Régulation de SRY - Département de biologie
... where CTCF binds at one or more sites but can protect against methylation elsewhere. This structure may be associated with the nuclear matrix and involve proteins in addition to CTCF. Tissue-specific variation in higher-order structure could be due to different CTCF-dependent cis elements forming th ...
... where CTCF binds at one or more sites but can protect against methylation elsewhere. This structure may be associated with the nuclear matrix and involve proteins in addition to CTCF. Tissue-specific variation in higher-order structure could be due to different CTCF-dependent cis elements forming th ...
Genetics Quiz- Matching, Short answer
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
Characterizing the Imprintome
... expression so that one parent’s allele is selectively expressed. Together, these imprinted genes make up the imprintome. Scientists used to search for imprinted genes one by one, but thanks to modern sequencing techniques, they can now scan entire genomes. The precise size of the imprintome is uncer ...
... expression so that one parent’s allele is selectively expressed. Together, these imprinted genes make up the imprintome. Scientists used to search for imprinted genes one by one, but thanks to modern sequencing techniques, they can now scan entire genomes. The precise size of the imprintome is uncer ...
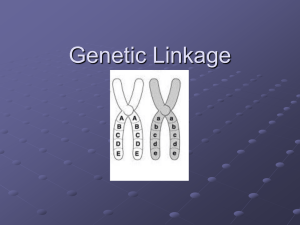
Gene linkage ppt
... Linked genes are pairs or groups of genes which are inherited together, carried on the same chromosome (usually close together) ...
... Linked genes are pairs or groups of genes which are inherited together, carried on the same chromosome (usually close together) ...
Relating Mendelism to Chromosomes
... 15.3 Linked Genes 4. Distinguish between linked genes and sex-linked genes. 5. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 6. Explain why Mendel did not find linkage between seed color and flower color, despite the fact that these genes are on th ...
... 15.3 Linked Genes 4. Distinguish between linked genes and sex-linked genes. 5. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 6. Explain why Mendel did not find linkage between seed color and flower color, despite the fact that these genes are on th ...
Heredity
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
Slide 1
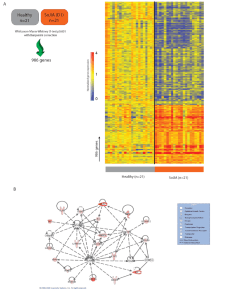
... imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s measurement in the healthy controls. To identify transcripts differentially expressed between study groups that might serve as classifiers, class comparison an ...
... imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s measurement in the healthy controls. To identify transcripts differentially expressed between study groups that might serve as classifiers, class comparison an ...
Review of relevant topics prior to “Linkage” lectures
... Have to visualize gene (locus)/alleles/chromosomes/metaphase/chromatids segregating/gamete formation 1. Stretch of DNA that codes for a protein; in the middle of a bunch of bases that are not encoding 2. The location of that gene (sequence) relative to the chromosome it exists on 3. The specific cop ...
... Have to visualize gene (locus)/alleles/chromosomes/metaphase/chromatids segregating/gamete formation 1. Stretch of DNA that codes for a protein; in the middle of a bunch of bases that are not encoding 2. The location of that gene (sequence) relative to the chromosome it exists on 3. The specific cop ...
Gene and Gene Regulation
... Process of using genes from DNA to synthesize proteins to express/show traits/characteristics on an organism. ...
... Process of using genes from DNA to synthesize proteins to express/show traits/characteristics on an organism. ...
Epigenetics: We often discuss genes as if their presence in our cells
... or off, and this can be good (most of the time) or bad (sometimes). We understand the mechanisms in some cases, but not others. Section 14.3 in our text (genomic imprinting) is but one example. Sections 10.7-10.11 deal with the processes involved with differentiation of cells as we develop from a si ...
... or off, and this can be good (most of the time) or bad (sometimes). We understand the mechanisms in some cases, but not others. Section 14.3 in our text (genomic imprinting) is but one example. Sections 10.7-10.11 deal with the processes involved with differentiation of cells as we develop from a si ...
Cells Chapter 4 Review Powerpoint
... recessive genes show up? Dominant traits are expressed even if only one copy of the allele codes for them. (Dd) If a trait is recessive, it is expressed only if both alleles code for it (dd). ...
... recessive genes show up? Dominant traits are expressed even if only one copy of the allele codes for them. (Dd) If a trait is recessive, it is expressed only if both alleles code for it (dd). ...
- Journal of Clinical Investigation
... ing on the parent of origin. The resulting allelic asymmetry distinguishes imprinting from other forms of epigenetic regulation. For a number of imprinted genes, the imprint appears to silence gene expression, and in working parlance the “imprinted allele” is often identified with the silent one. St ...
... ing on the parent of origin. The resulting allelic asymmetry distinguishes imprinting from other forms of epigenetic regulation. For a number of imprinted genes, the imprint appears to silence gene expression, and in working parlance the “imprinted allele” is often identified with the silent one. St ...
NOVA – Cracking the Code of Life
... 5. It was long thought that humans had around 100,000 genes. The initial survey of the human genome indicated that there were only about __________ genes in humans. What interesting fact about human genes allows humans to be so much more complex than something like a fruit fly? ...
... 5. It was long thought that humans had around 100,000 genes. The initial survey of the human genome indicated that there were only about __________ genes in humans. What interesting fact about human genes allows humans to be so much more complex than something like a fruit fly? ...
Imprinted Genes
... -Either maternal allele OR paternal allele is expressed • Paternal genes are thought to extract maternal resources for the benefit of the offspring – Growth promoters • Maternal genes are thought to allocate resources ‘equitably’ between offspring and mother. – Growth suppressors • Thus, imprinted g ...
... -Either maternal allele OR paternal allele is expressed • Paternal genes are thought to extract maternal resources for the benefit of the offspring – Growth promoters • Maternal genes are thought to allocate resources ‘equitably’ between offspring and mother. – Growth suppressors • Thus, imprinted g ...
Imprinted green beards: a little less than kin and more than kind The
... for the first and second backward steps would resolve into factors of either one ...
... for the first and second backward steps would resolve into factors of either one ...
Document
... Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. About 78 genes (code for about 25 ...
... Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. About 78 genes (code for about 25 ...
Chapter 21 The human genome appears to have only about as
... 1. The human genome appears to have only about as many genes as the simple nematode worm, C. elegans. Which of the following best explains how the more complex humans can have relatively few genes? a. Human genes have unusually long introns involved in the regulation of gene expression. b. More than ...
... 1. The human genome appears to have only about as many genes as the simple nematode worm, C. elegans. Which of the following best explains how the more complex humans can have relatively few genes? a. Human genes have unusually long introns involved in the regulation of gene expression. b. More than ...
sex-linked traits: traits controlled by genes located on thr sex
... SEX-LINKED TRAITS: TRAITS CONTROLLED BY GENES LOCATED ON THR SEX CHROMOSOMES. X = FEMALE SEX CHROMOSOME Y = MALE SEX CHROMOSOME (SMALLER THAN X AND DOES NOT CONTAIN AS MANY GENES) Objectives: 1) Define through example sex-linked traits and polygenic inheritance. 2) Identify other factors that might ...
... SEX-LINKED TRAITS: TRAITS CONTROLLED BY GENES LOCATED ON THR SEX CHROMOSOMES. X = FEMALE SEX CHROMOSOME Y = MALE SEX CHROMOSOME (SMALLER THAN X AND DOES NOT CONTAIN AS MANY GENES) Objectives: 1) Define through example sex-linked traits and polygenic inheritance. 2) Identify other factors that might ...
Crossing Over and Linkage
... linked down the generations, greatly reducing the number of gene permutations possible at each generation. Crossing over allows a child to inherit, for example, his grandmother’s green eyes without also inheriting her defective sodium channel gene (page 331), although both genes are on chromosome 19 ...
... linked down the generations, greatly reducing the number of gene permutations possible at each generation. Crossing over allows a child to inherit, for example, his grandmother’s green eyes without also inheriting her defective sodium channel gene (page 331), although both genes are on chromosome 19 ...
Bill Nye - Genetics (worksheet)
... 5) What did irradiating (exposing them to x-rays) do to the genes of the bread mold? 6) The Beadle and Tatum breakthrough was the “one gene, one _______________” hypothesis. ...
... 5) What did irradiating (exposing them to x-rays) do to the genes of the bread mold? 6) The Beadle and Tatum breakthrough was the “one gene, one _______________” hypothesis. ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
Can environmental factors acting on an organism cause inherited
... Angelman syndrome patients are hyperactive, have unusual seizures and repetitive symmetrical muscle movements and show mental deficiencies. Both syndromes involve a small deletion in human chromosome 15 (locus 3), if this deletion is inherited from the maternal parent, it leads to Angelman syndrome, ...
... Angelman syndrome patients are hyperactive, have unusual seizures and repetitive symmetrical muscle movements and show mental deficiencies. Both syndromes involve a small deletion in human chromosome 15 (locus 3), if this deletion is inherited from the maternal parent, it leads to Angelman syndrome, ...
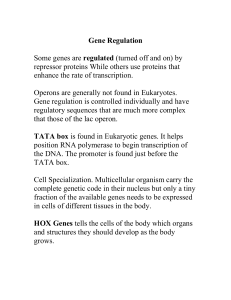
Gene Regulation
... Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the lac operon. TATA box is found in Eukaryotic genes. It helps position RNA polymerase to begin transcription of the DNA. The promoter is ...
... Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the lac operon. TATA box is found in Eukaryotic genes. It helps position RNA polymerase to begin transcription of the DNA. The promoter is ...
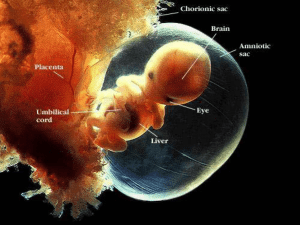
Of wolves and men: the role of paternal child care in the
... this theory, genes expressed from the paternal allele favour the acquisition of maternal resources and hence the growth of the foetus, whereas genes expressed from the maternal allele restrict foetal growth to preserve the mother’s resources for future pregnancies. Good examples for these peculiar e ...
... this theory, genes expressed from the paternal allele favour the acquisition of maternal resources and hence the growth of the foetus, whereas genes expressed from the maternal allele restrict foetal growth to preserve the mother’s resources for future pregnancies. Good examples for these peculiar e ...