Identification of all gene functions within reach
... Simultaneous analysis of all genes possible for the first time This quantum leap is the result of a new procedure with which makes it possible to analyse complex biological processes in all the genes of the fruit fly simultaneously. This unusually extensive gene analysis was only made possible by us ...
... Simultaneous analysis of all genes possible for the first time This quantum leap is the result of a new procedure with which makes it possible to analyse complex biological processes in all the genes of the fruit fly simultaneously. This unusually extensive gene analysis was only made possible by us ...
DO NOW 8 TRAITS
... should be established to regulate cloning? Share your answer with a partner in your group. S7L3.c Recognize that selective breading can produce plants or animals with desired traits. S7L3.a Explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. ...
... should be established to regulate cloning? Share your answer with a partner in your group. S7L3.c Recognize that selective breading can produce plants or animals with desired traits. S7L3.a Explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. ...
Gene Regulation - Cloudfront.net
... the cell may regulate the transcription of individual genes through regulatory molecules (ex. steroids may stimulate the production of certain proteins) certain parts of eukaryotic chromosomes are in a highly condensed, compact state making it inaccessible to RNA polymerase some of these areas are s ...
... the cell may regulate the transcription of individual genes through regulatory molecules (ex. steroids may stimulate the production of certain proteins) certain parts of eukaryotic chromosomes are in a highly condensed, compact state making it inaccessible to RNA polymerase some of these areas are s ...
Test: Gene Regulation Free Response Questions It is known that
... Differences between cells with same genome are a result of differential gene expression. DNA packing and location – genes with highly condensed heterochromatin are not expressed Histone acetylation – attachment of acetyl group to histone tails opens chromatin for transcription DNA methylation – addi ...
... Differences between cells with same genome are a result of differential gene expression. DNA packing and location – genes with highly condensed heterochromatin are not expressed Histone acetylation – attachment of acetyl group to histone tails opens chromatin for transcription DNA methylation – addi ...
Student Notes
... _________________move by means of a DNA intermediate _________________move by means of a RNA intermediate and leave a copy at the original site. The process involves reverse transcriptase (remember this guy? Retroviruses!) Jumping Genes! ...
... _________________move by means of a DNA intermediate _________________move by means of a RNA intermediate and leave a copy at the original site. The process involves reverse transcriptase (remember this guy? Retroviruses!) Jumping Genes! ...
Genes
... Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the affected person has an extra 47th chromosome i ...
... Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the affected person has an extra 47th chromosome i ...
0.-intro-to-biopsych..
... unexpressed genes Phenotype: only expressed genes ◦ EX: the violent gene may never evolve into a phenotype ◦ EX: you may be coded for freckles, but if you don’t go into the sun, you won’t develop them ...
... unexpressed genes Phenotype: only expressed genes ◦ EX: the violent gene may never evolve into a phenotype ◦ EX: you may be coded for freckles, but if you don’t go into the sun, you won’t develop them ...
Control of Gene Expression
... • Methylation of bases also turns off transcription • DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation • In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of either the maternal or paternal alleles of certain genes at the start of development • Although the ...
... • Methylation of bases also turns off transcription • DNA methylation can cause long-term inactivation of genes in cellular differentiation • In genomic imprinting, methylation regulates expression of either the maternal or paternal alleles of certain genes at the start of development • Although the ...
7.1 Reinforcement
... been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the d ...
... been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the d ...
Inheritance Assessment
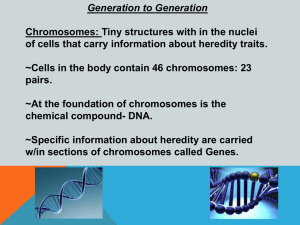
... complement of genetic material. In humans this would be 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) ...
... complement of genetic material. In humans this would be 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) ...
Regulation and Expression of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase in Normal
... Aberrant changes of DNA methylation, histone modification and chromatin compartments are commonly associated with the progression of human cancers. Hypermethylation of CpG islands is the most well categorised epigenetic change to occur in tumours. Many CpG islands associated with transcription of a ...
... Aberrant changes of DNA methylation, histone modification and chromatin compartments are commonly associated with the progression of human cancers. Hypermethylation of CpG islands is the most well categorised epigenetic change to occur in tumours. Many CpG islands associated with transcription of a ...
Control of Gene Express in Prokaryotes
... structural genes, located between the promoter and structural genes, contains the operator site. • Operator Site -region where the repressor attaches • Regulatory genes-codes for repressor proteins • Polycistronic mRNA-transcript for several polypeptides ...
... structural genes, located between the promoter and structural genes, contains the operator site. • Operator Site -region where the repressor attaches • Regulatory genes-codes for repressor proteins • Polycistronic mRNA-transcript for several polypeptides ...
Notes 4-4
... 2. Describe how a cell produces proteins. 3. Identify how mutations can affect an organism. 4-4 The DNA Connection A. The Genetic Code 1. The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits. 2. G ...
... 2. Describe how a cell produces proteins. 3. Identify how mutations can affect an organism. 4-4 The DNA Connection A. The Genetic Code 1. The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits. 2. G ...
Mutations
... way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that develop in specific parts of the body b. Genes tell cells in the bod ...
... way a complex organism develops from single fertilized cell. 1. Hox genes- controls organs and tissues that develop in various parts of the embryo a. Mutation in one of these “master control genes” can completely change organs that develop in specific parts of the body b. Genes tell cells in the bod ...
File - Great 7th grade Scientists
... inside the cell. The directions come from the , which is the command center of the cell. ...
... inside the cell. The directions come from the , which is the command center of the cell. ...
SEMINAR CANCELED- Rescheduled to January 28, 2016
... compared to in vitro growth. Infection profiles suggest that Sut1 acts in the same pathway as Zap1, and we verify that functional relationship with the finding that overexpression of either ZAP1 or the Zap1-dependent zinc transporter gene ZRT2 restores pathogenicity to a sut1 mutant. Perturbation wi ...
... compared to in vitro growth. Infection profiles suggest that Sut1 acts in the same pathway as Zap1, and we verify that functional relationship with the finding that overexpression of either ZAP1 or the Zap1-dependent zinc transporter gene ZRT2 restores pathogenicity to a sut1 mutant. Perturbation wi ...
genetics study guide
... 6. Y chromosome - male characteristics, Y chromosome is much smaller and has genes only for sex determination 7. Why are males more likely to than females to have genetic disorders? All sexlinked genes are expressed, even recessive. Females have a backup X chromosome.. Sex linked genes are NEVER on ...
... 6. Y chromosome - male characteristics, Y chromosome is much smaller and has genes only for sex determination 7. Why are males more likely to than females to have genetic disorders? All sexlinked genes are expressed, even recessive. Females have a backup X chromosome.. Sex linked genes are NEVER on ...
6.5 , 7.1
... disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the disorder. • Sex-linked genes: Genes on the sex-chromosomes (th ...
... disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the disorder. • Sex-linked genes: Genes on the sex-chromosomes (th ...
R 7.1
... disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the disorder. • Sex-linked genes: Genes on the sex-chromosomes (th ...
... disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the disorder. • Sex-linked genes: Genes on the sex-chromosomes (th ...
Gene expression An organism`s genome is the complete set of
... Gene expression An organism’s genome is the complete set of genes in each of its cells. Given an organism, every one of its cells has a copy of the exact same genome, but ◆ not all its cells express the same genes ◆ different genes express under different conditions Measure the levels of the various ...
... Gene expression An organism’s genome is the complete set of genes in each of its cells. Given an organism, every one of its cells has a copy of the exact same genome, but ◆ not all its cells express the same genes ◆ different genes express under different conditions Measure the levels of the various ...