2011 Lecture 22: Transport in Bulk Electrolytes
... voltage. In the NP equation, the flux is decomposed into to contributions, chemical diffusion due to concentrated gradients, and electromigration, or drift, in the electric field. Conservation of mass implies, ∂ci + ∇ · (~uci + F~i ) = Ri ∂t ...
... voltage. In the NP equation, the flux is decomposed into to contributions, chemical diffusion due to concentrated gradients, and electromigration, or drift, in the electric field. Conservation of mass implies, ∂ci + ∇ · (~uci + F~i ) = Ri ∂t ...
Honors Chemistry
... 5. In combustion reactions, the water, CO2, and O2 are gases. The hydrocarbon is hard to tell, but is usually a liquid after C=5 or higher. 6. Most other covalent compounds are gases. 7. Acids (chemicals starting with hydrogen) are always aqueous. ...
... 5. In combustion reactions, the water, CO2, and O2 are gases. The hydrocarbon is hard to tell, but is usually a liquid after C=5 or higher. 6. Most other covalent compounds are gases. 7. Acids (chemicals starting with hydrogen) are always aqueous. ...
chemistry 11 exam review
... 6. 45 mL of gas at 15C and 790 torr is changed to 23C and 810 torr. What is the new volume? (45 mL) 7. 175 mL of gas at –30.0C and 2.57 atm is changed to standard conditions. What is the new volume? (505 mL) 8. What pressure is needed to change 130 mL of gas at 740 torr to 150 mL? (641 torr) 9. W ...
... 6. 45 mL of gas at 15C and 790 torr is changed to 23C and 810 torr. What is the new volume? (45 mL) 7. 175 mL of gas at –30.0C and 2.57 atm is changed to standard conditions. What is the new volume? (505 mL) 8. What pressure is needed to change 130 mL of gas at 740 torr to 150 mL? (641 torr) 9. W ...
Notes for powerpoint and worksheets PDF
... This should makes sense because Al has a +3 charge and Cl has a ‐1 charge 3. The subscript is ONLY associated with the element symbol to the immediate left. TRY THESE: ...
... This should makes sense because Al has a +3 charge and Cl has a ‐1 charge 3. The subscript is ONLY associated with the element symbol to the immediate left. TRY THESE: ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... 21. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of [OH-] = 3.0 x 10-2 M? What is the pH? 22. What is the pH of a solution if the [H+] = 3.4 x 10-5 M? What is the hydroxide concentration? 23. Determine the pH of a 2.0 x 10-2 M Sr(OH)2? 24. The pH of a solution is measured and determined to be 7.52? What i ...
... 21. What is the hydrogen ion concentration of [OH-] = 3.0 x 10-2 M? What is the pH? 22. What is the pH of a solution if the [H+] = 3.4 x 10-5 M? What is the hydroxide concentration? 23. Determine the pH of a 2.0 x 10-2 M Sr(OH)2? 24. The pH of a solution is measured and determined to be 7.52? What i ...
Full answers
... atom is a large, many-electron atom so its electron cloud is more easily polarised than the C or H in CH4 and therefore I2 has stronger dispersion forces and the higher melting point. NaCl is an ionic compound with strong coulombic attraction between the Na+ ions and the Cl– ions packed together in ...
... atom is a large, many-electron atom so its electron cloud is more easily polarised than the C or H in CH4 and therefore I2 has stronger dispersion forces and the higher melting point. NaCl is an ionic compound with strong coulombic attraction between the Na+ ions and the Cl– ions packed together in ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Using Algebra
... Step 1. Assign a variable to each unknown coefficient. ...
... Step 1. Assign a variable to each unknown coefficient. ...
11U CHEMISTRY EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS June 2010
... 20. Describe the Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry definitions of an acid and a base. ...
... 20. Describe the Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry definitions of an acid and a base. ...
Formation of Solutions
... Sodium Chloride dissolves by dissociation. This is how an Ionic Compound separates into ions. ...
... Sodium Chloride dissolves by dissociation. This is how an Ionic Compound separates into ions. ...
makeup6
... 4. A 4.0 g sample of impure Ca(NO3)2 was found to contain 0.85 g of calcium. What percentage of Ca(NO3)2 was in the original sample? (molar mass of Ca(NO3)2 = 164.1 g mol¯1) (A) 13 % (B) 36 % (C) 64 % (D) 87 % 5. Aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is insoluble in water, but dissolves readily in both acidi ...
... 4. A 4.0 g sample of impure Ca(NO3)2 was found to contain 0.85 g of calcium. What percentage of Ca(NO3)2 was in the original sample? (molar mass of Ca(NO3)2 = 164.1 g mol¯1) (A) 13 % (B) 36 % (C) 64 % (D) 87 % 5. Aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is insoluble in water, but dissolves readily in both acidi ...
What other element has similar properties to Chlorine Cl (#17)
... 7. How many atoms of lithium would it take to ionically bond to one atom of nitrogen? 8. Which equation is balanced? Balance the one that is not already balanced. A) H3PO4 + KOH => K3PO4 + H2O B) HCl + NaOH => NaCl + H2O 9. How many water molecules are needed to balance this equation 2 NaOH + H2CO3 ...
... 7. How many atoms of lithium would it take to ionically bond to one atom of nitrogen? 8. Which equation is balanced? Balance the one that is not already balanced. A) H3PO4 + KOH => K3PO4 + H2O B) HCl + NaOH => NaCl + H2O 9. How many water molecules are needed to balance this equation 2 NaOH + H2CO3 ...
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 1998 - University of Waterloo
... 22. Two flexible containers for gases are at the same temperature and pressure. One holds 0.50 grams of hydrogen and the other holds 8.0 grams of oxygen. Which one of the following statements regarding these gas samples is false? (The relative atomic mass of oxygen is 16.0 and that of hydrogen is 1. ...
... 22. Two flexible containers for gases are at the same temperature and pressure. One holds 0.50 grams of hydrogen and the other holds 8.0 grams of oxygen. Which one of the following statements regarding these gas samples is false? (The relative atomic mass of oxygen is 16.0 and that of hydrogen is 1. ...
General Chemistry Review Problems
... a. How many calories are transferred to 75.0 g water when the initial temperature of water was 26.2C and the final temperature was 37.0C? (Heat capacity of water is 1cal/gC). b. Due to heat loss to the surroundings, the amount you calculated is lower than it should have been. Suppose under perfec ...
... a. How many calories are transferred to 75.0 g water when the initial temperature of water was 26.2C and the final temperature was 37.0C? (Heat capacity of water is 1cal/gC). b. Due to heat loss to the surroundings, the amount you calculated is lower than it should have been. Suppose under perfec ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Have a sour taste. Vinegar owes its taste to acetic acid. Citrus fruits contain citric acid. Cause color changes in plant dyes. React with certain metals to produce hydrogen gas. 2HCl (aq) + Mg (s) ...
... Have a sour taste. Vinegar owes its taste to acetic acid. Citrus fruits contain citric acid. Cause color changes in plant dyes. React with certain metals to produce hydrogen gas. 2HCl (aq) + Mg (s) ...
Document
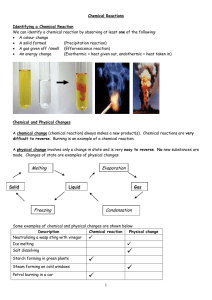
... present in a reaction mixture (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. • Sometimes there is no visible change in the solution, but the reaction still occurred ...
... present in a reaction mixture (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. • Sometimes there is no visible change in the solution, but the reaction still occurred ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.