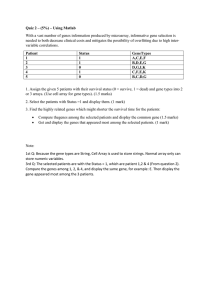
5` 3`
... Different proteins can be generated from single precursor polypeptide through post-translational events …so can have larger proteome (set of proteins) than predicted from number of genes in genome ...
... Different proteins can be generated from single precursor polypeptide through post-translational events …so can have larger proteome (set of proteins) than predicted from number of genes in genome ...
Name
... 1. Which statement best describes a population of organisms if cloning is the only method used to reproduce this population? (1) The population would be more likely to adapt to a changing environment. (2) There would be little chance for variation within the population. (3) The population would evol ...
... 1. Which statement best describes a population of organisms if cloning is the only method used to reproduce this population? (1) The population would be more likely to adapt to a changing environment. (2) There would be little chance for variation within the population. (3) The population would evol ...
Sex & Death: Introduction to the Philosophy of Biology
... • Disadvantage of viewing genes as ‘difference makers’ is that it becomes unclear whether they have an independent reality as a gene ...
... • Disadvantage of viewing genes as ‘difference makers’ is that it becomes unclear whether they have an independent reality as a gene ...
MENDEL & Variations of Mendel
... and fertilization. • Under normal Mendelian genetic rules, we would not expect linked genes to recombine into assortments of alleles not found in the parents. – If the seed color and seed coat genes were linked, we would expect the F1 offspring to produce only two types of gametes, YR and yr when th ...
... and fertilization. • Under normal Mendelian genetic rules, we would not expect linked genes to recombine into assortments of alleles not found in the parents. – If the seed color and seed coat genes were linked, we would expect the F1 offspring to produce only two types of gametes, YR and yr when th ...
Airgas template
... alleles). The physical trait that results from a certain genotype is termed phenotype. An easy way to remember this is the first two letters of the term and its description: phenotype/physical trait. ...
... alleles). The physical trait that results from a certain genotype is termed phenotype. An easy way to remember this is the first two letters of the term and its description: phenotype/physical trait. ...
doc - FSU Biology
... genome about 120 RNA genes. These genes code for a variety of RNA products, most of which have known functions. Examples are the three ribosomal RNA genes which code for the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs found in all bacterial ribosomes, and the 50 or more different transfer RNA (tRNA) genes that are transc ...
... genome about 120 RNA genes. These genes code for a variety of RNA products, most of which have known functions. Examples are the three ribosomal RNA genes which code for the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs found in all bacterial ribosomes, and the 50 or more different transfer RNA (tRNA) genes that are transc ...
Chapter 12
... a. germ cell mutation-change is in the gametes so it affects the offspring and not the parent organism b. somatic cell mutation-change is in an organism’s body cells will affect the organism but not the offspring ex; certain types of skin cancer, leukemia ...
... a. germ cell mutation-change is in the gametes so it affects the offspring and not the parent organism b. somatic cell mutation-change is in an organism’s body cells will affect the organism but not the offspring ex; certain types of skin cancer, leukemia ...
Ch. 10.4: Meiosis & Mendel`s Principles
... If genes on diff. Chromosomes did NOT sort independently, then yellow smooth and green wrinkled parents could not produce yellow winkled or green smooth offspring. ...
... If genes on diff. Chromosomes did NOT sort independently, then yellow smooth and green wrinkled parents could not produce yellow winkled or green smooth offspring. ...
Document
... 1. Chromatin condenses more tightly in dividing cells (12.6) 2. DNA is packed with important proteins to create “chromatin” in non-dividing cells (19.2); chromosome territories E. Much of our genome is “non-gene” ...
... 1. Chromatin condenses more tightly in dividing cells (12.6) 2. DNA is packed with important proteins to create “chromatin” in non-dividing cells (19.2); chromosome territories E. Much of our genome is “non-gene” ...
1 BIOL 213 Fifth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... Explain the significance of the following statement from Figure 8-27 in Alberts, et al. (your Text). "Whereas the general transcription factors that assemble at the promoter are the same for all genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, the gene regulatory proteins and the locations of their binding s ...
... Explain the significance of the following statement from Figure 8-27 in Alberts, et al. (your Text). "Whereas the general transcription factors that assemble at the promoter are the same for all genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, the gene regulatory proteins and the locations of their binding s ...
Bis2A 8.2 The Flow of Genetic Information
... Figure 2 above depicts this idea. We will explore the links between genotype and phenotype over the next several modules. note: ...
... Figure 2 above depicts this idea. We will explore the links between genotype and phenotype over the next several modules. note: ...
Term
... Permanent Loss of (enzyme) function (or activity) This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from p ...
... Permanent Loss of (enzyme) function (or activity) This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from p ...
PDF
... collaborate with Ubx to directly repress sal in the haltere. This repression occurs via a sal cis-regulatory element that contains closely spaced Smad and Ubx binding sites and is perfectly conserved among four Drosophila species. Because Smad and Ubx proteins appear not to interact directly, the au ...
... collaborate with Ubx to directly repress sal in the haltere. This repression occurs via a sal cis-regulatory element that contains closely spaced Smad and Ubx binding sites and is perfectly conserved among four Drosophila species. Because Smad and Ubx proteins appear not to interact directly, the au ...
PDF
... collaborate with Ubx to directly repress sal in the haltere. This repression occurs via a sal cis-regulatory element that contains closely spaced Smad and Ubx binding sites and is perfectly conserved among four Drosophila species. Because Smad and Ubx proteins appear not to interact directly, the au ...
... collaborate with Ubx to directly repress sal in the haltere. This repression occurs via a sal cis-regulatory element that contains closely spaced Smad and Ubx binding sites and is perfectly conserved among four Drosophila species. Because Smad and Ubx proteins appear not to interact directly, the au ...
PDF
... collaborate with Ubx to directly repress sal in the haltere. This repression occurs via a sal cis-regulatory element that contains closely spaced Smad and Ubx binding sites and is perfectly conserved among four Drosophila species. Because Smad and Ubx proteins appear not to interact directly, the au ...
... collaborate with Ubx to directly repress sal in the haltere. This repression occurs via a sal cis-regulatory element that contains closely spaced Smad and Ubx binding sites and is perfectly conserved among four Drosophila species. Because Smad and Ubx proteins appear not to interact directly, the au ...
Chromosomes
... • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself and ...
... • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself and ...
Slide ()
... Effects of translocations. The first observed cancer-associated chromosomal abnormality was a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, resulting in the so-called Philadelphia chromosome, identified in CML patients. The functional result of this genetic event is the creation of the BCR- ...
... Effects of translocations. The first observed cancer-associated chromosomal abnormality was a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, resulting in the so-called Philadelphia chromosome, identified in CML patients. The functional result of this genetic event is the creation of the BCR- ...
Designer Genes - Heredity
... Transcription: Synthesis of RNA from a DNA Template. Requires DNA-dependent RNA polymerase plus the four nucleotides (ATP, GTP. CTP and UTP). Synthesis begins at a the initiation site on DNA The template strand is read 3' to 5' and the mRNA is synthesized 5' to 3' ...
... Transcription: Synthesis of RNA from a DNA Template. Requires DNA-dependent RNA polymerase plus the four nucleotides (ATP, GTP. CTP and UTP). Synthesis begins at a the initiation site on DNA The template strand is read 3' to 5' and the mRNA is synthesized 5' to 3' ...
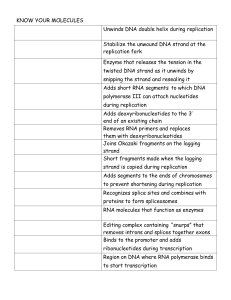
Know your molecules organizer
... DNA segment upstream from promoter that contains multiple control elements to speed up transcription Bind to operator sites of operons to “turn off” genes Place in an operon where the repressor binds to “turn off” a gene “death tag” that marks proteins for degradation by proteosomes Bind to mRNA’s ...
... DNA segment upstream from promoter that contains multiple control elements to speed up transcription Bind to operator sites of operons to “turn off” genes Place in an operon where the repressor binds to “turn off” a gene “death tag” that marks proteins for degradation by proteosomes Bind to mRNA’s ...
2368AOS1-genefunctiongenesinaction2
... Some genes are only active during the embryonic period whilst others such as Huntington’s disease are only expressed in the phenotype only when the individual is well into adulthood. Some genes are only active in certain tissues (eg. Genes that produce insulin are only active in the pancreas). ...
... Some genes are only active during the embryonic period whilst others such as Huntington’s disease are only expressed in the phenotype only when the individual is well into adulthood. Some genes are only active in certain tissues (eg. Genes that produce insulin are only active in the pancreas). ...