Acids and Bases Acids and Bases Conjugate Pair Question
... Acids and Bases The Danish chemist Johannes Brnsted and the English chemist Thomas Lowry put forward a model: ...
... Acids and Bases The Danish chemist Johannes Brnsted and the English chemist Thomas Lowry put forward a model: ...
Chapter 15a
... Acid/base problems may fall into 4 categories: strong acid/base, weak acid/base, buffers and hydrolysis. We will go through examples of each of these types of problems one at a time. Strong Acids and Strong Bases The strength of the acid is determined by how far the equilibrium lies to the right. Qu ...
... Acid/base problems may fall into 4 categories: strong acid/base, weak acid/base, buffers and hydrolysis. We will go through examples of each of these types of problems one at a time. Strong Acids and Strong Bases The strength of the acid is determined by how far the equilibrium lies to the right. Qu ...
CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
... 27. Describe the dissociation (ionization) of strong acids and bases versus weak acids and bases. 28. List the 6 strong acids and state the rule for strong bases. 29. What are the pH values for acids? Bases? 30. What is more acidic, a solution with a pH of 2 or 5? What is more basic, a solution with ...
Chapter 2 Notes - Duplin County Schools
... Mixture: a combination of substances in which the individual components retain their own properties Solution: a mixture in which one or more substances are distributed evenly in another substance – Two parts to every solution: 1. Solute --- What is being dissolved 2. Solvent -- What is doing the dis ...
... Mixture: a combination of substances in which the individual components retain their own properties Solution: a mixture in which one or more substances are distributed evenly in another substance – Two parts to every solution: 1. Solute --- What is being dissolved 2. Solvent -- What is doing the dis ...
Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
... point of the titration • Prior to the equivalence point, the known solution in the flask is in excess, so the pH is closest to its pH • The pH of the equivalence point depends on the pH of the salt solution – equivalence point of neutral salt, pH = 7 – equivalence point of acidic salt, pH < 7 – equi ...
... point of the titration • Prior to the equivalence point, the known solution in the flask is in excess, so the pH is closest to its pH • The pH of the equivalence point depends on the pH of the salt solution – equivalence point of neutral salt, pH = 7 – equivalence point of acidic salt, pH < 7 – equi ...
Semester 2 Review
... A. How will an increase in temperature change the concentration of hydrogen gas? ________ B. How will an increase in pressure affect the system? ___________________ C. Which direction will the addition of iodine gas shift the system? _________________ What does this do to the concentration of hydrog ...
... A. How will an increase in temperature change the concentration of hydrogen gas? ________ B. How will an increase in pressure affect the system? ___________________ C. Which direction will the addition of iodine gas shift the system? _________________ What does this do to the concentration of hydrog ...
5,6 Quiz - mvhs
... standard enthalpy (heat) of formation of cyclopropane. 3. Calculate the frequency (Hz), wavelength (nm) and energy/mol of the emitted photon when an electron drops from the n=4 to the n=2 level in a hydrogen atom. 4. Write/Draw the following for Ag atom and Ag+ ion. a. Condensed electron configurati ...
... standard enthalpy (heat) of formation of cyclopropane. 3. Calculate the frequency (Hz), wavelength (nm) and energy/mol of the emitted photon when an electron drops from the n=4 to the n=2 level in a hydrogen atom. 4. Write/Draw the following for Ag atom and Ag+ ion. a. Condensed electron configurati ...
Chemistry 1 - Edexcel
... (i) Place a tick (9) in one box in each row of the table to show the best method of separation for each mixture. ...
... (i) Place a tick (9) in one box in each row of the table to show the best method of separation for each mixture. ...
Dissociation
... — Although no compound is ever totally insoluble, compounds of very low solubility can be considered insoluble for most practical purposes — There is no easy method to predict whether a compound made up of a certain combination of ions will be soluble when put into water — However, general solubilit ...
... — Although no compound is ever totally insoluble, compounds of very low solubility can be considered insoluble for most practical purposes — There is no easy method to predict whether a compound made up of a certain combination of ions will be soluble when put into water — However, general solubilit ...
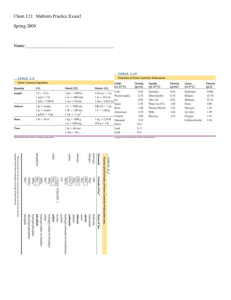
Name:_____________ Chemistry 114 Second Hour Exam
... NaCl has a lower melting point than MgS. Both are ionic and the ions are the same size, but MgS had +2 and -2 ions, making its lattice energy stronger so it will have stonger interaction in the solid and a higher melting point. H2S is a gas and H2O is a liquid at room temperature. H2O can form inter ...
... NaCl has a lower melting point than MgS. Both are ionic and the ions are the same size, but MgS had +2 and -2 ions, making its lattice energy stronger so it will have stonger interaction in the solid and a higher melting point. H2S is a gas and H2O is a liquid at room temperature. H2O can form inter ...
ch5_f08
... While reading a textbook of chemistry I came upon the statement, "nitric acid acts upon copper." I was getting tired of reading such absurd stuff and I was determined to see what this meant. Copper was more or less familiar to me, for copper cents were then in use. I had seen a bottle marked nitric ...
... While reading a textbook of chemistry I came upon the statement, "nitric acid acts upon copper." I was getting tired of reading such absurd stuff and I was determined to see what this meant. Copper was more or less familiar to me, for copper cents were then in use. I had seen a bottle marked nitric ...
Practice Exam #2 with Answers
... water bath at 99°C. The barometric pressure is 753 torr. If the mass of the liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
... water bath at 99°C. The barometric pressure is 753 torr. If the mass of the liquid retained in the flask is 1.362 g, what is its molar mass? a. ...
Chemistry II Aqueous Reactions and Solution Chemistry Chapter 4
... homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. ...
... homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. ...
Document
... The above problem is an example of how to make a molar solution from a solid. Now, we turn to preparation of a molar solution by dilution. Dilutions (Section 15.5) One of the most common lab techniques is the dilution of a more concentrated solution to make a less concentrated solution. The basic id ...
... The above problem is an example of how to make a molar solution from a solid. Now, we turn to preparation of a molar solution by dilution. Dilutions (Section 15.5) One of the most common lab techniques is the dilution of a more concentrated solution to make a less concentrated solution. The basic id ...
Final Exam Review Guide
... 3. The quantity 6.02 x 1023 is called a mole, and the periodic table lists the mass of 1 mole of each element’s atoms, called the molar mass of the element. 4. Coefficients are interpreted as either particle, mole, or (if everything is a gas) liter ratios. 5. Stoichiometry is the name given to the p ...
... 3. The quantity 6.02 x 1023 is called a mole, and the periodic table lists the mass of 1 mole of each element’s atoms, called the molar mass of the element. 4. Coefficients are interpreted as either particle, mole, or (if everything is a gas) liter ratios. 5. Stoichiometry is the name given to the p ...
Electrolysis answers - Barnard Castle School
... aqueous / a solution / dissolved (in water) / or sodium nitrate gains 1 mark (do not allow liquid) but aqueous / a solution / dissolved (in water) of sodium nitrate (*do not credit formulae) gains 2 marks ...
... aqueous / a solution / dissolved (in water) / or sodium nitrate gains 1 mark (do not allow liquid) but aqueous / a solution / dissolved (in water) of sodium nitrate (*do not credit formulae) gains 2 marks ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.