NO N2O3 ...
Atomic Theory: History of the Atom
... Why is atomic mass of carbon given as 12.011 amu instead of as 12 amu? Atomic masses shown on periodic table are average atomic masses taking into account the different isotopes of each element and their percent abundances. Isotopes are atoms of the same element but with a different mass. These isot ...
... Why is atomic mass of carbon given as 12.011 amu instead of as 12 amu? Atomic masses shown on periodic table are average atomic masses taking into account the different isotopes of each element and their percent abundances. Isotopes are atoms of the same element but with a different mass. These isot ...
Atoms and Elements
... 3. different elements have_______________ atoms 4. atoms combine in certain ______________________________ ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely __________________to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Problems with Dalton’s ...
... 3. different elements have_______________ atoms 4. atoms combine in certain ______________________________ ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely __________________to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Problems with Dalton’s ...
Chapter 2
... Atoms or groups of atoms with a charge. Cations- positive ions - get by losing electrons(s). Anions- negative ions - get by gaining electron(s). Ionic bonding- held together by the opposite ...
... Atoms or groups of atoms with a charge. Cations- positive ions - get by losing electrons(s). Anions- negative ions - get by gaining electron(s). Ionic bonding- held together by the opposite ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
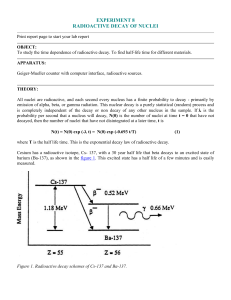
... Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is easily measured. ...
... Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is easily measured. ...
experiment 8 radioactive decay of nuclei
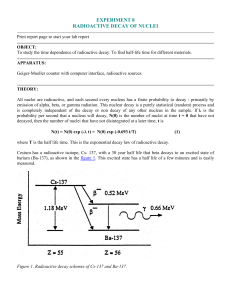
... Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is easily measured. ...
... Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is easily measured. ...
Determination of the Atomic Weight of Magnesium CHEM 101
... the balance. Other potential sources of experimental uncertainty are: the reaction might not be complete; if not enough time was allowed for total oxidation, less than complete oxidation of the magnesium might have, in part, reacted with nitrogen in the air (incorrect reaction); the magnesium oxide ...
... the balance. Other potential sources of experimental uncertainty are: the reaction might not be complete; if not enough time was allowed for total oxidation, less than complete oxidation of the magnesium might have, in part, reacted with nitrogen in the air (incorrect reaction); the magnesium oxide ...
Chapter 2 : The Chemistry of Life Section 3 : Carbon
... • Chemical reaction – process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another • Mass and energy are conserved during the reaction • The law of conservation of energy states that energy may neither be created nor destroyed. ...
... • Chemical reaction – process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another • Mass and energy are conserved during the reaction • The law of conservation of energy states that energy may neither be created nor destroyed. ...
Ch 11 HW
... Exact composition of the nucleus is ____________________. Recently, scientists have found that protons and neutrons are made of even smaller particles called _________________________. These quarks have +2/3 charge: ____________, ________________, __________________. These quarks have -1/3 charge: _ ...
... Exact composition of the nucleus is ____________________. Recently, scientists have found that protons and neutrons are made of even smaller particles called _________________________. These quarks have +2/3 charge: ____________, ________________, __________________. These quarks have -1/3 charge: _ ...
Mole Introduction
... The reaction between 2.74g of hydrogen gas and 97.26g of chlorine gas makes 100g of hydrogen chloride. What is the relative mass of a chlorine atom to a hydrogen atom? ...
... The reaction between 2.74g of hydrogen gas and 97.26g of chlorine gas makes 100g of hydrogen chloride. What is the relative mass of a chlorine atom to a hydrogen atom? ...
Use of Reduced Carbon Compounds
... --- the ability to reduce atmospheric N2 to NH3 --- requires considerable energy and specialized enzymes --- a few bacteria possess this ability and are required by Earth’s more complex life forms as a source of useable nitrogen ...
... --- the ability to reduce atmospheric N2 to NH3 --- requires considerable energy and specialized enzymes --- a few bacteria possess this ability and are required by Earth’s more complex life forms as a source of useable nitrogen ...
Chapter 8 Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions
... C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O Combustion of ethanol: CH3CH2OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O Synthesis Reactions • In a synthesis reaction a single compound forms from two or more reactants. • Two elements form a binary compound C + O2 CO2 2C + O2 2CO • Two compounds form a ternary compound CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca( ...
... C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O Combustion of ethanol: CH3CH2OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O Synthesis Reactions • In a synthesis reaction a single compound forms from two or more reactants. • Two elements form a binary compound C + O2 CO2 2C + O2 2CO • Two compounds form a ternary compound CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca( ...
SiO 2 - Wits Structural Chemistry
... Electronic configuration – ns2 np2 Generally exhibit +4 oxidation state and changes to +2 as the group is descended. ...
... Electronic configuration – ns2 np2 Generally exhibit +4 oxidation state and changes to +2 as the group is descended. ...
Bal Equations notes.cwk (WP)
... that involve an element and a compound can be much more interesting. These reactions are called single replacement reactions because one of the elements in the compound is replaced by another element. Example: copper reacts with silver nitrate solution to from silver and copper (II) nitrate solution ...
... that involve an element and a compound can be much more interesting. These reactions are called single replacement reactions because one of the elements in the compound is replaced by another element. Example: copper reacts with silver nitrate solution to from silver and copper (II) nitrate solution ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.