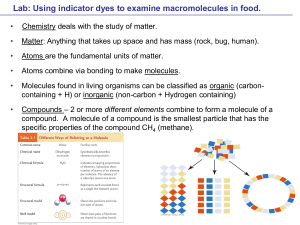
8.1 Classifying inorganic compounds
... Salts = any ionic substance that does not have an H+ or OH- ion. ...
... Salts = any ionic substance that does not have an H+ or OH- ion. ...
u11_tqs
... 38. Fill in the missing information. neutral solution: pH = 7.0 basic solution: pH > 7.0 acidic solution: pH < 7.0 ...
... 38. Fill in the missing information. neutral solution: pH = 7.0 basic solution: pH > 7.0 acidic solution: pH < 7.0 ...
Class Activity
... physical state of each of the element or compound a. Sodium metal plus water yields hydrogen gas and an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution b. An aqueous phosphoric acid solution plus an aqueous calcium hydroxide solution yields water and solid calcium phosphate c. Solid phenol (C6H6O) reacts with oxy ...
... physical state of each of the element or compound a. Sodium metal plus water yields hydrogen gas and an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution b. An aqueous phosphoric acid solution plus an aqueous calcium hydroxide solution yields water and solid calcium phosphate c. Solid phenol (C6H6O) reacts with oxy ...
TYPES OF SOLUTION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... c. analyte—the substance being analyzed; with a known formula, mass or volumed. indicator- a substance added at the beginning of a titration that changes colors. 5. Procedure for titration a. A standard solution of an acid or base is loaded into a buret. b. The unknown solution of known volume is pl ...
... c. analyte—the substance being analyzed; with a known formula, mass or volumed. indicator- a substance added at the beginning of a titration that changes colors. 5. Procedure for titration a. A standard solution of an acid or base is loaded into a buret. b. The unknown solution of known volume is pl ...
Study Questions
... b) At what pH is methyl red orange? c) What is the Ka of an indicator that changes color at pH 3.5? d) What is a good indicator to use when titrating sodium nitrite (NaNO2) with HCl? 3. How many ml of 2.00 M HNO3 would be required to neutralize 12.5 ml of 0.0800 M NH3? (optional: What is the pH of t ...
... b) At what pH is methyl red orange? c) What is the Ka of an indicator that changes color at pH 3.5? d) What is a good indicator to use when titrating sodium nitrite (NaNO2) with HCl? 3. How many ml of 2.00 M HNO3 would be required to neutralize 12.5 ml of 0.0800 M NH3? (optional: What is the pH of t ...
A buffer solution is one that will maintain a rather constant pH value
... The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to prepare buffer solutions and to estimate charges on ionizable species in solution, such as amino acid side chains in proteins. Caution must be exercised in using this equation because pH is sensitive to changes in temperature and salt concentration i ...
... The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to prepare buffer solutions and to estimate charges on ionizable species in solution, such as amino acid side chains in proteins. Caution must be exercised in using this equation because pH is sensitive to changes in temperature and salt concentration i ...
acids: bases - IDS-chem2-Rn-10
... •do not furnish OHions by dissociation. •react with water to furnish the OH- ...
... •do not furnish OHions by dissociation. •react with water to furnish the OH- ...
Chemistry Review - Woodlawn School Wiki
... show work to find out what ion or ions were in my solution. 2) A 1.42-g sample of a pure compound, with formula M2SO4 , was dissolved in a water and treated with an excess of aqueous barium chloride, resulting in the precipitation of all the sulfate ions as barium sulfate. The precipitate was collec ...
... show work to find out what ion or ions were in my solution. 2) A 1.42-g sample of a pure compound, with formula M2SO4 , was dissolved in a water and treated with an excess of aqueous barium chloride, resulting in the precipitation of all the sulfate ions as barium sulfate. The precipitate was collec ...
Quiz 1
... 7. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning solution A with a pH of 11.5 compared to solution B with a pH of 10.0? Solution A… a. has a smaller [OH¯] than solution B b. has a larger number of [H+] than solution B c. is more basic than solution B d. is more acidic than solution B e. h ...
... 7. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning solution A with a pH of 11.5 compared to solution B with a pH of 10.0? Solution A… a. has a smaller [OH¯] than solution B b. has a larger number of [H+] than solution B c. is more basic than solution B d. is more acidic than solution B e. h ...
Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH - Chemwiki
... ChemWiki: The Dynamic Chemistry E-textbook > Physical Chemistry > Acids and Bases > Ionization Constants > Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH ...
... ChemWiki: The Dynamic Chemistry E-textbook > Physical Chemistry > Acids and Bases > Ionization Constants > Calculating a Ka Value from a Known pH ...
Ch. 2-2 Properties of Water
... The pH scale • Chemists have devised a measurement system called the pH scale to indicate the concentration of H+ ions in solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. • At a pH of 7, concentration of H+ and OHions is equal. • Pure water has a pH of 7 ...
... The pH scale • Chemists have devised a measurement system called the pH scale to indicate the concentration of H+ ions in solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. • At a pH of 7, concentration of H+ and OHions is equal. • Pure water has a pH of 7 ...
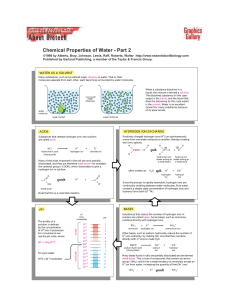
WATER AS A SOLVENT ACIDS HYDROGEN ION EXCHANGE pH
... hydroxyl ion (water acting as (water acting as a weak base) a weak acid) ...
... hydroxyl ion (water acting as (water acting as a weak base) a weak acid) ...
Acid-Base Theories Arrhenius Acids and Bases • An acid is a
... Acid-Base Theories Arrhenius Acids and Bases ...
... Acid-Base Theories Arrhenius Acids and Bases ...
(activity) of hydrogen ions
... associate with water molecules to form hydronium (H3O+) ions, pH is often expressed in terms of the concentration of hydronium ions. ...
... associate with water molecules to form hydronium (H3O+) ions, pH is often expressed in terms of the concentration of hydronium ions. ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.