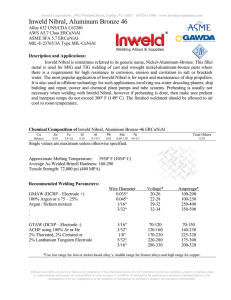
Chemistry@YIA – additional information
... There are 3 basic problems making the jump: The first is making sure there are no gaps in your knowledge from GCSE. That is the main purpose of this pack. Second is the quantity of material that you have to cover and sorting out what’s important. It’s useful to identify patterns that you can then ‘h ...
... There are 3 basic problems making the jump: The first is making sure there are no gaps in your knowledge from GCSE. That is the main purpose of this pack. Second is the quantity of material that you have to cover and sorting out what’s important. It’s useful to identify patterns that you can then ‘h ...
final exam review chapter 1-4
... 1. Write the empirical and molecular formula for the following molecule: 9 Carbons, 6 Bromines, 3 Oxygens, and 9 Hydrogens 2. Complete and balance the following reactions: a. Combination ___ H2 + ___ F2 b. Decomposition ___ B2O3 ...
... 1. Write the empirical and molecular formula for the following molecule: 9 Carbons, 6 Bromines, 3 Oxygens, and 9 Hydrogens 2. Complete and balance the following reactions: a. Combination ___ H2 + ___ F2 b. Decomposition ___ B2O3 ...
SCIENCE 10: Chemical Reactions – Atomic Structure
... o A table of polyatomic ions can be found on your Periodic Table of Ions. o If more than one polyatomic ion is needed to balance the positive and negative charges, then the polyatomic ion is written in brackets and the number placed after and lower. o Don’t change the ending of the non-metal polyato ...
... o A table of polyatomic ions can be found on your Periodic Table of Ions. o If more than one polyatomic ion is needed to balance the positive and negative charges, then the polyatomic ion is written in brackets and the number placed after and lower. o Don’t change the ending of the non-metal polyato ...
The Mole Ratio · the ratio between the molar amounts of any two
... · the method of predicting the quantity of a reactant or product in a chemical reaction based on the quantity of another reactant or product in the reaction ...
... · the method of predicting the quantity of a reactant or product in a chemical reaction based on the quantity of another reactant or product in the reaction ...
SCH3U - Norbraten
... 14. Hydrogen gas reacts with sulphur to produce hydrogen sulphide gas. 15. Liquid hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen. 16. When lithium hydroxide pellets are added to a solution of sulphuric acid, dissolved lithium sulphate and water are formed. 17. When crystalline C6H12O6 (glucose) ...
... 14. Hydrogen gas reacts with sulphur to produce hydrogen sulphide gas. 15. Liquid hydrogen peroxide breaks down into water and oxygen. 16. When lithium hydroxide pellets are added to a solution of sulphuric acid, dissolved lithium sulphate and water are formed. 17. When crystalline C6H12O6 (glucose) ...
chemistry important question i
... (i) Where R is an alkyl group, R3P=O exists but R3N=O does not. (ii) PbCl4 is more covalent than PbCl2 (iii) At room temperature, N2 is much less reactive. What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g ...
... (i) Where R is an alkyl group, R3P=O exists but R3N=O does not. (ii) PbCl4 is more covalent than PbCl2 (iii) At room temperature, N2 is much less reactive. What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... pencil. Make a heavy, full mark, but no stray marks. If you decide to change an answer, erase the unwanted mark very carefully. ! There is only one correct answer to each question. Any questions for which more than one response has been blackened will not be counted. ! Your score is based solely on ...
... pencil. Make a heavy, full mark, but no stray marks. If you decide to change an answer, erase the unwanted mark very carefully. ! There is only one correct answer to each question. Any questions for which more than one response has been blackened will not be counted. ! Your score is based solely on ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... contain the hydroxide ion before being dissolved in water but ammonia combines with water molecules to form an ammonium ion and a hydroxide ion. Therefore it is considered to be a base. There are strong bases and weak bases as with the acids. NaOH, KOH and Ca(OH)2 are considered to be strong since t ...
... contain the hydroxide ion before being dissolved in water but ammonia combines with water molecules to form an ammonium ion and a hydroxide ion. Therefore it is considered to be a base. There are strong bases and weak bases as with the acids. NaOH, KOH and Ca(OH)2 are considered to be strong since t ...
Chapter 10
... Balanced Chemical Equations Skeleton equations do not reflect the fact that matter is conserved during a reaction. An equation must reflect that the same number of each kind of atom on both sides of the arrow. This is called a balanced chemical equation. To balance a chemical equation, use coef ...
... Balanced Chemical Equations Skeleton equations do not reflect the fact that matter is conserved during a reaction. An equation must reflect that the same number of each kind of atom on both sides of the arrow. This is called a balanced chemical equation. To balance a chemical equation, use coef ...
12. Acids and Bases
... What did they say? They tried to fix the definition of acids and bases. In a solution, the H+ travels to either accept or donate. ...
... What did they say? They tried to fix the definition of acids and bases. In a solution, the H+ travels to either accept or donate. ...
Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4)
... The double arrows indicate that the reaction occurs in both directions. The longer arrow (pointing to the left) indicates that at chemical equilibrium, the concentration of the undissociated acetic acid is greater than that of its dissociated ions. NOTE: ...
... The double arrows indicate that the reaction occurs in both directions. The longer arrow (pointing to the left) indicates that at chemical equilibrium, the concentration of the undissociated acetic acid is greater than that of its dissociated ions. NOTE: ...
CP Chemistry Final Review – Chap. 10-19
... Chapter 13/14 – Gases 1. Convert 4.2 atm into mmHg, torr, Pa, and PSI. 2. The side of a manometer open to the atmosphere is 100 mm higher than the side open to a gas sample. Assuming that atmospheric pressure 780 mm Hg, determine the pressure of the gas sample. 3. The gas pressure in a 20-L tank is ...
... Chapter 13/14 – Gases 1. Convert 4.2 atm into mmHg, torr, Pa, and PSI. 2. The side of a manometer open to the atmosphere is 100 mm higher than the side open to a gas sample. Assuming that atmospheric pressure 780 mm Hg, determine the pressure of the gas sample. 3. The gas pressure in a 20-L tank is ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.