Section 11.2 - CPO Science
... to 1916) examined the nucleus of the cell of a grasshopper under a microscope. • Sutton observed cell parts separating during cell division. • Soon chromosomes were discovered to contain genes. ...
... to 1916) examined the nucleus of the cell of a grasshopper under a microscope. • Sutton observed cell parts separating during cell division. • Soon chromosomes were discovered to contain genes. ...
Abstract The phenomena of gene fusion and fission occur
... which are two otherwise unrelated genes that both share homology with a larger gene. We intend to identify the number of composites and the relationship of any conserved phenomena with each other, with neighbouring genes and with the evolutionary timeline across 114 fungal genomes to investigate the ...
... which are two otherwise unrelated genes that both share homology with a larger gene. We intend to identify the number of composites and the relationship of any conserved phenomena with each other, with neighbouring genes and with the evolutionary timeline across 114 fungal genomes to investigate the ...
Human Genetics
... Where do our genes come from? • We had said that a pair of genes determines which traits we will inherit from our parents • Why would it be a pair of genes? •Each parent provides a sex cell in order for fertilization to occur •The father will provide a sperm cell that has 23 chromosomes •The mother ...
... Where do our genes come from? • We had said that a pair of genes determines which traits we will inherit from our parents • Why would it be a pair of genes? •Each parent provides a sex cell in order for fertilization to occur •The father will provide a sperm cell that has 23 chromosomes •The mother ...
CHAPTER 14 VOCAB
... mono- one (monosomic: a chromosomal condition in which a particular cell has only one copy of a chromosome, instead of the normal two; the cell is said to be monosomic for that chromosome) non- not; dis- separate (nondisjunction: an accident of meiosis or mitosis, in which both members of a pair of ...
... mono- one (monosomic: a chromosomal condition in which a particular cell has only one copy of a chromosome, instead of the normal two; the cell is said to be monosomic for that chromosome) non- not; dis- separate (nondisjunction: an accident of meiosis or mitosis, in which both members of a pair of ...
review 13-15
... Codominance-2 alleles are dominant & affect phenotype in 2 diff but = ways (blood type) Incomplete dominance-when the F1 hybrids have a phenotype in b/w both parents usually a 1:2:1 ratio ...
... Codominance-2 alleles are dominant & affect phenotype in 2 diff but = ways (blood type) Incomplete dominance-when the F1 hybrids have a phenotype in b/w both parents usually a 1:2:1 ratio ...
No Slide Title
... Somatic mutation within V region genes Finally, combinations of pairing of H chain isotypes and L-chain subtypes (kappa and lambda) ...
... Somatic mutation within V region genes Finally, combinations of pairing of H chain isotypes and L-chain subtypes (kappa and lambda) ...
Genetic Diversity of Offspring
... Genetic Diversity of Offspring • Genes have a better • Why do you think it would chance of survival if be advantageous to have they are rearranged genes rearrange each at each generation generation? • Only offspring that are • Are you a twin, or do you not diverse are twins know any twins? Do you – ...
... Genetic Diversity of Offspring • Genes have a better • Why do you think it would chance of survival if be advantageous to have they are rearranged genes rearrange each at each generation generation? • Only offspring that are • Are you a twin, or do you not diverse are twins know any twins? Do you – ...
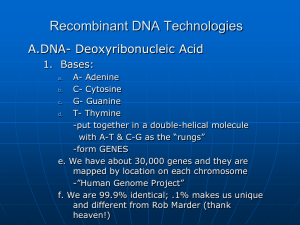
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... (i.e. what do we know that inserts genes over existing ones…. Think “poison”) Called “vectors” ...
... (i.e. what do we know that inserts genes over existing ones…. Think “poison”) Called “vectors” ...
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
... • Ranks all genes on array based on their differential expression • Identifies gene sets whose member genes are clustered either towards top or bottom of the ranked list (i.e. up- or down regulated) • Enrichment score calculated for each category • Permutation test to identify significantly enriched ...
... • Ranks all genes on array based on their differential expression • Identifies gene sets whose member genes are clustered either towards top or bottom of the ranked list (i.e. up- or down regulated) • Enrichment score calculated for each category • Permutation test to identify significantly enriched ...
CRACKING THE CODE OF LIFE QUESTIONS
... 12. What was every week like at Solaris? 13. How many of the 17 children have arthritis? 14. What are the “guys in the funny suits” making? 15. BRCA mutations cause what percentage of breast cancers? 16. What would most changes we make to DNA today do to the machine? 17. What do you come away from r ...
... 12. What was every week like at Solaris? 13. How many of the 17 children have arthritis? 14. What are the “guys in the funny suits” making? 15. BRCA mutations cause what percentage of breast cancers? 16. What would most changes we make to DNA today do to the machine? 17. What do you come away from r ...
Unit I: Genes, Nucleic A...d Chromosomes - BioWiki
... Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant DNA technology and the polymerase chain reaction, are discussed in Chapter 3. In addition, this chapter explores some of the insights into gen ...
... Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant DNA technology and the polymerase chain reaction, are discussed in Chapter 3. In addition, this chapter explores some of the insights into gen ...
The timing of gene expression
... the beginning of limbs. Position of limb buds is determined by HOX genes that start the gene cascade. Genes at the start of the cascade are switched on and as each gene is expressed, the next is turned on. In humans, limbs develop in weeks 5 and 6 and in a precise pattern: shoulders to fingers, thum ...
... the beginning of limbs. Position of limb buds is determined by HOX genes that start the gene cascade. Genes at the start of the cascade are switched on and as each gene is expressed, the next is turned on. In humans, limbs develop in weeks 5 and 6 and in a precise pattern: shoulders to fingers, thum ...
Ghost in Your Genes Response
... 10. In a remote and poor Northern Sweden community it was found that the grandsons of grandfathers who experienced ______________________ in ____________________ were more likely to die of illnesses related to diabetes. Interestingly, granddaughters of grandmothers who experienced _________________ ...
... 10. In a remote and poor Northern Sweden community it was found that the grandsons of grandfathers who experienced ______________________ in ____________________ were more likely to die of illnesses related to diabetes. Interestingly, granddaughters of grandmothers who experienced _________________ ...
Alleles segregate during gamete formation, but do they do
... the formation of gametes. • Leads to genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms. ...
... the formation of gametes. • Leads to genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms. ...
Heredity Review Sheet - Heredity: the passing of ______ from one
... ** In order for a recessive trait to be seen, both alleles must be little, bb. - Heterozygous: (aka ____________) when two alleles are different, Bb. ...
... ** In order for a recessive trait to be seen, both alleles must be little, bb. - Heterozygous: (aka ____________) when two alleles are different, Bb. ...
Comparative Genomics
... 41 genes may have been transferred in this way For example: MAOs, monoamine oxidases These enzymes deactivate neurotransmitters ...
... 41 genes may have been transferred in this way For example: MAOs, monoamine oxidases These enzymes deactivate neurotransmitters ...
Print Preview - C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\e3temp_6820\.aptcache
... should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y chromosome interact to produce a phenotypic trait; ...
... should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y chromosome interact to produce a phenotypic trait; ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y chromosome interact to produce a phenotypic trait; ...
... should indicate that females (XX) can only pass on an X chromosome and males (XY) can only pass on either Autosomal gene expression: Two alleles that one X or one Y chromosome interact to produce a phenotypic trait; ...
SexChrom_posted
... can be a perfectly normal female. If the SRY gene becomes translocated to another chromosome, an XX individual can be a phenotypically normal (but sterile) male. ...
... can be a perfectly normal female. If the SRY gene becomes translocated to another chromosome, an XX individual can be a phenotypically normal (but sterile) male. ...
Human Genetics
... - A pair of sex chromosomes - Females have two X chromosomes - Males have one X and a Y ...
... - A pair of sex chromosomes - Females have two X chromosomes - Males have one X and a Y ...
Silencing Genes for Life - royalsocietyhighlands.org.au
... Genomics is a branch of biotechnology concerned with the study and manipulation of the genome (the complete set of DNA within a single cell of an organism). One branch of Genomics is called RNA interference (RNAi). [RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid]. Its inventors Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (Stanfor ...
... Genomics is a branch of biotechnology concerned with the study and manipulation of the genome (the complete set of DNA within a single cell of an organism). One branch of Genomics is called RNA interference (RNAi). [RNA stands for Ribonucleic Acid]. Its inventors Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (Stanfor ...
Chapter 11.5
... Certain alleles that are linked on the same chromosome tend to remain together during meiosis because they are positioned closer together on the chromosome This eventually led to the generalization that the probability that a crossover will disrupt linkage of two genes is proportional to the dista ...
... Certain alleles that are linked on the same chromosome tend to remain together during meiosis because they are positioned closer together on the chromosome This eventually led to the generalization that the probability that a crossover will disrupt linkage of two genes is proportional to the dista ...