CH 17 Study Guide with answer Key
... reactants and products, changing the volume of the reaction vessel causes no (11) ________________________ in the equilibrium. Changing the temperature of a reaction at equilibrium alters both the equilibrium (12) ________________________ and the equilibrium position. When a reaction is (13) _______ ...
... reactants and products, changing the volume of the reaction vessel causes no (11) ________________________ in the equilibrium. Changing the temperature of a reaction at equilibrium alters both the equilibrium (12) ________________________ and the equilibrium position. When a reaction is (13) _______ ...
Chemistry Syllabus - Madison County Schools
... Properties of acids and bases, including how they affect indicators and the relative pH of the solution Formation of acidic and basic solutions Definition of pH in terms of the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide concentration The pH or pOH from the hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion co ...
... Properties of acids and bases, including how they affect indicators and the relative pH of the solution Formation of acidic and basic solutions Definition of pH in terms of the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide concentration The pH or pOH from the hydrogen ion or hydroxide ion co ...
Activity Series Unit
... 26. Generally speaking, what happens to the metals in these reactions? The metals are losing electrons in these reactions. 27. When looking at electrons, what can be said about the term, oxidation? When a species is oxidized, it loses electrons. 28. Count the number of electrons in each of the oxyge ...
... 26. Generally speaking, what happens to the metals in these reactions? The metals are losing electrons in these reactions. 27. When looking at electrons, what can be said about the term, oxidation? When a species is oxidized, it loses electrons. 28. Count the number of electrons in each of the oxyge ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... Chemical reaction rates affected by temperature, concentration, surface area, pressure, mixing, and the presence of a catalyst LeChatelier’s Principle 5a. Analyze and explain acid/base reactions. (DOK 2) Properties of acids and bases, including how they affect indicators and the relative pH of ...
... Chemical reaction rates affected by temperature, concentration, surface area, pressure, mixing, and the presence of a catalyst LeChatelier’s Principle 5a. Analyze and explain acid/base reactions. (DOK 2) Properties of acids and bases, including how they affect indicators and the relative pH of ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... It has only qualitative meaning, until the equation is balanced are given. Provide valuable information such as the number of moles or atoms of the elements or formulas contained in the equation. Example methane + oxygen →carbon dioxide and water CH4(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) Unbalanced CH4(g) + ...
... It has only qualitative meaning, until the equation is balanced are given. Provide valuable information such as the number of moles or atoms of the elements or formulas contained in the equation. Example methane + oxygen →carbon dioxide and water CH4(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) Unbalanced CH4(g) + ...
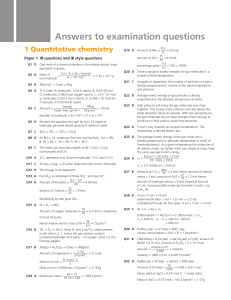
Answers to examination questions
... has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater than bonding pair repulsion. Q7 A Hydrogen bonding would only be expected to occur in CH2CH3COOH since it contains hydrogen bonded directly to oxygen. The −OH group is a ...
... has two lone pairs around the central atom, compared with one for ammonia and none for methane. Lone pair repulsion is greater than bonding pair repulsion. Q7 A Hydrogen bonding would only be expected to occur in CH2CH3COOH since it contains hydrogen bonded directly to oxygen. The −OH group is a ...
1st-Year-ch-wise-test
... Q.No.1: Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best option followed by each question. (1) Which formula shows highest percentage of nitrogen by mass (a) NH3 (b) H2H4 (c) NO (d) NH4OH (2) During combustion analysis, CO2 is absorbed in (a) Mg (ClO4) 2 (b) Conc. H2SO4 (c) 50% KOH (d) lime stone (3) The ...
... Q.No.1: Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best option followed by each question. (1) Which formula shows highest percentage of nitrogen by mass (a) NH3 (b) H2H4 (c) NO (d) NH4OH (2) During combustion analysis, CO2 is absorbed in (a) Mg (ClO4) 2 (b) Conc. H2SO4 (c) 50% KOH (d) lime stone (3) The ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The distance between stars is several light years on the average. Hydrogen is also the major constituent of the interstellar space. There are about 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The empty space between galaxies is vast. For example, the Milky W ...
... of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The distance between stars is several light years on the average. Hydrogen is also the major constituent of the interstellar space. There are about 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The empty space between galaxies is vast. For example, the Milky W ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... consisting of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The distance between stars is several light years on the average. Hydrogen is also the major constituent of the interstellar space. There are about 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The empty space between galaxies is vast. For example, ...
... consisting of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The distance between stars is several light years on the average. Hydrogen is also the major constituent of the interstellar space. There are about 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The empty space between galaxies is vast. For example, ...
Problem 1: A brief history of life in the universe
... consisting of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The distance between stars is several light years on the average. Hydrogen is also the major constituent of the interstellar space. There are about 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The empty space between galaxies is vast. For example, ...
... consisting of over 100 billion stars, is rich in hydrogen. The distance between stars is several light years on the average. Hydrogen is also the major constituent of the interstellar space. There are about 100 billion galaxies in the universe. The empty space between galaxies is vast. For example, ...
Ordinary Level - State Examination Commission
... of which is the element carbon. Coal often contains small quantities of sulfur in the form of iron sulfide (FeS). Name the two oxides of carbon that can be produced when coal is burned. Which one of these oxides is acidic? Figure 17 ...
... of which is the element carbon. Coal often contains small quantities of sulfur in the form of iron sulfide (FeS). Name the two oxides of carbon that can be produced when coal is burned. Which one of these oxides is acidic? Figure 17 ...
Supramolecular Assemblies Built from Lanthanide
... examples of lanthanide ions bound to three adjacent carbonyl groups of CB6: the first to have been reported involves the praseodymium ion, in a structure quite analogous to the present one, but for one cation being present at each portal and the replacement of the included β-al ligand by a nitrate i ...
... examples of lanthanide ions bound to three adjacent carbonyl groups of CB6: the first to have been reported involves the praseodymium ion, in a structure quite analogous to the present one, but for one cation being present at each portal and the replacement of the included β-al ligand by a nitrate i ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... Ans.1 Metallic solids Metallic solids are conductors of electricity in solid state as well as in molten state. Ionic solids Ionic solids are insulators in solid state but conductors in molten state and in aqueous solutions. Ans.2 In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to a given su ...
... Ans.1 Metallic solids Metallic solids are conductors of electricity in solid state as well as in molten state. Ionic solids Ionic solids are insulators in solid state but conductors in molten state and in aqueous solutions. Ans.2 In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to a given su ...
Word - Chemistry and More
... d) Determine the mass percentage of each element in barium hydroxide. e) Determine the number of moles of oxygen in 49.7 grams of barium hydroxide. 13. (Chapter 10) A calorimeter containing water is used to measure the heat produced by a chemical reaction. If the water absorbs 58.5 kJ when the tempe ...
... d) Determine the mass percentage of each element in barium hydroxide. e) Determine the number of moles of oxygen in 49.7 grams of barium hydroxide. 13. (Chapter 10) A calorimeter containing water is used to measure the heat produced by a chemical reaction. If the water absorbs 58.5 kJ when the tempe ...
Evaluation of Interaction Effect of Sulfate and Chloride Ions on
... The material of the electrodes applied in the test was GB/T700 Q235A carbon steel, with a chemical composition of (wt.%): C 0.22% Si 0.30% Mn 1.40% P 0.045% S 0.05% Cr 0.01% Ni 0.01% and Fe being the balance. The specimens used as the working electrode were machined in a dimension of 10×10×3 mm3 (a ...
... The material of the electrodes applied in the test was GB/T700 Q235A carbon steel, with a chemical composition of (wt.%): C 0.22% Si 0.30% Mn 1.40% P 0.045% S 0.05% Cr 0.01% Ni 0.01% and Fe being the balance. The specimens used as the working electrode were machined in a dimension of 10×10×3 mm3 (a ...
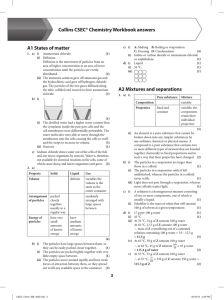
Collins CSEC® Chemistry Workbook answers A1 States of matter
... Döbereiner found that if certain groups of three elements that possessed similar properties were arranged in increasing relative atomic mass, the relative atomic mass of the middle element was close to the average of the other two elements. Mendeleev created the first version of the periodic table. ...
... Döbereiner found that if certain groups of three elements that possessed similar properties were arranged in increasing relative atomic mass, the relative atomic mass of the middle element was close to the average of the other two elements. Mendeleev created the first version of the periodic table. ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.