Final Exam Review
... acid. heat of solution, H, has these units: kcal per mole. Convert cal to kcal and plug in your data.] (Ch. 10) a. –1.78 kcal/mole d. –17. 8 kcal/mole b. –8.9 kcal/mole e. –17,800 kcal/mole c. –9.81 kcal/mole 32. An isotope of krypton, 89Kr, has a half-life of 3.2 minutes. If the original sample wa ...
... acid. heat of solution, H, has these units: kcal per mole. Convert cal to kcal and plug in your data.] (Ch. 10) a. –1.78 kcal/mole d. –17. 8 kcal/mole b. –8.9 kcal/mole e. –17,800 kcal/mole c. –9.81 kcal/mole 32. An isotope of krypton, 89Kr, has a half-life of 3.2 minutes. If the original sample wa ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Note: You could also calculate Kp by using the ideal gas law - more on that later. ...
... Note: You could also calculate Kp by using the ideal gas law - more on that later. ...
Large Gate Modulation in the Current of a Room Temperature
... is determined by statistical analysis of a large number of molecular junctions (Figure 1a).7 A large gate field is achieved using an electrochemical gate in which the gate voltage is applied between the source and a gate in the electrolyte.8 Since the gate voltage falls across the double layers at t ...
... is determined by statistical analysis of a large number of molecular junctions (Figure 1a).7 A large gate field is achieved using an electrochemical gate in which the gate voltage is applied between the source and a gate in the electrolyte.8 Since the gate voltage falls across the double layers at t ...
Burning to Learn: An Introduction to Flame Retardants
... Background This activity demonstrates the effectiveness of flame retardants. Background information about combustion and flame retardants can be found in the work of Kesner and de Vos (1), which led to this Activity. The use of boric acid was suggested by a children’s science experiment written by R ...
... Background This activity demonstrates the effectiveness of flame retardants. Background information about combustion and flame retardants can be found in the work of Kesner and de Vos (1), which led to this Activity. The use of boric acid was suggested by a children’s science experiment written by R ...
1994 AP Chemistry Multiple Choice
... 36. Zn(s) + Cu2+ _ Zn2+ + Cu(s) An electrolytic cell based on the reaction represented above was constructed from zinc and copper half– cells. The observed voltage was found to be 1.00 volt instead of the standard cell potential, E_, of 1.10 volts. Which of the following could correctly account for ...
... 36. Zn(s) + Cu2+ _ Zn2+ + Cu(s) An electrolytic cell based on the reaction represented above was constructed from zinc and copper half– cells. The observed voltage was found to be 1.00 volt instead of the standard cell potential, E_, of 1.10 volts. Which of the following could correctly account for ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... the exam, please ask the proctor. Open and start this exam when instructed. When finished, place your Scantron form and note card in the appropriate stacks. You may keep the exam packet, so please show your work and mark the answers you selected on it. 1 inch = 2.54 cm (exact) 1000 mm = 1 m 1 mole ( ...
... the exam, please ask the proctor. Open and start this exam when instructed. When finished, place your Scantron form and note card in the appropriate stacks. You may keep the exam packet, so please show your work and mark the answers you selected on it. 1 inch = 2.54 cm (exact) 1000 mm = 1 m 1 mole ( ...
Extractible Synthesis and Characterization of Cu (II) Complex with
... Organic solution of copper (II) carboxylate was prepared by solvent extraction from an aqueous CuSO4.5H2O solution. During the extraction operation, the aqueous solution pH was adjusted at around pH 7 by the addition of dilute NaOH solution. The initial concentration copper (II) concentration was 0. ...
... Organic solution of copper (II) carboxylate was prepared by solvent extraction from an aqueous CuSO4.5H2O solution. During the extraction operation, the aqueous solution pH was adjusted at around pH 7 by the addition of dilute NaOH solution. The initial concentration copper (II) concentration was 0. ...
File
... product of the following reactions: 2 Na(s) + SrBr2(aq) NR CrI3(aq) + 3 KCl(aq) CrCl3(s) + 3 KI(aq) (DR – ppt) Zn(s) + H2SO3(aq) ZnSO3(aq) + H2(g) (SR – metal + acid) K2CO3(aq) + 2 HI(aq) 2 KI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) (DR – gas) ...
... product of the following reactions: 2 Na(s) + SrBr2(aq) NR CrI3(aq) + 3 KCl(aq) CrCl3(s) + 3 KI(aq) (DR – ppt) Zn(s) + H2SO3(aq) ZnSO3(aq) + H2(g) (SR – metal + acid) K2CO3(aq) + 2 HI(aq) 2 KI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) (DR – gas) ...
chemistry - Kanpur University
... Electronic structure, oxidation states and ionic radii and lanthanide contraction, complex formation, occurrence and isolation, ceric ammonium sulphate and its analytical uses. ...
... Electronic structure, oxidation states and ionic radii and lanthanide contraction, complex formation, occurrence and isolation, ceric ammonium sulphate and its analytical uses. ...
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
... Neither PbCl2 nor PbF2 are appreciably soluble in water. If solid PbCl2 and solid PbF2 are placed in separate beakers, in which beaker is the [Pb2+] greatest? Explain your choice. The equilibrium constants for the solids dissolving in water are: ...
... Neither PbCl2 nor PbF2 are appreciably soluble in water. If solid PbCl2 and solid PbF2 are placed in separate beakers, in which beaker is the [Pb2+] greatest? Explain your choice. The equilibrium constants for the solids dissolving in water are: ...
A) Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e
... A) Br 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the iodide ion. B) Br2 will oxidize the iodide ion, but not the chloride ion. C) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. D) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. E) Cl 2 will oxidize the bromide ion, but not the ...
... A) Br 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the iodide ion. B) Br2 will oxidize the iodide ion, but not the chloride ion. C) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. D) I 2 will oxidize the chloride ion, but not the bromide ion. E) Cl 2 will oxidize the bromide ion, but not the ...
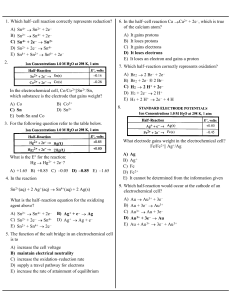
electrochemistry
... where the total battery potential is equal to the sum of the potentials of the individual cells. There are three types of batteries – primary batteries, secondary batteries, and the fuel cell. Primary batteries are not re-chargeable, where as secondary batteries are re-chargeable. Fuel cell will las ...
... where the total battery potential is equal to the sum of the potentials of the individual cells. There are three types of batteries – primary batteries, secondary batteries, and the fuel cell. Primary batteries are not re-chargeable, where as secondary batteries are re-chargeable. Fuel cell will las ...
aq - Byron High School
... Neutralization Reactions When a strong acid reacts with a strong base, the net ionic equation is… HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + OH-(aq) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + H2O (l) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + H2O (l) ...
... Neutralization Reactions When a strong acid reacts with a strong base, the net ionic equation is… HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + OH-(aq) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + H2O (l) H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + H2O (l) ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.