AP Biology - Renton School District
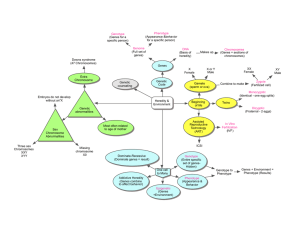
... 11. Compare and contrast a genetic map, a linkage map, and a cytogenetic map. ...
... 11. Compare and contrast a genetic map, a linkage map, and a cytogenetic map. ...
Mapping Life
... known, the information can be used to repair problems or improve the organism. Plant genes can be changed to make the plant more resistant to drought, to better withstand attacks by pests, or to use nutrients more efficiently. That could save resources, like fertilizer and water. Animal genes can be ...
... known, the information can be used to repair problems or improve the organism. Plant genes can be changed to make the plant more resistant to drought, to better withstand attacks by pests, or to use nutrients more efficiently. That could save resources, like fertilizer and water. Animal genes can be ...
Imprinted green beards: a little less than kin and more than kind
... allele A8 that retains the mesiRNA but is insensitive to its effects and an allele A* that encodes a new mesiRNA (lower right). Subscripts m and p indicate madumnal and padumnal alleles. Squares represent the coding sequence of an mRNA. Circles and triangles represent coding sequences of mesiRNAs. F ...
... allele A8 that retains the mesiRNA but is insensitive to its effects and an allele A* that encodes a new mesiRNA (lower right). Subscripts m and p indicate madumnal and padumnal alleles. Squares represent the coding sequence of an mRNA. Circles and triangles represent coding sequences of mesiRNAs. F ...
0.-intro-to-biopsych..
... how) for how genes should appear. Genes: parts of the chromosome that tell us our traits Our genes tell us the results of puberty (height, muscle development, deepening voices, etc) BUT our chromosomes tell our body when to start these changes- you don’t begin puberty at 4 unless you have a severe c ...
... how) for how genes should appear. Genes: parts of the chromosome that tell us our traits Our genes tell us the results of puberty (height, muscle development, deepening voices, etc) BUT our chromosomes tell our body when to start these changes- you don’t begin puberty at 4 unless you have a severe c ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes ...
... consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes ...
Genetics Lecture Part 2
... occurs between a large piece of chromosome 22 and a small piece on tip 9 = much shorter chromosome 22 (Philadelphia chromosome) in white blood cells IV. Some inheritance patterns are exceptions to the standard chromosome theory Normally occurring exceptions : sex of parent contributing an allele is ...
... occurs between a large piece of chromosome 22 and a small piece on tip 9 = much shorter chromosome 22 (Philadelphia chromosome) in white blood cells IV. Some inheritance patterns are exceptions to the standard chromosome theory Normally occurring exceptions : sex of parent contributing an allele is ...
Chapter 14 and 15 - Madeira City Schools
... Know the following disorders and causes for the disorders: • down syndrome • Klinefelter syndrome •Turner syndrome • cri du chat ...
... Know the following disorders and causes for the disorders: • down syndrome • Klinefelter syndrome •Turner syndrome • cri du chat ...
Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
Lecture #6 Date - Cloudfront.net
... crossover will occur between them and therefore the higher the recombination frequency (# CO / total ) * 100 = %CO; m.u.=%CO / 2 Linkage maps: Genetic map based on ...
... crossover will occur between them and therefore the higher the recombination frequency (# CO / total ) * 100 = %CO; m.u.=%CO / 2 Linkage maps: Genetic map based on ...
the maternal grandsire - Weimaraner Club of America
... was considered relevant. Again, however, Mendelian expectations were confounded, as the all-female gene pairings resulted in large placentas with little embryonic material. The all-male gene pairings produced the opposite result: small placentas with large embryos. Surani’s team concluded that some ...
... was considered relevant. Again, however, Mendelian expectations were confounded, as the all-female gene pairings resulted in large placentas with little embryonic material. The all-male gene pairings produced the opposite result: small placentas with large embryos. Surani’s team concluded that some ...
THE STUDY OF HERITABLE CHANGES IN GENE FUNCTION THAT
... Histones in sperm are replaced by protamines. This allows sperm DNA to ...
... Histones in sperm are replaced by protamines. This allows sperm DNA to ...
DeKalb County - Purdue University
... f. XX chromosome means what sex: ______________________ g. XY chromosome means what sex: ______________________ h. It is the chromosome from which parent that determines the sex of the kit: ___________ 6. List the correct term for each definition: minute rod-like structures on which genes are locate ...
... f. XX chromosome means what sex: ______________________ g. XY chromosome means what sex: ______________________ h. It is the chromosome from which parent that determines the sex of the kit: ___________ 6. List the correct term for each definition: minute rod-like structures on which genes are locate ...
Multiple choice questions
... (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) Insulators Delimit functional domains Delimit structural domains Stimulate gene expression are usually smaller than 1000 bp overcome positional effects in gene expression Locus control regions Are located close to genes Stimulate gene expr ...
... (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) Insulators Delimit functional domains Delimit structural domains Stimulate gene expression are usually smaller than 1000 bp overcome positional effects in gene expression Locus control regions Are located close to genes Stimulate gene expr ...
Ch.5
... Uniparental Disomy-rare inheritance of a double dose of genetic material from 1 parent but none from the other; the term literally means “2 bodies from one parent”; caused by nondisjunction during meiosis II of both parents. Genomic imprinting-a phenotype that is different depending upon the sex of ...
... Uniparental Disomy-rare inheritance of a double dose of genetic material from 1 parent but none from the other; the term literally means “2 bodies from one parent”; caused by nondisjunction during meiosis II of both parents. Genomic imprinting-a phenotype that is different depending upon the sex of ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Males and females express the same levels of certain genes found on the X chromosome Dosage compensation In females one X chromosome is randomly selected for modification 13.3 Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA is inherited only from the egg cell. 1 ...
... Males and females express the same levels of certain genes found on the X chromosome Dosage compensation In females one X chromosome is randomly selected for modification 13.3 Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA is inherited only from the egg cell. 1 ...
Macroevolution
... – Humans and chimps diverged from a common ancestor about 5 mya. share about 98.7% of genes ...
... – Humans and chimps diverged from a common ancestor about 5 mya. share about 98.7% of genes ...
Genes and Natural Selection
... Who started this • Darwin proposed his theory of evolution, cell division, genes, and chromosomes had not yet been discovered ...
... Who started this • Darwin proposed his theory of evolution, cell division, genes, and chromosomes had not yet been discovered ...
Document
... A. In humans XX is female and XY is male 1. The SRY gene has been shown to trigger the development into a male fetus at about 2 months old. 2. SRY probably regulates other genes 3. Some XX male and XY females exist with mutated SRY genes ...
... A. In humans XX is female and XY is male 1. The SRY gene has been shown to trigger the development into a male fetus at about 2 months old. 2. SRY probably regulates other genes 3. Some XX male and XY females exist with mutated SRY genes ...
Development Through the Lifespan
... an individual Genetic Foundations Chromosomes – store and transmit genetic information. Genes – segments of DNA located along the chromosomes DNA – substance of which genes and chromosomes are made. Dominant-Recessive Inheritance X-Linked Inheritance Genetic Imprinting and Mutation Imprinting ...
... an individual Genetic Foundations Chromosomes – store and transmit genetic information. Genes – segments of DNA located along the chromosomes DNA – substance of which genes and chromosomes are made. Dominant-Recessive Inheritance X-Linked Inheritance Genetic Imprinting and Mutation Imprinting ...
NEWS W Einstein Cancer Center
... usually come to mind. But mutations are not the only culprits in cancer. Scientists now know that gene expression—whether a gene turns on or stays silent—is directed by chemicals that latch onto genes. These chemical alterations are referred to as “epigenetic” changes because—unlike mutations— they ...
... usually come to mind. But mutations are not the only culprits in cancer. Scientists now know that gene expression—whether a gene turns on or stays silent—is directed by chemicals that latch onto genes. These chemical alterations are referred to as “epigenetic” changes because—unlike mutations— they ...