![[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000095863_1-918f0427052f54159a7c908528a2e159-300x300.png)
irreversible cell
... 7. Define a reference electrode. Give one example. Reference electrode is the electrode whose potential is known (or) arbitrarily fixed as Zero. It is used to measure the electrode potential of another unknown electrode by combining with it. Example : Standard Hydrogen Electrode ; Calomel Electrode ...
... 7. Define a reference electrode. Give one example. Reference electrode is the electrode whose potential is known (or) arbitrarily fixed as Zero. It is used to measure the electrode potential of another unknown electrode by combining with it. Example : Standard Hydrogen Electrode ; Calomel Electrode ...
Solutions Foldable
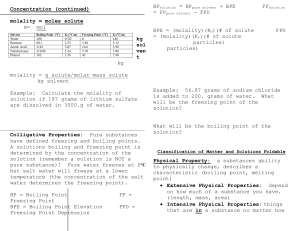
... lone pairs of electrons on central atom) o CO2, CH4, SO3, C2H6, F2 Ionic compounds = positive and negative ions bonded (usually contains a metal and a nonmetal or a metal and a polyatomic ion) o Li2SO4, MgO, Na2O, Ca(OH)2 Now that we know what will mix to make a solution how do we know how MUCH s ...
... lone pairs of electrons on central atom) o CO2, CH4, SO3, C2H6, F2 Ionic compounds = positive and negative ions bonded (usually contains a metal and a nonmetal or a metal and a polyatomic ion) o Li2SO4, MgO, Na2O, Ca(OH)2 Now that we know what will mix to make a solution how do we know how MUCH s ...
Regents Chemistry Review Questions
... What is the symbol for molarity? Describe how you would prepare 2L of a 10M sodium chloride solution. Describe how you would make a 0.5M solution of BaNO3 given 1L of 5M BaNO3. What is a precipitate? Is it soluble or insoluble? Write the chemical reaction that occurs when solutions of sodium chlorid ...
... What is the symbol for molarity? Describe how you would prepare 2L of a 10M sodium chloride solution. Describe how you would make a 0.5M solution of BaNO3 given 1L of 5M BaNO3. What is a precipitate? Is it soluble or insoluble? Write the chemical reaction that occurs when solutions of sodium chlorid ...
unit 6 - writing and balancing chemical equations
... On some occasions, a variety of information will be written above or below the arrows. This information, such as a value for temperature, shows what conditions need to be present for a reaction to occur. For example, in the graphic below, the notation above and below the arrows shows that we need a ...
... On some occasions, a variety of information will be written above or below the arrows. This information, such as a value for temperature, shows what conditions need to be present for a reaction to occur. For example, in the graphic below, the notation above and below the arrows shows that we need a ...
97KB - NZQA
... have a bung in it, with a delivery tube going into a test-tube of limewater. If the limewater turns from colourless to cloudy during heating, this indicates that carbon dioxide gas has been produced and the white solid is either calcium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate. If the colourless solut ...
... have a bung in it, with a delivery tube going into a test-tube of limewater. If the limewater turns from colourless to cloudy during heating, this indicates that carbon dioxide gas has been produced and the white solid is either calcium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate. If the colourless solut ...
Unit Objectives- States of Matter
... 6. Explain Avogadro’s hypothesis and use it to solve problems involving gas stoichiometry. 7. Perform calculations using the combined and ideal gas laws to solve for pressure, volume, temperature, number of moles of a gas, density, and molar mass. 8. Explain Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures and be ...
... 6. Explain Avogadro’s hypothesis and use it to solve problems involving gas stoichiometry. 7. Perform calculations using the combined and ideal gas laws to solve for pressure, volume, temperature, number of moles of a gas, density, and molar mass. 8. Explain Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures and be ...
Basic Chemistry
... Water, Acids, Bases and pH Mixing an acid with a base a chemical reaction will change the pH of the mixture Hydrogen ions will react with the hydroxyl ions and form water H + + OHHOH If the ions are in equal amounts, the mixture becomes neutral (pH 7) This is called a neutralization reaction. ...
... Water, Acids, Bases and pH Mixing an acid with a base a chemical reaction will change the pH of the mixture Hydrogen ions will react with the hydroxyl ions and form water H + + OHHOH If the ions are in equal amounts, the mixture becomes neutral (pH 7) This is called a neutralization reaction. ...
Old EXAM I - gozips.uakron.edu
... There is no change in the masses or concentrations of products or reactants. The reaction stops occurring in both the forward and reverse directions. The system must be closed if it contains gaseous products. The forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate. The ratio of products to reacta ...
... There is no change in the masses or concentrations of products or reactants. The reaction stops occurring in both the forward and reverse directions. The system must be closed if it contains gaseous products. The forward and reverse reactions proceed at the same rate. The ratio of products to reacta ...
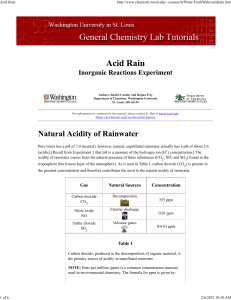
Acid Rain - Department of Chemistry
... details on relief work (e.g., the faces on a statue), but generally does not affect the structural integrity of the building. The degree of damage is determined not only by the acidity of the rainwater, but also by the amount of water flow that a region of the surface receives. Regions exposed to di ...
... details on relief work (e.g., the faces on a statue), but generally does not affect the structural integrity of the building. The degree of damage is determined not only by the acidity of the rainwater, but also by the amount of water flow that a region of the surface receives. Regions exposed to di ...
CHAPTER 7 READING GUIDE – IONIC COMPOUNDS AND METALS
... 23. Because chemists around the world need to be able to communicate with one another, they have developed a set of rules for __________________ compounds. 24. A ___________________ ion is a one-atom ion such as ________ or _________. 25. The charge of a monatomic ion is known as its _______________ ...
... 23. Because chemists around the world need to be able to communicate with one another, they have developed a set of rules for __________________ compounds. 24. A ___________________ ion is a one-atom ion such as ________ or _________. 25. The charge of a monatomic ion is known as its _______________ ...
ic199p5a
... (b) Explain why KNO3(s) is highly soluble in water despite this observation regarding the temperature change on solution. If it is readily soluble, the G for solution is likely to be negative, which means the increase in entropy on dissolution (the TS term) is sufficient to overcome the positive ...
... (b) Explain why KNO3(s) is highly soluble in water despite this observation regarding the temperature change on solution. If it is readily soluble, the G for solution is likely to be negative, which means the increase in entropy on dissolution (the TS term) is sufficient to overcome the positive ...
Miami-Dade College
... j. Relating the strength of acids and bases to their equilibrium constants. k. Describing the effect of adding a “common ion” on the equilibrium. l. Recognizing a buffer solution and giving illustrations of its operation. m. Predicting the effect upon the pH when adding a strong acid or a strong bas ...
... j. Relating the strength of acids and bases to their equilibrium constants. k. Describing the effect of adding a “common ion” on the equilibrium. l. Recognizing a buffer solution and giving illustrations of its operation. m. Predicting the effect upon the pH when adding a strong acid or a strong bas ...
Second Semester Final Review Guide
... Solution C: pH of 4 a) A, B, C b) C, B, A c) B, C, A 18. In a neutralization reaction, a. the base in the reaction is neutralized. b. the acid in the reaction is neutralized. c. a salt is formed. d. All of the above are correct. 19. Ammonia is a weak base. If the initial concentration of ammonia is ...
... Solution C: pH of 4 a) A, B, C b) C, B, A c) B, C, A 18. In a neutralization reaction, a. the base in the reaction is neutralized. b. the acid in the reaction is neutralized. c. a salt is formed. d. All of the above are correct. 19. Ammonia is a weak base. If the initial concentration of ammonia is ...
introduction into Analytical Chemistry
... - is a solution of known concentration - prepared by dissolving a known amount of the substance (primary standard substance)in a known volume of liquid - They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations -Two types,, primary and secondary standard solution ...
... - is a solution of known concentration - prepared by dissolving a known amount of the substance (primary standard substance)in a known volume of liquid - They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations -Two types,, primary and secondary standard solution ...
Ch2hon ppt part 3
... Here we need to convert prefixes to numbers of atoms (see Table 2.4). Because there is no prefix for carbon in (a), it means that there is only one carbon atom present. Solution (a) Because there are two sulfur atoms and one carbon atom present, the formula is CS2. (b) There are two silicon atoms an ...
... Here we need to convert prefixes to numbers of atoms (see Table 2.4). Because there is no prefix for carbon in (a), it means that there is only one carbon atom present. Solution (a) Because there are two sulfur atoms and one carbon atom present, the formula is CS2. (b) There are two silicon atoms an ...
Unit 5 Study Guide
... 2. What does each of the following symbols mean? a. (l) d. (g) b. (aq) e. ∆ written above the arrow c. (s) 3. What are the signs of a chemical reaction? ...
... 2. What does each of the following symbols mean? a. (l) d. (g) b. (aq) e. ∆ written above the arrow c. (s) 3. What are the signs of a chemical reaction? ...
material safety data sheet
... MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET I - IDENTIFICATION AND USE PRODUCT NAME: FLO-CLENE PRODUCT USE: LIQUID DRAIN OPENER SUPPLIER: ...
... MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET I - IDENTIFICATION AND USE PRODUCT NAME: FLO-CLENE PRODUCT USE: LIQUID DRAIN OPENER SUPPLIER: ...
Chemistry 111: Exam 1 Topics
... pressure/temp/volume based on molecular collisions Understand how to read a barometer Understand how to read a manometer Be able to convert pressure units Remember to use Kelvin! Understand what’s held constant in Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law Use combined gas law (P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 is given). ...
... pressure/temp/volume based on molecular collisions Understand how to read a barometer Understand how to read a manometer Be able to convert pressure units Remember to use Kelvin! Understand what’s held constant in Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law Use combined gas law (P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 is given). ...
CHAPTER 4: AQUEOUS REACTIONS AND SOLUTION
... Water is considered the universal solvent because of its ability to dissolve many substances. The other dissolved substances are called the solutes. A solvent dissolves a solute. ...
... Water is considered the universal solvent because of its ability to dissolve many substances. The other dissolved substances are called the solutes. A solvent dissolves a solute. ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... and has 0.65 kJ of PV work done on it by its surroundings. What are the values of deltaH and deltaE for this process? ...
... and has 0.65 kJ of PV work done on it by its surroundings. What are the values of deltaH and deltaE for this process? ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.
![+ [H 2 CO 3 ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001130480_1-81612c04e4e5fb35027131a7b7feb9b6-300x300.png)