CO 2(g) - cloudfront.net
... • In a chemical reaction, all the atoms present at the beginning are still present at the end. If all the atoms are still there, then the mass ...
... • In a chemical reaction, all the atoms present at the beginning are still present at the end. If all the atoms are still there, then the mass ...
U-Ti alloy as a promising storage material for hydrogen isotopes
... used as a storage medium, it should satisfy certain requirements such as high hydrogen storage capacity, facile reversibility of hydride formation and decomposition reactions, compatible absorption- ...
... used as a storage medium, it should satisfy certain requirements such as high hydrogen storage capacity, facile reversibility of hydride formation and decomposition reactions, compatible absorption- ...
Name the following
... structure or composition of atoms. • He attributed the difference in chemical properties of various elements to the fact that atoms of one element are different from atoms of the others. • Accordingly, at that time, in order to form a certain compound a specific number of atoms of the right kind mus ...
... structure or composition of atoms. • He attributed the difference in chemical properties of various elements to the fact that atoms of one element are different from atoms of the others. • Accordingly, at that time, in order to form a certain compound a specific number of atoms of the right kind mus ...
F. The Quantum Atom Theory - River Dell Regional School District
... 1. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element have the same chemical properties while atoms of different elements have different properties 3. Not all atoms of an element have the same mass, but they all have a definite average mass which is characteristic. ( ...
... 1. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element have the same chemical properties while atoms of different elements have different properties 3. Not all atoms of an element have the same mass, but they all have a definite average mass which is characteristic. ( ...
UNIT 7 – CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... 2. A correctly written ___________________________ describes exactly which and how many atoms are rearranged during the course of a reaction. 3. Atoms and mass are conserved in chemical reactions. 4. Coefficients written in front of the reactants and products indicate the amounts of each that are pr ...
... 2. A correctly written ___________________________ describes exactly which and how many atoms are rearranged during the course of a reaction. 3. Atoms and mass are conserved in chemical reactions. 4. Coefficients written in front of the reactants and products indicate the amounts of each that are pr ...
Organic Macromolecules
... Proteins contain nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and carbon Extremely long polymers of monomers called amino acids Responsible for almost all of our day to day functions Used ...
... Proteins contain nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and carbon Extremely long polymers of monomers called amino acids Responsible for almost all of our day to day functions Used ...
Carbon Chapter 5: The Large Biological Molecules
... 5. It form single, double or triple bonds. 6. Carbon compounds to not readily dissociate in water. 7. There is no limit to the size of the molecule. 8. Can bond with a wide variety or other elements and functional groups. 9. Only carbon has all of these characteristics. ...
... 5. It form single, double or triple bonds. 6. Carbon compounds to not readily dissociate in water. 7. There is no limit to the size of the molecule. 8. Can bond with a wide variety or other elements and functional groups. 9. Only carbon has all of these characteristics. ...
set2
... 1.000 g of oxygen. The atomic mass of O is assumed to be 16.00. • If the formula is InO, what is the atomic mass of indium? • If the formula is In2O3, what is the atomic mass of indium? • Which is correct? ...
... 1.000 g of oxygen. The atomic mass of O is assumed to be 16.00. • If the formula is InO, what is the atomic mass of indium? • If the formula is In2O3, what is the atomic mass of indium? • Which is correct? ...
Mole Ratio and Stoichiometry
... Background information In Chemistry, the mole is used as a base unit to measure amount of substances needed for chemical reactions. Chemists have found that chemicals react with one another in proportion based on mole ratios, and generally speaking, do not react proportionately when measure in other ...
... Background information In Chemistry, the mole is used as a base unit to measure amount of substances needed for chemical reactions. Chemists have found that chemicals react with one another in proportion based on mole ratios, and generally speaking, do not react proportionately when measure in other ...
File
... 19) Which of the following does NOT describe a nonmetal? A) tend to gain electrons B) found in the upper right hand corner of the periodic table C) poor conductor of electricity D) nonmetals are generally unreactive E) poor conductor of heat 20) An ionic bond is best described as A) the sharing of ...
... 19) Which of the following does NOT describe a nonmetal? A) tend to gain electrons B) found in the upper right hand corner of the periodic table C) poor conductor of electricity D) nonmetals are generally unreactive E) poor conductor of heat 20) An ionic bond is best described as A) the sharing of ...
02-Atoms-Molecules
... isotope breaks down into particles with lower atomic numbers Radioactive isotopes are used in 1. Medicine Tracers are taken up and used by the body Emissions are detected using special lab equipment 2. Dating fossils The rate of decay of a radioactive element is constant The amount of ...
... isotope breaks down into particles with lower atomic numbers Radioactive isotopes are used in 1. Medicine Tracers are taken up and used by the body Emissions are detected using special lab equipment 2. Dating fossils The rate of decay of a radioactive element is constant The amount of ...
- Catalyst
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
Name: Midterm Review (Part II) Fill in the blanks (Chapter 6.1 – 6.3
... Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes, Cl-35 and Cl-37. The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45. Which of these two isotopes of chlorine is more abundant?(p. 116) Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass numbe ...
... Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes, Cl-35 and Cl-37. The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45. Which of these two isotopes of chlorine is more abundant?(p. 116) Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass numbe ...
File
... • Q3 – Hydrated barium chloride is heated. Its mass decreases from 30.5g to 26.0g. What is the formula of the hydrated salt? • Q4 – Hydrated sodium carbonate, Na2CO3·xH2O was found to contain 62.9% water by mass. Calculate the value of x • Q5 – Potash alum has the formula K2SO4·Al2(SO4)3·yH2O, calc ...
... • Q3 – Hydrated barium chloride is heated. Its mass decreases from 30.5g to 26.0g. What is the formula of the hydrated salt? • Q4 – Hydrated sodium carbonate, Na2CO3·xH2O was found to contain 62.9% water by mass. Calculate the value of x • Q5 – Potash alum has the formula K2SO4·Al2(SO4)3·yH2O, calc ...
Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry….
... •Noise is bad. It is random and incoherent and does not possess information. We go to tremendous expense and effort to eliminate, suppress, and finesse our way past noise. •Signals are good. They give us information. •Noise limits our ability to even observe very weak signals or to quantify somewhat ...
... •Noise is bad. It is random and incoherent and does not possess information. We go to tremendous expense and effort to eliminate, suppress, and finesse our way past noise. •Signals are good. They give us information. •Noise limits our ability to even observe very weak signals or to quantify somewhat ...
Document
... • The gyromagnetic ratio (characteristic of the nucleus) • The local magnetic field 1. Ho the External field 2. Local variations due to the chemical environment In real situations, we measure the Larmor frequency relative to a reference. The frequency for a signal attached to a given nucleus, relati ...
... • The gyromagnetic ratio (characteristic of the nucleus) • The local magnetic field 1. Ho the External field 2. Local variations due to the chemical environment In real situations, we measure the Larmor frequency relative to a reference. The frequency for a signal attached to a given nucleus, relati ...
Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life About 25 of the 92 natural
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms. C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms. D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shel ...
... B) protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms. C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms. D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shel ...
1 of 3 Biochemistry Final exam Block 3, 2008 Name Answer all of
... It is an inhibitor of electron transfer; its addition lowers the NAD+/NADH ratio because NADH produced by oxidative reactions in mitochondria can no longer be reoxidized by electron flow to O2. As a result, lifetimes of reactive oxygen species on the electron transport are increased allowing them to ...
... It is an inhibitor of electron transfer; its addition lowers the NAD+/NADH ratio because NADH produced by oxidative reactions in mitochondria can no longer be reoxidized by electron flow to O2. As a result, lifetimes of reactive oxygen species on the electron transport are increased allowing them to ...
Radioactivity Reading Assignment Name: Chemistry Date: Hour
... All substance are made of atoms. These have electrons (e–) around the outside and a nucleus in the middle. The nucleus consists of protons (p+) and neutrons (n0) and is extremely small. (Atoms are almost entirely made of empty space!) In some types of atoms, the nucleus is unstable and will decay in ...
... All substance are made of atoms. These have electrons (e–) around the outside and a nucleus in the middle. The nucleus consists of protons (p+) and neutrons (n0) and is extremely small. (Atoms are almost entirely made of empty space!) In some types of atoms, the nucleus is unstable and will decay in ...
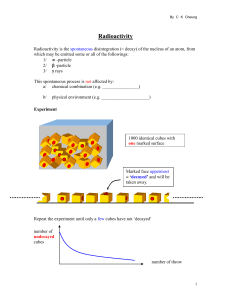
Radioactivity
... Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration (= decay) of the nucleus of an atom, from which may be emitted some or all of the followings: 1/ -particle 2/ -particle 3/ rays This spontaneous process is not affected by: a/ chemical combination (e.g. ________________) b/ ...
... Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration (= decay) of the nucleus of an atom, from which may be emitted some or all of the followings: 1/ -particle 2/ -particle 3/ rays This spontaneous process is not affected by: a/ chemical combination (e.g. ________________) b/ ...
Photosynthesis in the Higher Plant, Vicia.faba
... S. SHERRILL KENT,2 FREDERICK D. PINKERTON, AND GARY A. STROBEL Department of Plant Pathology, Montana State University, Bozeman, Montana 59715 ...
... S. SHERRILL KENT,2 FREDERICK D. PINKERTON, AND GARY A. STROBEL Department of Plant Pathology, Montana State University, Bozeman, Montana 59715 ...
Final Exam Study Guide Page 1 Quiz
... c. 1.5 x 1025 moles d. none of the above 2. How many grams are in 6.2 moles of NH4? a. .34 g b. 111.8 g c. 6.2 g d. 11.6 g 3. One mole of CaCO3 is equal to how many molecules of CaCO3? a. 765 molecules b. 249 molecules c. 7.6 x 1024 molecules d. 6.02 x 1023 molecules 4. How many grams of sodium are ...
... c. 1.5 x 1025 moles d. none of the above 2. How many grams are in 6.2 moles of NH4? a. .34 g b. 111.8 g c. 6.2 g d. 11.6 g 3. One mole of CaCO3 is equal to how many molecules of CaCO3? a. 765 molecules b. 249 molecules c. 7.6 x 1024 molecules d. 6.02 x 1023 molecules 4. How many grams of sodium are ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.