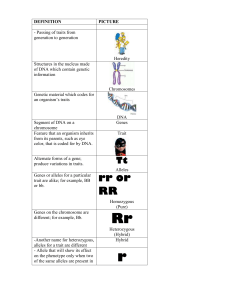
1. Instructions for how an organism develops are found
... come from each parent’s sex cells. 6. Chromosomes in a pair carry the same genes in the same place, but that there are different versions of genes called alleles. 7. A person may have two alleles the same or two different alleles for any gene. 8. Offspring may have some similarity to their parents b ...
... come from each parent’s sex cells. 6. Chromosomes in a pair carry the same genes in the same place, but that there are different versions of genes called alleles. 7. A person may have two alleles the same or two different alleles for any gene. 8. Offspring may have some similarity to their parents b ...
46556-2-12118
... expression and higher-level phenotypes. However, the large number p of genes and genetic loci to analyse as random variables exceeds by far the available number of multivariate observations n, precluding the direct application of classical multivariate techniques that start with a saturated model. M ...
... expression and higher-level phenotypes. However, the large number p of genes and genetic loci to analyse as random variables exceeds by far the available number of multivariate observations n, precluding the direct application of classical multivariate techniques that start with a saturated model. M ...
9 Genetics Mendel
... Mendel and the Gene Idea 1. Name two or three of the characteristics used in his legendary experiments. What plant did he use? 2. Describe the difference between dominant and recessive genes, between homozygous, heterozygous, and hemizygous gene combinations, and between genotype and phenotype. 3. W ...
... Mendel and the Gene Idea 1. Name two or three of the characteristics used in his legendary experiments. What plant did he use? 2. Describe the difference between dominant and recessive genes, between homozygous, heterozygous, and hemizygous gene combinations, and between genotype and phenotype. 3. W ...
Mendel`s Laws of Segregation
... This references meiosis, when the chromosome number changes from diploid to haploid (for example, in humans from 46 to 23). The genes are sorted into separate gametes, resulting in variation. “This sorting process depends on genetic “recombination”. During this time, genes mix and match in a random ...
... This references meiosis, when the chromosome number changes from diploid to haploid (for example, in humans from 46 to 23). The genes are sorted into separate gametes, resulting in variation. “This sorting process depends on genetic “recombination”. During this time, genes mix and match in a random ...
chromosomes
... What is DNA? • A molecule that is present in all living cells and that contains the information that determines traits that a living thing inherits and needs to live. ...
... What is DNA? • A molecule that is present in all living cells and that contains the information that determines traits that a living thing inherits and needs to live. ...
1/25
... localized to a sequenced region of the chromosome, then look for genes that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
... localized to a sequenced region of the chromosome, then look for genes that could be involved in the process under study • Last step: confirm gene identification – Rescue of phenotype – Mutations in same gene in different alleles ...
Genetics Review
... on anatomy & physiology? Genes control the layout, make-up and function of the bodies of all organisms. Examples of traits influenced by genes: • Appearance (hair, skin, eyes, height, etc.) • Body structure of an organism • Susceptibility to diseases • Personality traits • Behavior (instincts as wel ...
... on anatomy & physiology? Genes control the layout, make-up and function of the bodies of all organisms. Examples of traits influenced by genes: • Appearance (hair, skin, eyes, height, etc.) • Body structure of an organism • Susceptibility to diseases • Personality traits • Behavior (instincts as wel ...
Gene Section PEG3 (paternally expressed 3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... breast cancers and other gynecologic cancers (Kohda et al., 2001; Dowdy et al., 2005; Feng et al., 2008). There are several studies revealed murine Peg3 acts as an intermediary between p53 and Bax in a cell death pathway activated by DNA damage in primary mouse cortical neurons, inhibiting Peg3 acti ...
... breast cancers and other gynecologic cancers (Kohda et al., 2001; Dowdy et al., 2005; Feng et al., 2008). There are several studies revealed murine Peg3 acts as an intermediary between p53 and Bax in a cell death pathway activated by DNA damage in primary mouse cortical neurons, inhibiting Peg3 acti ...
definition - Humble ISD
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
Inheritance Poster 1
... transmission of two traits together, e.g. shape and colour of seed (green and wrinkled). ...
... transmission of two traits together, e.g. shape and colour of seed (green and wrinkled). ...
ethylene - IQMrevision
... These are dominoes. Cut each out. They join into a circle when matched correctly. ...
... These are dominoes. Cut each out. They join into a circle when matched correctly. ...
Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in
... Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells ...
... Methyl CpG binding protein 2 binding sites on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma B cells ...
Genome-Scale CRISPR-Mediated Control of the Gene
... ● Reveal mechanisms by which cancer cells develop resistance to anti-cancer drugs ● Identify cellular targets of new drugs ...
... ● Reveal mechanisms by which cancer cells develop resistance to anti-cancer drugs ● Identify cellular targets of new drugs ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... the trait are equally dominant and both are expressed in the offspring. Inheritance pattern where the individual only inherits two alleles but there are 3 or more possible alleles in the whole population. ...
... the trait are equally dominant and both are expressed in the offspring. Inheritance pattern where the individual only inherits two alleles but there are 3 or more possible alleles in the whole population. ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 16. What did Rosalyn Franklin die of? #7- Messenger RNA ...
... 16. What did Rosalyn Franklin die of? #7- Messenger RNA ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... 7. A mutation involves a base change in a gene, sequence of DNA. 8. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced by another. 9. An example of a disease caused by a base substitution mutation in humans is sickle cell anemia. 10. Natural selection has main ...
... 7. A mutation involves a base change in a gene, sequence of DNA. 8. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced by another. 9. An example of a disease caused by a base substitution mutation in humans is sickle cell anemia. 10. Natural selection has main ...
Genetics Chapter 5 outline
... 3. The closer the 2 genes are on a chromosome the ________ likely they will ___________________ or separate, due to physical distance. 4. The further apart the 2 genes are on a chromosome the ________________ likely they will crossover or separate, due to _______________ _____________. B. Linkage Ma ...
... 3. The closer the 2 genes are on a chromosome the ________ likely they will ___________________ or separate, due to physical distance. 4. The further apart the 2 genes are on a chromosome the ________________ likely they will crossover or separate, due to _______________ _____________. B. Linkage Ma ...
Chromosomal Inheritance - Bishop Seabury Academy
... In 1902, he provided sufficient evidence for the theory that genes are parts of chromosomes from direct observations on the behavior of chromosomes in reduction division. In 1903, he showed that the chromosomes behave by random segregation in the sex cells and recombination in fertilization, exactly ...
... In 1902, he provided sufficient evidence for the theory that genes are parts of chromosomes from direct observations on the behavior of chromosomes in reduction division. In 1903, he showed that the chromosomes behave by random segregation in the sex cells and recombination in fertilization, exactly ...