Special Topics in Heredity
... used to indicate family history. • Carriers: Individuals that are heterozygous for a particular negative trait. The individual doesn’t have the trait, but they carry one bad gene that could be potentially passed onto offspring. ...
... used to indicate family history. • Carriers: Individuals that are heterozygous for a particular negative trait. The individual doesn’t have the trait, but they carry one bad gene that could be potentially passed onto offspring. ...
Lecture 2 PSY391S John Yeomans
... • Can separate and then self-replicate. • Hold all genetic information in higher animals. • Human genome 3.1 billion bases (2000). ...
... • Can separate and then self-replicate. • Hold all genetic information in higher animals. • Human genome 3.1 billion bases (2000). ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
Gene Regulation I. Gene regulation: The ability of an organism to
... same order as the genes on the chromosome. 1. Control what body part will develop in a given location. 2. Similar clusters of Hox genes that control body plans have been found in all animals. C. RNA interference 1. Small pieces of double-stranded RNA in cytoplasm of cell are cut by enzyme called ...
... same order as the genes on the chromosome. 1. Control what body part will develop in a given location. 2. Similar clusters of Hox genes that control body plans have been found in all animals. C. RNA interference 1. Small pieces of double-stranded RNA in cytoplasm of cell are cut by enzyme called ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... Why can’t one cell in a multi-cellular organism function independently of that organism? Even though all cells in an organism contain the same genes, they can vary greatly in structure and function. How is this possible? What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging ...
... Why can’t one cell in a multi-cellular organism function independently of that organism? Even though all cells in an organism contain the same genes, they can vary greatly in structure and function. How is this possible? What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging ...
Interferon-lambda and therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus infection
... promoters of both the IFN-β gene (IFNB) and the IFN-λ genes . ...
... promoters of both the IFN-β gene (IFNB) and the IFN-λ genes . ...
Chem 431C Lecture 10a Test 2 grade distribution Chapter 28
... Promoter = DNA sequence enabling a gene to be transcribed. Promoter is recognized by RNA polymerase. Operator = DNA segment that a regulatory protein binds to. Usually segment between promoter and the genes of the operon. A regulatory protein can be a repressor or activator or selectivity factor. ...
... Promoter = DNA sequence enabling a gene to be transcribed. Promoter is recognized by RNA polymerase. Operator = DNA segment that a regulatory protein binds to. Usually segment between promoter and the genes of the operon. A regulatory protein can be a repressor or activator or selectivity factor. ...
DeKalb County - Purdue University
... c. How many chromosomes are in each cell of the rabbit: _______ or _______ pair. d. How many chromosomes come from the doe: _______ e. How many chromosomes come from the buck: _______ f. XX chromosome means what sex: ______________________ g. XY chromosome means what sex: ______________________ h. I ...
... c. How many chromosomes are in each cell of the rabbit: _______ or _______ pair. d. How many chromosomes come from the doe: _______ e. How many chromosomes come from the buck: _______ f. XX chromosome means what sex: ______________________ g. XY chromosome means what sex: ______________________ h. I ...
Genes - Bill Nye
... 4. ____________ is the chemical genes are made of. 5. _________________ of genes are joined together to make a chromosome. 6. If you uncoil chromosomes, you get long strands of ______________. 7. Genes tell your cells _____________________________. 8. Humans have ______ pairs of chromosomes. 9. Huma ...
... 4. ____________ is the chemical genes are made of. 5. _________________ of genes are joined together to make a chromosome. 6. If you uncoil chromosomes, you get long strands of ______________. 7. Genes tell your cells _____________________________. 8. Humans have ______ pairs of chromosomes. 9. Huma ...
Functional Characterization of Soybean Transcription Factor
... INTRODUCTION: Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences in DNA. Transcription factors are among the major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Memb ...
... INTRODUCTION: Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences in DNA. Transcription factors are among the major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Memb ...
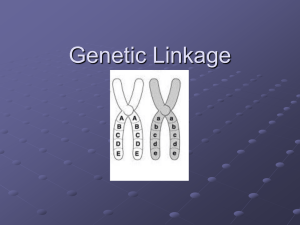
Gene linkage ppt
... Linked genes are pairs or groups of genes which are inherited together, carried on the same chromosome (usually close together) ...
... Linked genes are pairs or groups of genes which are inherited together, carried on the same chromosome (usually close together) ...
What happens to the repressor when lactose is present?
... sequence is found directly before the RNA Polymerase starting point for __________________. This region is known as the TATA _______ Box ...
... sequence is found directly before the RNA Polymerase starting point for __________________. This region is known as the TATA _______ Box ...
Genome-Scale CRISPR-Mediated Control of the Gene
... What they found ● Control of transcript levels for endogenous genes across a high dynamic range (up to ~1000-fold) reveals how gene dose controls function ● Mapping of complex pathways through complementary information provided by CRISPRi and CRISPRa ● CRISPRi provides strong (typically 90%–99%) k ...
... What they found ● Control of transcript levels for endogenous genes across a high dynamic range (up to ~1000-fold) reveals how gene dose controls function ● Mapping of complex pathways through complementary information provided by CRISPRi and CRISPRa ● CRISPRi provides strong (typically 90%–99%) k ...
Regulatory genes
... 3 parts to an operon 1. Operator – controls access of RNA polymerase to the promoter 2. Promoter – where RNA polymerase attaches to begin transcription of genes 3. Genes – code for expression of proteins related to one particular function (e.g. breaking down galactosidase) ...
... 3 parts to an operon 1. Operator – controls access of RNA polymerase to the promoter 2. Promoter – where RNA polymerase attaches to begin transcription of genes 3. Genes – code for expression of proteins related to one particular function (e.g. breaking down galactosidase) ...
PPT
... Perspective: Historically, the conclusions of genetic experiments were based on the results of selected matings; In other words, we didn’t know what was happening inside the cell, but we could make conclusions based on the phenotypic results (e.g. ratios) of the offspring. It was only recently that ...
... Perspective: Historically, the conclusions of genetic experiments were based on the results of selected matings; In other words, we didn’t know what was happening inside the cell, but we could make conclusions based on the phenotypic results (e.g. ratios) of the offspring. It was only recently that ...
Notes from Lecture 1 - Tufts Computer Science
... Genes are the parts of the DNA that code for proteins. You can get different proteins from the same portion of DNA via splicing. ...
... Genes are the parts of the DNA that code for proteins. You can get different proteins from the same portion of DNA via splicing. ...
Title: On two statistical elements of gene expression data analysis
... in nasopharyngeal cancer cells comparing cells grouped according to expression of the Epstein-Barr virus. After reviewing some basic issues and popular approaches to data analysis, I will turn to the problem of assessing enrichment of predefined gene sets (categories) for differentially expressed (D ...
... in nasopharyngeal cancer cells comparing cells grouped according to expression of the Epstein-Barr virus. After reviewing some basic issues and popular approaches to data analysis, I will turn to the problem of assessing enrichment of predefined gene sets (categories) for differentially expressed (D ...
Transcription and Translation
... During transcription, the entire gene is copied into a pre-mRNA, which includes exons and introns. During the process of RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons joined to form a contiguous coding sequence. ...
... During transcription, the entire gene is copied into a pre-mRNA, which includes exons and introns. During the process of RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons joined to form a contiguous coding sequence. ...
sex-linked traits: traits controlled by genes located on thr sex
... SEX-LINKED TRAITS: TRAITS CONTROLLED BY GENES LOCATED ON THR SEX CHROMOSOMES. X = FEMALE SEX CHROMOSOME Y = MALE SEX CHROMOSOME (SMALLER THAN X AND DOES NOT CONTAIN AS MANY GENES) Objectives: 1) Define through example sex-linked traits and polygenic inheritance. 2) Identify other factors that might ...
... SEX-LINKED TRAITS: TRAITS CONTROLLED BY GENES LOCATED ON THR SEX CHROMOSOMES. X = FEMALE SEX CHROMOSOME Y = MALE SEX CHROMOSOME (SMALLER THAN X AND DOES NOT CONTAIN AS MANY GENES) Objectives: 1) Define through example sex-linked traits and polygenic inheritance. 2) Identify other factors that might ...
Presentation
... histones and DNA of chromatin influence both chromatin structure and gene expression Acetylation prevents histones from packing tightly, which allows genes to be expressed. Methylation causes histones to pack tightly so that genes are not expressed. ...
... histones and DNA of chromatin influence both chromatin structure and gene expression Acetylation prevents histones from packing tightly, which allows genes to be expressed. Methylation causes histones to pack tightly so that genes are not expressed. ...
The modern synthesis
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...