Chemistry II Exams and Keys 2013 Season
... Chemistry II Exam March 2013 Answer the following questions on the answer sheet provided. Each correct response is worth 4 points. Use the letters in parentheses for your answers. Choose the letter that best completes or answers the item. Be certain that erasures are complete. Please PRINT your name ...
... Chemistry II Exam March 2013 Answer the following questions on the answer sheet provided. Each correct response is worth 4 points. Use the letters in parentheses for your answers. Choose the letter that best completes or answers the item. Be certain that erasures are complete. Please PRINT your name ...
experiment 10 - Faculty Web Pages
... where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ and B¯. The formation of a precipitate, the evolution of a gas, and a temperatu ...
... where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ and B¯. The formation of a precipitate, the evolution of a gas, and a temperatu ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions and Equations Study Guide
... 4. What information do you have to know before you can write the formula for an ionic compound? symbol and charge 5. When determining the subscripts in an ionic compound’s formula, what net charge do you want the compound to have? ...
... 4. What information do you have to know before you can write the formula for an ionic compound? symbol and charge 5. When determining the subscripts in an ionic compound’s formula, what net charge do you want the compound to have? ...
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Separation of components using decantation, filtration, extraction and sublimation methods ...
... • Separation of components using decantation, filtration, extraction and sublimation methods ...
Lectures 1-6 - TCD Chemistry
... Understand thermodynamics cycles to explain qualitatively ΔH and ΔS of solution for ideal non-ionic and ionic solids. ΔH of hydration of ions. Effect of temperature on solubility and its relationship to ΔH of solution (ΔHsoln ) ...
... Understand thermodynamics cycles to explain qualitatively ΔH and ΔS of solution for ideal non-ionic and ionic solids. ΔH of hydration of ions. Effect of temperature on solubility and its relationship to ΔH of solution (ΔHsoln ) ...
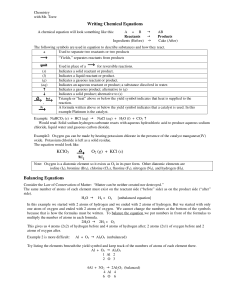
Writing Chemical Equations KClO3 O2 (g) + KCl (s) Balancing
... A formula written above or below the yield symbol indicates that a catalyst is used. In this example Platinum is the catalyst. ...
... A formula written above or below the yield symbol indicates that a catalyst is used. In this example Platinum is the catalyst. ...
8B31A38F-1279-3B00-CDA90244BEA11A7B
... • There are 3 forms bonding atoms: • Ionic—complete transfer of 1 or more electrons from one atom to another (one loses, the other gains) • Covalent—some valence electrons shared between atoms • Metallic – holds atoms of a metal together ...
... • There are 3 forms bonding atoms: • Ionic—complete transfer of 1 or more electrons from one atom to another (one loses, the other gains) • Covalent—some valence electrons shared between atoms • Metallic – holds atoms of a metal together ...
Practice with Chemical Equilibrium (Chapter 14) (Due 2/17)
... Here are four additional practice exercises concerning chemical equilibrium (Chapter 14). See your instructor if you have questions. Note that for these questions, the symbol "=" is used to indicate a reversible reaction. Your textbook uses a double-headed arrow. 1. Suppose that equal molar amounts ...
... Here are four additional practice exercises concerning chemical equilibrium (Chapter 14). See your instructor if you have questions. Note that for these questions, the symbol "=" is used to indicate a reversible reaction. Your textbook uses a double-headed arrow. 1. Suppose that equal molar amounts ...
Exam 2
... 6. In the reduction of 2-butanone to (2)-butanol using the (S)-CBS reagent (2-methyloxazaborolidine + BH3), what is transferred in the critical step in the reaction mechanism? a) a hydride ion, H- b) a hydrogen radical, H c) a proton, H+ d) both hydrogens simultaneously as molecular hydrogen, H2 e) ...
... 6. In the reduction of 2-butanone to (2)-butanol using the (S)-CBS reagent (2-methyloxazaborolidine + BH3), what is transferred in the critical step in the reaction mechanism? a) a hydride ion, H- b) a hydrogen radical, H c) a proton, H+ d) both hydrogens simultaneously as molecular hydrogen, H2 e) ...
The Copper Cycle
... and excess hydronium ions (H3O+) remain from the nitric acid used. 2nd Beaker: Adding NaOH(aq) to the blue solution results in the OH– ions neutralizing the H3O+ ions to form water: H3O+(aq) + OH–(aq) → 2 H2O(l). The Na+ ions and resulting water molecules are not shown. 3rd and 4th Beakers: Once all ...
... and excess hydronium ions (H3O+) remain from the nitric acid used. 2nd Beaker: Adding NaOH(aq) to the blue solution results in the OH– ions neutralizing the H3O+ ions to form water: H3O+(aq) + OH–(aq) → 2 H2O(l). The Na+ ions and resulting water molecules are not shown. 3rd and 4th Beakers: Once all ...
ENVE3503 – Environmental Engineering Expectations for Chapter 2
... b. Mercury levels in Lake Erie walleye averaged 0.3 ppm in 1977. Express this in an appropriate mass/mass format. 4. Understand how mass/volume and mole/volume concentration units are applied in expressing contaminant levels in water. 5. Be able to perform mass/volume and mole/volume calculations, e ...
... b. Mercury levels in Lake Erie walleye averaged 0.3 ppm in 1977. Express this in an appropriate mass/mass format. 4. Understand how mass/volume and mole/volume concentration units are applied in expressing contaminant levels in water. 5. Be able to perform mass/volume and mole/volume calculations, e ...
2014-15 FINAL REVIEW Nomenclature: Chemical Name Chemical
... 1. What is the molarity of 5.00 g of NaOH in 750.0 mL of solution? 2. What weight (in grams) of H2SO4 would be needed to make 750.0 mL of 2.00 M solution? ...
... 1. What is the molarity of 5.00 g of NaOH in 750.0 mL of solution? 2. What weight (in grams) of H2SO4 would be needed to make 750.0 mL of 2.00 M solution? ...
1999 Advanced Placement Chemistry Exam Section I: Multiple
... efficients reduced to lowest whole-number (B) Separate layers of immiscible liquids form terms, the coefficient for OH–(aq) is with a blue layer on top. (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (C) The color of the solution turns from light (D) 4 (E) 6 blue to dark blue. (D) Bubbles of ammonia gas form. 43. A sample of 61 ...
... efficients reduced to lowest whole-number (B) Separate layers of immiscible liquids form terms, the coefficient for OH–(aq) is with a blue layer on top. (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (C) The color of the solution turns from light (D) 4 (E) 6 blue to dark blue. (D) Bubbles of ammonia gas form. 43. A sample of 61 ...
Combined
... Answer ALL questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided. 1. (a) A sodium hydroxide solution has been exposed to air for a long time. When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to it, colourless gas bubbles are given out. Explain the observation with the help of equations. ...
... Answer ALL questions. Write your answers in the spaces provided. 1. (a) A sodium hydroxide solution has been exposed to air for a long time. When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to it, colourless gas bubbles are given out. Explain the observation with the help of equations. ...
Chemistry 40S – Exam Review
... At equilibrium, the [NOCl] was 0.34 mol/L. What is the Keq. 5. a) Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following balanced equation: 2SO3(g) + 188.1 kJ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) b) What can be done to maximize the amount of SO2(g) + O2(g) produced. 6. Consider the following equilibrium equation: ...
... At equilibrium, the [NOCl] was 0.34 mol/L. What is the Keq. 5. a) Write the equilibrium constant expression for the following balanced equation: 2SO3(g) + 188.1 kJ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) b) What can be done to maximize the amount of SO2(g) + O2(g) produced. 6. Consider the following equilibrium equation: ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.