CP Chemistry Final Exam Review Sheet
... 50. What is the octet rule? The octet rule states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full octet (8 e-) in the valence (outermost) shell of an atom. 51. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge created by the transfer (loss or gaining) of electrons. 52. What is a c ...
... 50. What is the octet rule? The octet rule states that atoms will gain, lose, or share electrons in order to get a full octet (8 e-) in the valence (outermost) shell of an atom. 51. An ion is a particle with an electrical charge created by the transfer (loss or gaining) of electrons. 52. What is a c ...
Catalyst (4 min) - Schurz High School
... If an atom has 11 protons, how many electrons does it have? ...
... If an atom has 11 protons, how many electrons does it have? ...
Atomic Mass
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
Notes - Ms. Dawkins
... A neutron has about the ______________ ___________ as a proton. They are grouped together in the ______________________. Atoms are extremely ________________. The electron cloud is about _______________ times the size of the __________________. Electrons are much smaller than _____________________ ...
... A neutron has about the ______________ ___________ as a proton. They are grouped together in the ______________________. Atoms are extremely ________________. The electron cloud is about _______________ times the size of the __________________. Electrons are much smaller than _____________________ ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... • are particular types of dipole-dipole attractions between molecules in which hydrogen atoms are bonded to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine. • The hydrogen atom carries a partial positive charge and is attracted to the electronegative atom in another molecule. Thus, H acts as a bridge between two elect ...
... • are particular types of dipole-dipole attractions between molecules in which hydrogen atoms are bonded to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine. • The hydrogen atom carries a partial positive charge and is attracted to the electronegative atom in another molecule. Thus, H acts as a bridge between two elect ...
Elements and Compounds Chapter 3
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
Chemistry Final Review 2017 1. List a set of elements
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
cond-mat/0306381 PDF
... Isotopic disorder affects the primary interatomic interactions through the changes of inter-ion distances only. The influence of the isotopic composition on the lattice constant can be described as the combined effect of the third order anharmonic terms in the potential energy of the lattice expande ...
... Isotopic disorder affects the primary interatomic interactions through the changes of inter-ion distances only. The influence of the isotopic composition on the lattice constant can be described as the combined effect of the third order anharmonic terms in the potential energy of the lattice expande ...
Applications of C in animals: Diet and resource partitioning
... scale as d13Corg and using the 3 ‰ fractionation value they can be plotted as diet…. ...
... scale as d13Corg and using the 3 ‰ fractionation value they can be plotted as diet…. ...
Arnoldi
... teacher’s idea of a joke. We’re playing with beans, plain and simple. Our Beanium exists in three isotopic forms: white, speckled, and brown. While real atoms of a particular isotope will always have the same mass, Beanium beans will not. However, by calculating the average mass of each isotope form ...
... teacher’s idea of a joke. We’re playing with beans, plain and simple. Our Beanium exists in three isotopic forms: white, speckled, and brown. While real atoms of a particular isotope will always have the same mass, Beanium beans will not. However, by calculating the average mass of each isotope form ...
iClicker PARTICIPATION Question: Development of the Modern
... 3. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties, and are different from every other element. 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
... 3. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties, and are different from every other element. 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
Chp3,Mole_Definitions
... (a) What is the mass of one 12C atom in atomic mass units (amu)? ____________ (b) What is the mass of an average C atom in atomic mass units (amu)? ____________ (c) What is the mass of an average Cl atom in amu? ____________ (d) What is the mass of an average Br atom in amu? ____________ 2. The mola ...
... (a) What is the mass of one 12C atom in atomic mass units (amu)? ____________ (b) What is the mass of an average C atom in atomic mass units (amu)? ____________ (c) What is the mass of an average Cl atom in amu? ____________ (d) What is the mass of an average Br atom in amu? ____________ 2. The mola ...
Radioactive decay of nucleus
... 7. In an experiment, a researcher studied the decay of Po-210, which decays by the alpha emission and releases a stable Pb-206 atom. The half-life of Po-210 is 138.4 days. The mass of the Po-210 sample at the start of the experiment was 34.0g. (a)Write an equation for the alpha-decay of Po-210 (b)Wh ...
... 7. In an experiment, a researcher studied the decay of Po-210, which decays by the alpha emission and releases a stable Pb-206 atom. The half-life of Po-210 is 138.4 days. The mass of the Po-210 sample at the start of the experiment was 34.0g. (a)Write an equation for the alpha-decay of Po-210 (b)Wh ...
Chp 1,2 rev
... How many grams are in 100ml of a solution with a density of 2.5g/ml? Describe Solids, Liquids, and Gases. Calculate the volume of 15 g of a solid with density of 6g/ml. ...
... How many grams are in 100ml of a solution with a density of 2.5g/ml? Describe Solids, Liquids, and Gases. Calculate the volume of 15 g of a solid with density of 6g/ml. ...
of the atom.
... 3. Multiply step one by step two. Grams to Moles 1. Find the number of grams given in the ...
... 3. Multiply step one by step two. Grams to Moles 1. Find the number of grams given in the ...
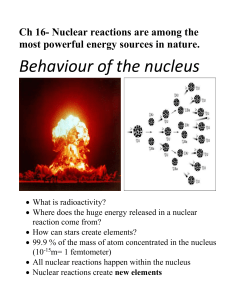
Physics and Chemistry 1501 – Nuclear Science Part I VO Atomic
... element. This is called radioactive decay. Another term for radioactive decay is transmutation. In 1896, a French physicist, Henri Becquerel, discovered that compounds containing uranium emitted penetrating rays. Two years later, Marie and Pierre Curie were the first to isolate two undiscovered radi ...
... element. This is called radioactive decay. Another term for radioactive decay is transmutation. In 1896, a French physicist, Henri Becquerel, discovered that compounds containing uranium emitted penetrating rays. Two years later, Marie and Pierre Curie were the first to isolate two undiscovered radi ...
Cell - My CCSD
... mostly of carbon and hydrogen with a small amount of oxygen. (ie. fats, oils, waxes) • They are insoluble in water because their molecules are nonpolar and are not attracted by water molecules. ...
... mostly of carbon and hydrogen with a small amount of oxygen. (ie. fats, oils, waxes) • They are insoluble in water because their molecules are nonpolar and are not attracted by water molecules. ...
Chapter 2
... Web/CD Activity2B: Structure of the Atomic Nucleus Web/CD Activity2C: Electron Arrangement Web/CD Activity2D: Build an Atom Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules (pp. 33-36, FIGURES 2.12 and 2.14) Chemical bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent b ...
... Web/CD Activity2B: Structure of the Atomic Nucleus Web/CD Activity2C: Electron Arrangement Web/CD Activity2D: Build an Atom Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules (pp. 33-36, FIGURES 2.12 and 2.14) Chemical bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent b ...
AP Biology
... Web/CD Activity2B: Structure of the Atomic Nucleus Web/CD Activity2C: Electron Arrangement Web/CD Activity2D: Build an Atom Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules (pp. 33-36, FIGURES 2.12 and 2.14) Chemical bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent b ...
... Web/CD Activity2B: Structure of the Atomic Nucleus Web/CD Activity2C: Electron Arrangement Web/CD Activity2D: Build an Atom Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules (pp. 33-36, FIGURES 2.12 and 2.14) Chemical bonds form when atoms interact and complete their valence shells. A covalent b ...
Introduction - HCC Learning Web
... The properties of any substance depend in part on the chemical bonds that hold the atoms of the substance together. The consequences of this dependence are very important in chemical reactions. Because bonds are formed or broken during a reaction, the properties of product molecules differ from thos ...
... The properties of any substance depend in part on the chemical bonds that hold the atoms of the substance together. The consequences of this dependence are very important in chemical reactions. Because bonds are formed or broken during a reaction, the properties of product molecules differ from thos ...
inorganic-chemistry-gp-i-alkali-metals
... The colour of the superoxide’s is due to the paramagnetic behaviour, the O2- is having two covalent bonds and a single electron, which when move from one to other atom releases photon of visible range giving the compounds colour, and also the paramagnetic behaviour The stability of peroxides and s ...
... The colour of the superoxide’s is due to the paramagnetic behaviour, the O2- is having two covalent bonds and a single electron, which when move from one to other atom releases photon of visible range giving the compounds colour, and also the paramagnetic behaviour The stability of peroxides and s ...
MATTER-Ch. 3-homogeneous vs. heterogeneous, elements
... Which part of an atom has a mass approximately equal to 1/2000 of the mass of a common hydrogen atom? a. nucleus c. proton b. electron d. electron cloud ____ 26. The mass of a neutron is a. about the same as that of a proton. c. double that of a proton. b. about the same as that of an electron. d. d ...
... Which part of an atom has a mass approximately equal to 1/2000 of the mass of a common hydrogen atom? a. nucleus c. proton b. electron d. electron cloud ____ 26. The mass of a neutron is a. about the same as that of a proton. c. double that of a proton. b. about the same as that of an electron. d. d ...
Structural Biochemistry/Metabolism
... chemical reactions is via gene regulations. For example, if a bacterial cell is not exposed to a particular sugar in its environment, it will turn off the genes that encode the enzymes that are needed to breakdown the sugar. Alternatively, if the sugar becomes available, the genes are switched on. 2 ...
... chemical reactions is via gene regulations. For example, if a bacterial cell is not exposed to a particular sugar in its environment, it will turn off the genes that encode the enzymes that are needed to breakdown the sugar. Alternatively, if the sugar becomes available, the genes are switched on. 2 ...
CO 2(g) - cloudfront.net
... • In a chemical reaction, all the atoms present at the beginning are still present at the end. If all the atoms are still there, then the mass ...
... • In a chemical reaction, all the atoms present at the beginning are still present at the end. If all the atoms are still there, then the mass ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.