Chapter 19 review - Iowa State University
... to be the phenotype of a larva in which the bicoid gene was expressed in both the anterior region and the posterior region of the oocyte? ...
... to be the phenotype of a larva in which the bicoid gene was expressed in both the anterior region and the posterior region of the oocyte? ...
Mendel chp 5 notes
... EX. Polydactyly- (extra fingers or toes) iii. variably expressive – intensity varies in different people 1. some people may have an extra digit on every extremity or some may just have a partial digit on one extremity h. Pleiotropy - one gene (protein) controls several functions or has more than one ...
... EX. Polydactyly- (extra fingers or toes) iii. variably expressive – intensity varies in different people 1. some people may have an extra digit on every extremity or some may just have a partial digit on one extremity h. Pleiotropy - one gene (protein) controls several functions or has more than one ...
Biology 105 - Montgomery College
... each other in the moonlight. Becoming intoxicated in each other’s pheromones (sexual attractant molecules), and being consenting adults, they decide to procreate. The fertilized eggs are laid and the ensuing spring brings forth their offspring- a veritable plague of 1000 little striders. Each of the ...
... each other in the moonlight. Becoming intoxicated in each other’s pheromones (sexual attractant molecules), and being consenting adults, they decide to procreate. The fertilized eggs are laid and the ensuing spring brings forth their offspring- a veritable plague of 1000 little striders. Each of the ...
Introduction to Genetics and Genomics
... a great number of sequential steps from array preparation • Application -- molecular profiles correlate to disease states -- they can be used as ...
... a great number of sequential steps from array preparation • Application -- molecular profiles correlate to disease states -- they can be used as ...
Introduction to Genetics (Genetics)
... Genetic information is encoded and transmitted from generation to generation in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is a coiled molecule organized into structures called chromosomes within cells. Segments along the length of a DNA molecule form genes. Genes direct the synthesis of proteins, the molecul ...
... Genetic information is encoded and transmitted from generation to generation in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is a coiled molecule organized into structures called chromosomes within cells. Segments along the length of a DNA molecule form genes. Genes direct the synthesis of proteins, the molecul ...
Natural Selection on the Olfactory Receptor Gene Family in
... Human have more than 1000 OR genes, and about 40% have intact (non-mutated) coding region : functional 68 to 72% for apes Comparing the variations at the OR genes with at intergenic region (a stretch of DNA sequences located between clusters of genes that contain few or no genes) ...
... Human have more than 1000 OR genes, and about 40% have intact (non-mutated) coding region : functional 68 to 72% for apes Comparing the variations at the OR genes with at intergenic region (a stretch of DNA sequences located between clusters of genes that contain few or no genes) ...
Exam 4 Key Fa08
... transcription of a cluster of genes. (1 pt) [operator] 7. Any observable trait in an individual. (1 pt) [phenotype] ...
... transcription of a cluster of genes. (1 pt) [operator] 7. Any observable trait in an individual. (1 pt) [phenotype] ...
Genetics Lecture Part 2
... Normally occurring exceptions : sex of parent contributing an allele is a factor 1. Genomic imprinting: genes inside nucleus a. 2 to 3 dozen traits in mammals that depend on which parent passed the trait b. Occurs during gamete formation = results in silencing one of the alleles c. Imprinted differe ...
... Normally occurring exceptions : sex of parent contributing an allele is a factor 1. Genomic imprinting: genes inside nucleus a. 2 to 3 dozen traits in mammals that depend on which parent passed the trait b. Occurs during gamete formation = results in silencing one of the alleles c. Imprinted differe ...
Project Title: Characterization of new genes mediating exchange of
... This REP grant was funded to pursue two major Aims, involving application of DNA repair assays developed in my lab to identify new genes required to fix broken chromosomes during normal cell growth and also in meiosis. Two graduate students, Rachel Roberts and Jennifer Summers, with some assistance ...
... This REP grant was funded to pursue two major Aims, involving application of DNA repair assays developed in my lab to identify new genes required to fix broken chromosomes during normal cell growth and also in meiosis. Two graduate students, Rachel Roberts and Jennifer Summers, with some assistance ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
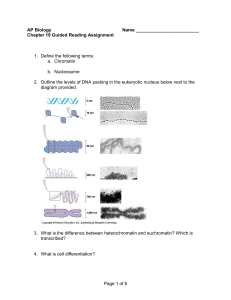
... 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
Unit 3- Section 2
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
Ch. 19 – Eukaryotic Genomes
... Extra copies of genes (like those for RNA) can be beneficial in the embryo Conversely it is also observed in cancer cells Transposons: regions of DNA that can move from one location to another…position effects this impact. 10% of human genome, 50% in some plants Retrotransposons : move with help of ...
... Extra copies of genes (like those for RNA) can be beneficial in the embryo Conversely it is also observed in cancer cells Transposons: regions of DNA that can move from one location to another…position effects this impact. 10% of human genome, 50% in some plants Retrotransposons : move with help of ...
Molecular biology
... found in an organism • Phenotype is the visible expression of the genotype – Wild-type phenotype is the most common or generally accepted standard – Mutant alleles are usually recessive – Example? ...
... found in an organism • Phenotype is the visible expression of the genotype – Wild-type phenotype is the most common or generally accepted standard – Mutant alleles are usually recessive – Example? ...
41040-2-12118
... experiment. We propose a method for investigation of potential effects of silencing, before physically performing an experiment. This should allow a more efficient design and organization of the experiment and considerable savings in terms of time and money. The statistical components of this approa ...
... experiment. We propose a method for investigation of potential effects of silencing, before physically performing an experiment. This should allow a more efficient design and organization of the experiment and considerable savings in terms of time and money. The statistical components of this approa ...
Genetics and Intelligence
... Rare but cool examples can be found Hygienic behavior in bees- behavior controlled two genes ...
... Rare but cool examples can be found Hygienic behavior in bees- behavior controlled two genes ...
The timing of gene expression
... ancestral vertebrate gene homologues in lower animal classes Gene homologue: Similar DNA sequences in different organisms. Homeotic genes often are homologous, coding for the same function in many different organisms similar homologue genes have been found in every eukaryote studied including: inver ...
... ancestral vertebrate gene homologues in lower animal classes Gene homologue: Similar DNA sequences in different organisms. Homeotic genes often are homologous, coding for the same function in many different organisms similar homologue genes have been found in every eukaryote studied including: inver ...
Revision sheet Biology Grade 12 A Genes in Action In the space
... a. heritable (passed on to the next generation). b. not heritable c.similar in effect to body cell mutations. d. _____ 10. Nondisjunction can result in a. polyploidy. b. a normal number of chromosomes. c. a gene rearrangement. Using the word bank below, fill in each blank provided. ...
... a. heritable (passed on to the next generation). b. not heritable c.similar in effect to body cell mutations. d. _____ 10. Nondisjunction can result in a. polyploidy. b. a normal number of chromosomes. c. a gene rearrangement. Using the word bank below, fill in each blank provided. ...
Effects of FGF-4 Growth Factor on Axolotl Fibroblast`s Gene
... Although vertebrae develop limbs as embryos, only salamanders (urodele amphibians) are able to regenerate limbs as adults. Recent studies of salamanders indicate how gene expression varies amongst different stages of regeneration in vivo; however, little is known about regulating gene expression in ...
... Although vertebrae develop limbs as embryos, only salamanders (urodele amphibians) are able to regenerate limbs as adults. Recent studies of salamanders indicate how gene expression varies amongst different stages of regeneration in vivo; however, little is known about regulating gene expression in ...
INSERT A-3c
... 3. Why can a person carrying a translocation be normal except, for the inability to have children? Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s ...
... 3. Why can a person carrying a translocation be normal except, for the inability to have children? Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s ...
Regulation of gene expression powerpoint
... from one another; why do lung cells look different than skin cells under a microscope? How do you ...
... from one another; why do lung cells look different than skin cells under a microscope? How do you ...
Expression of yolk protein genes in liver Beekman, Johanna
... It is clear from tho rosults presented in this thesis that regulation of gene expression is a complexprocess, that involves transcription factors that can bind to regulatory regions in several genes. The specific combinationof binding sites and the presence of specific transcription factors in the c ...
... It is clear from tho rosults presented in this thesis that regulation of gene expression is a complexprocess, that involves transcription factors that can bind to regulatory regions in several genes. The specific combinationof binding sites and the presence of specific transcription factors in the c ...
Expression of yolk protein genes in liver Beekman, Johanna
... It is clear from tho rosults presented in this thesis that regulation of gene expression is a complexprocess, that involves transcription factors that can bind to regulatory regions in several genes. The specific combinationof binding sites and the presence of specific transcription factors in the c ...
... It is clear from tho rosults presented in this thesis that regulation of gene expression is a complexprocess, that involves transcription factors that can bind to regulatory regions in several genes. The specific combinationof binding sites and the presence of specific transcription factors in the c ...
Chapter 21 The Genetic Control of Animal Development
... Development in Vertebrates Geneticists can study development in vertebrates by applying knowledge gained from the study of model invertebrates, by analyzing mutations and phenocopies of mutant genes in model vertebrates such as mice and zebrafish, and by examining the differentiation of stem cells. ...
... Development in Vertebrates Geneticists can study development in vertebrates by applying knowledge gained from the study of model invertebrates, by analyzing mutations and phenocopies of mutant genes in model vertebrates such as mice and zebrafish, and by examining the differentiation of stem cells. ...