DNA FRQ practice
... (b) Describe the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of organizing genes into chromosomes. (c) How does the function and structure of the chromosome differ in prokaryotes? ...
... (b) Describe the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of organizing genes into chromosomes. (c) How does the function and structure of the chromosome differ in prokaryotes? ...
Chapter 17.1-Genes and Variation
... - Most organisms contain two sets of genes - One allele from each parent ...
... - Most organisms contain two sets of genes - One allele from each parent ...
I. Down Syndrome - Plain Local Schools
... D. Translocation occurs when a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a non-homologous chromosome IV. Jumping Genes A. Single genes may move from one location to another in a chromosome or to a different chromosome B. This was discovered by Barbara McClintock in the 1940’s C. These genes can land in ...
... D. Translocation occurs when a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a non-homologous chromosome IV. Jumping Genes A. Single genes may move from one location to another in a chromosome or to a different chromosome B. This was discovered by Barbara McClintock in the 1940’s C. These genes can land in ...
Obesity caused BBC tumors to form at a faster rate compared to lean
... • What is the relationship between prenatal arsenic exposure and changes to gene expression? • Are any of the genes that are altered in association with arsenic controlled by the epigenetic mechanism DNA methylation? ...
... • What is the relationship between prenatal arsenic exposure and changes to gene expression? • Are any of the genes that are altered in association with arsenic controlled by the epigenetic mechanism DNA methylation? ...
chap12studyguide
... 19. A mutation in a series of genes, called the ____________________, can change the organs that develop in specific parts of an embryo. Short Answer 20. What is a bacteriophage? 21. What are the three main parts of an RNA nucleotide? 22. What must happen to a DNA molecule before RNA polymerase can ...
... 19. A mutation in a series of genes, called the ____________________, can change the organs that develop in specific parts of an embryo. Short Answer 20. What is a bacteriophage? 21. What are the three main parts of an RNA nucleotide? 22. What must happen to a DNA molecule before RNA polymerase can ...
Biologically active oligosaccharides (oligosaccharins
... developmental genetic changes responsible for changes in body plan and the origin of important plant innovations such as roots, leaves, and vascular tissue. We have focused on tracing the evolutionary history of genes involved in pattern formation. In particular, we have investigated the history of ...
... developmental genetic changes responsible for changes in body plan and the origin of important plant innovations such as roots, leaves, and vascular tissue. We have focused on tracing the evolutionary history of genes involved in pattern formation. In particular, we have investigated the history of ...
Barbara McClintock
... Mosaicism is caused by Ds transposing in random cells and not every cell. Size of the spot is determined by seed development Transposition of Ds is determined by the number of Ac copies Ac controls the transposition of Ds from chromosome 9 and when Ds is moved there is a breakage in the chromosome. ...
... Mosaicism is caused by Ds transposing in random cells and not every cell. Size of the spot is determined by seed development Transposition of Ds is determined by the number of Ac copies Ac controls the transposition of Ds from chromosome 9 and when Ds is moved there is a breakage in the chromosome. ...
HEREDITY AND GENETICS vocabulary terms and
... Pairs of genes that occupy a specific position on a chromosome; genes that code for the same trait; alternate forms of the same gene ...
... Pairs of genes that occupy a specific position on a chromosome; genes that code for the same trait; alternate forms of the same gene ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... the oncogenesis of bladder cancer, yet its role is still obscure. The HCCS gene is located on the X chromosome and to date, there are no reports linking it to bladder cancer. Yet, it is one of the few activated genes that were common to all samples. Through this study, we were able to identify sever ...
... the oncogenesis of bladder cancer, yet its role is still obscure. The HCCS gene is located on the X chromosome and to date, there are no reports linking it to bladder cancer. Yet, it is one of the few activated genes that were common to all samples. Through this study, we were able to identify sever ...
Chapter 11
... – Random inactivation of either the maternal or paternal chromosome – Occurs early in embryonic development and all cellular descendants have the same inactivated chromosome – Inactivated X chromosome is called a Barr body – Tortoiseshell fur coloration is due to inactivation of X chromosomes in he ...
... – Random inactivation of either the maternal or paternal chromosome – Occurs early in embryonic development and all cellular descendants have the same inactivated chromosome – Inactivated X chromosome is called a Barr body – Tortoiseshell fur coloration is due to inactivation of X chromosomes in he ...
Constructing gene networks underlying fat - BDPorc
... filter out indirect pair-wise correlations. Transcriptomic phenotype network was notably denser and showed much higher correlation values between traits. Besides, a weighted gene co-expression network (WGCN) was constructed on the basis of soft thresholding, using a power function and scale free top ...
... filter out indirect pair-wise correlations. Transcriptomic phenotype network was notably denser and showed much higher correlation values between traits. Besides, a weighted gene co-expression network (WGCN) was constructed on the basis of soft thresholding, using a power function and scale free top ...
Genes - ASW Moodle
... A. Genes are sections of DNA that code for that usually has one or more versions, or Some genes determine traits in an organism B. Trait is a physical characteristic in an organism that usually has more than one variation ex: Trait – Alleles – ...
... A. Genes are sections of DNA that code for that usually has one or more versions, or Some genes determine traits in an organism B. Trait is a physical characteristic in an organism that usually has more than one variation ex: Trait – Alleles – ...
Document
... Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype (physical). • Mendel studied autosomal gene traits, like hair texture. Autosome – chromosome with genes not related to sex of organism (body cells) ...
... Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype (physical). • Mendel studied autosomal gene traits, like hair texture. Autosome – chromosome with genes not related to sex of organism (body cells) ...
scientists and philosophers find that gene has a multitude of meanings
... guanine, adenine, thymine and cytosine, which are read by the cell when genes are active. Intron A segment of a protein-coding gene that is edited out of an RNA transcript. Noncoding RNA Molecules of RNA produced from DNA that are not used to produce proteins. Protein A molecule (like collagen or he ...
... guanine, adenine, thymine and cytosine, which are read by the cell when genes are active. Intron A segment of a protein-coding gene that is edited out of an RNA transcript. Noncoding RNA Molecules of RNA produced from DNA that are not used to produce proteins. Protein A molecule (like collagen or he ...
3rd- 9 Weeks Test Review
... ü Genes can be turned on and off (expressed or not expressed). ü Transcription and translation occur only when cells need the gene product; cells don’t make all possible proteins all of the time. ...
... ü Genes can be turned on and off (expressed or not expressed). ü Transcription and translation occur only when cells need the gene product; cells don’t make all possible proteins all of the time. ...
tay-sachs disease - Tay
... • An allele is an alternative form of a gene that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome • 2/per gene • They come from our parents whether they carry the trait or not • Recessive= r Dominate= R • Dominant means you are more likely to inherit something from your parents • Recessiv ...
... • An allele is an alternative form of a gene that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome • 2/per gene • They come from our parents whether they carry the trait or not • Recessive= r Dominate= R • Dominant means you are more likely to inherit something from your parents • Recessiv ...
AP Biology Study Guide Key Chapter 18
... a. Repressible enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways. The pathway’s product serves as a corepressor to activate the repressor and turn off enzyme synthesis and prevent overproduction of the product of the pathway. Genes for repressible enzymes are usually switched on and the repressor is syn ...
... a. Repressible enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways. The pathway’s product serves as a corepressor to activate the repressor and turn off enzyme synthesis and prevent overproduction of the product of the pathway. Genes for repressible enzymes are usually switched on and the repressor is syn ...
Biology - Genetics OEQs
... processes of gene regulation to be discovered involved molecular ‘switches’ that regulate transcription at gene promoters. In the last 20 years, genomic research has uncovered many new types of gene regulation that earlier researchers would have never imagined. Genes can be regulated by repressors, ...
... processes of gene regulation to be discovered involved molecular ‘switches’ that regulate transcription at gene promoters. In the last 20 years, genomic research has uncovered many new types of gene regulation that earlier researchers would have never imagined. Genes can be regulated by repressors, ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
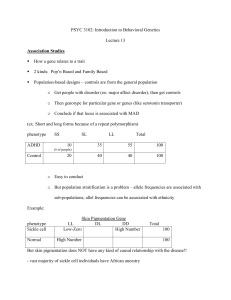
Lecture 13
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
... 9 to 1 ratio of men to women with violent crimes In this sense the Y chromosome has a VERY high association with violent crimes, it is a genetic marker in this sense But, does the Y chromosome cause crime????? This is just a statistical association HOW do genes and environment interact? Y is a predi ...
The Basics of Cancer Biology
... properties, epithelial cancer cells must lose some of their epithelial characteristics and become more similar to a mesodermal (mesenchymal) cell. This phenomenon is called EMT. It involves changing surface adhesion molecules (from Ecadherin to N-cadherin), changing cytoskeletal structure to allow m ...
... properties, epithelial cancer cells must lose some of their epithelial characteristics and become more similar to a mesodermal (mesenchymal) cell. This phenomenon is called EMT. It involves changing surface adhesion molecules (from Ecadherin to N-cadherin), changing cytoskeletal structure to allow m ...
Gene Linkage
... • 3 generations, some members have the recessive trait of color blindness • Genotypes are written as XBXB – for female with normal vision, XBXb for a female who is normal but is a carrier for colorblind, and XbXb for a female who is colorblind; XBY for a male with normal vision and XbY for a male wh ...
... • 3 generations, some members have the recessive trait of color blindness • Genotypes are written as XBXB – for female with normal vision, XBXb for a female who is normal but is a carrier for colorblind, and XbXb for a female who is colorblind; XBY for a male with normal vision and XbY for a male wh ...