No Slide Title - McMaster Chemistry
... STRONG ACIDS - react completely with water to form H3O+ (aq) HCl (aq) + H2O H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) STRONG BASES - react completely with water to form OH- (aq) Li2O + H2O 2 Li+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Weak ACIDS/ weak BASES only react partially with water - an EQUILIBRIUM is formed : the conjugate ACID and ...
... STRONG ACIDS - react completely with water to form H3O+ (aq) HCl (aq) + H2O H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) STRONG BASES - react completely with water to form OH- (aq) Li2O + H2O 2 Li+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Weak ACIDS/ weak BASES only react partially with water - an EQUILIBRIUM is formed : the conjugate ACID and ...
Useful Rocks - We can`t sign you in
... anode where they lose an electron • The neutral chlorine atoms produced join up into pairs ...
... anode where they lose an electron • The neutral chlorine atoms produced join up into pairs ...
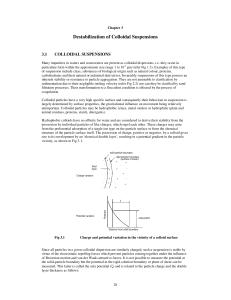
Destabilisation of colloidal suspensions
... The zeta potential is determined experimentally in an externally applied electric field. The ordinary range of zeta potential is 20 to 200 mV (Fair et al., 1968). Optimum coagulation may be expected to occur when the zeta potential has been reduced to zero (the isoelectric condition of the suspensio ...
... The zeta potential is determined experimentally in an externally applied electric field. The ordinary range of zeta potential is 20 to 200 mV (Fair et al., 1968). Optimum coagulation may be expected to occur when the zeta potential has been reduced to zero (the isoelectric condition of the suspensio ...
E - Analytical Chemistry
... To make a working cell, the reactants are separated into two half-cells which are connected with a salt bridge. The salt bridge is a U-shaped tube filled with a gel containing a high concentration of KNO3 (or other electrolyte that does not affect the cell reaction). The ends of the bridge are porou ...
... To make a working cell, the reactants are separated into two half-cells which are connected with a salt bridge. The salt bridge is a U-shaped tube filled with a gel containing a high concentration of KNO3 (or other electrolyte that does not affect the cell reaction). The ends of the bridge are porou ...
- Department of Chemistry, York University
... There are two (competing) theories: (1) Organic compounds were delivered to Earth by interplanetary dust, meteorites, comets and asteroids: “Panspermia” (2) Organic compounds were synthesized ...
... There are two (competing) theories: (1) Organic compounds were delivered to Earth by interplanetary dust, meteorites, comets and asteroids: “Panspermia” (2) Organic compounds were synthesized ...
Indian National Chemistry Olympiad Theory 2014
... Hydrogen is a renewable source of energy and considered as a fuel of the future. One of the problems of its use is storage and transportation. Research has shown that several metal hydrides act as ‘hydrogen tanks’. Large quantities of hydrogen can be absorbed on them and desorbed when needed through ...
... Hydrogen is a renewable source of energy and considered as a fuel of the future. One of the problems of its use is storage and transportation. Research has shown that several metal hydrides act as ‘hydrogen tanks’. Large quantities of hydrogen can be absorbed on them and desorbed when needed through ...
Multiphoton ionization of inner-valence electrons and fragmentation
... satisfactory model for this ‘no man’s land’. From the upper scale of Fig. 3, it is seen that our experiment is being done in the range of g - gcr so that using Eq. Ž4. is justified. To apply Eq. Ž4. in our case we make the following considerations. Firstly, the effect of the Franck– Condon factors o ...
... satisfactory model for this ‘no man’s land’. From the upper scale of Fig. 3, it is seen that our experiment is being done in the range of g - gcr so that using Eq. Ž4. is justified. To apply Eq. Ž4. in our case we make the following considerations. Firstly, the effect of the Franck– Condon factors o ...
Acids ,Bases and Salts
... (ii) For the backward reaction from right to left, NH4+ donates a proton to form NH3 and thus NH4+ is an ‘opposite’ proton donor. It is a Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid (b)(i)For the forward reaction from left to right, HCl donates a proton to form Cl- and thus HCl is a proton donor . It is a Bronste ...
... (ii) For the backward reaction from right to left, NH4+ donates a proton to form NH3 and thus NH4+ is an ‘opposite’ proton donor. It is a Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid (b)(i)For the forward reaction from left to right, HCl donates a proton to form Cl- and thus HCl is a proton donor . It is a Bronste ...
Concentration of Solutions
... In this section, we introduce two different ways of expressing the concentrations of solutions: molarity and m olality. Sometimes, solutions are referred to as “dilute” or “concentrated,” but these are not very definite terms. “Dilute” just means that there is a relatively small amount of solute i ...
... In this section, we introduce two different ways of expressing the concentrations of solutions: molarity and m olality. Sometimes, solutions are referred to as “dilute” or “concentrated,” but these are not very definite terms. “Dilute” just means that there is a relatively small amount of solute i ...
May/Jun 16 Paper 3 - Theory (Core) QP S2
... A copy of the Periodic Table is printed on page 20. You may lose marks if you do not show your working or if you do not use appropriate units. At the end of the examination, fasten all your work securely together. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part quest ...
... A copy of the Periodic Table is printed on page 20. You may lose marks if you do not show your working or if you do not use appropriate units. At the end of the examination, fasten all your work securely together. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part quest ...
AP Chemistry
... (c) For both Mg and Na, the first electron is removed from the 3s sublevel, and thus the greater nuclear charge on Mg gives it a higher first ionization energy. The second electron in Mg is also 3s, but in Na it is 2p, which is more tightly bound. (d) In Be, the first valence electron is in a filled ...
... (c) For both Mg and Na, the first electron is removed from the 3s sublevel, and thus the greater nuclear charge on Mg gives it a higher first ionization energy. The second electron in Mg is also 3s, but in Na it is 2p, which is more tightly bound. (d) In Be, the first valence electron is in a filled ...
MIDTERM REVIEW UNIT 1: Mass/Measurement
... 11. In a reaction between lead (II) nitrate and copper (II) bromide, do the following: a) write the formulas for the reactants and the products and balance the equation b) If 0.67 moles of copper (II) ...
... 11. In a reaction between lead (II) nitrate and copper (II) bromide, do the following: a) write the formulas for the reactants and the products and balance the equation b) If 0.67 moles of copper (II) ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.